As a baseball is being caught, its speed goes from 30.0 m/s to 0.0 m/s in about 0.0050 s. The mass of the baseball is 0.145 kg. What is the baseball's acceleration? What are the magnitude and direction of the force acting upon it? What are the magnitude and direction of the force acting upon the player who caught it?
a = -6000 m/s2
Fbaseball = 870 backwards
Fplayer = 870 forwards
What are the units of the friction coefficient μ in the formula:
Ffriction=μ⋅Fnormal
No Units
A popular sledding hill has an angle of 30∘ to the horizontal and has a vertical drop of 25m. If a sledder begins from rest and is traveling at 20m/s as they reach the bottom of the hill, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and snow?
g=10m/s2
1.15
A 200.0-gram mass (m1) and 50.0-gram mass (m2) are connected by a string. The string is stretched over a pulley. Determine the acceleration of the masses and the tension in the string.
a =5.88 m/s2
T = 0.784 N
A mass of 10 kg is suspended from a cable A and a light, rigid, horizontal bar B that is free to rotate, as shown. What is the tension, in Newtons, in cable A?
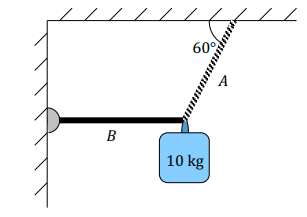
T=115.47 N
An air hockey table works by pumping air through thousands of tiny holes in a table to support light pucks. This allows the pucks to move around on cushions of air with very little resistance. One of these pucks has a mass of 0.25 kg and is pushed along by a 12.0 N force for 9.0 s. What is the puck's acceleration? What is the puck's final velocity?
a = 48 m/s2
v = 432 m/s
A box with mass 20kg is on a cement floor. The coefficient of static friction between the box and floor is 0.25. A man is pushing the box with a horizontal force of 35N. What is the magnitude of the force of static friction between the box and floor?
35 N
A young skier has lost control and is now traveling straight down a mountain. The skier is halfway down a 200m run with a slope of 30o and traveling at a rate of 10m/s. If the skier is traveling at a rate of 30m/s at the end of the run, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the skis and snow?
g=10m/s2
0.12
Consider the two-body situation below. A 20.0-gram hanging mass (m2) is attached to a 250.0-gram air track glider (m1). Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the string.

a = 0.726 m/s2
T = 0.181 N
The sign below hangs outside the physics classroom, advertising the most important truth to be found inside. The sign is supported by a diagonal cable and a rigid horizontal bar. If the sign has a mass of 50 kg, then determine the tension in the diagonal cable that supports its weight.
T = 980 N.
A person who weighs 800 N steps onto a scale that is on the floor of an elevator car. If the elevator accelerates upward at a rate of 5 m/s2, what will the scale read?
1200 N
A 48kg crate is loaded onto a pick-up truck, and the truck speeds away without the crate sliding. If the coefficient of static friction between the truck and the crate is 0.4, what is the maximum acceleration that the truck can undergo without the crate slipping?
3.92 m/s2
Given that the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3, what is the magnitude of the frictional force exerted on an object weighing 4.5kg lying on an incline with angle 60o to the horizontal?
g=10m/s2
7.5 N
Consider the two-body situation at the right. A 2.50x103-kg crate (m1) rests on an inclined plane and is connected by a cable to a 4.00x103-kg mass (m2). This second mass (m2) is suspended over a pulley. The incline angle is 30.0° and the surface is frictionless. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cable.
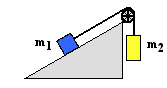
a = 4.15 m/s2
T = 2.26 x 104 N
After its most recent delivery, the infamous stork announces the good news. If the sign has a mass of 10 kg, then what is the tensional force in each cable? Use trigonometric functions and a sketch to assist in the solution.
T=56.6 N
A car has a mass of 710 kg. It starts from rest and travels 0.04 miles in 5 seconds. The car is uniformly accelerated during the entire time. What net force is exerted on it?
6311 N
A 40kg box is initially sitting at rest on a horizontal floor with a coefficient of static friction μs=0.4. A horizontal pushing force is applied to the box. What is the maximum pushing force that can be applied without moving the box?
156.8 N
A small child struggles to pull his heavy suitcase through an airport. He tugs it along with a rope at an angle of 30o to the ground. The child exerts a force of 50N, which is just enough to pull the suitcase along with constant velocity. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ground and the suitcase is μk=0.3
What is the mass of the child's suitcase?
17.28 kg
Consider the two-body situation at the right. A 3.50x103-kg crate (m1) rests on an inclined plane and is connected by a cable to a 1.00x103-kg mass (m2). This second mass (m2) is suspended over a pulley. The incline angle is 30.0° and the surface has a coefficient of friction of 0.210. Determine the acceleration of the system and the tension in the cable.
a = 0.247 m/s2
T = 10047 N
Suppose that a student pulls with two large forces (F1 and F2) in order to lift a 1-kg book by two cables. If the cables make a 1-degree angle with the horizontal, then what is the tension in the cable?
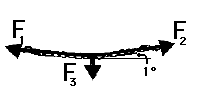
T = 281 N
A 2.75 x 106 N catapult jet plane is ready for takeoff. If the jet's engines supply a constant thrust of 6.35 x 106 N, how much runway will it need to reach its minimum takeoff speed of 285km/h?
135.73 m
A 5kg box slides across the floor with an initial velocity of 5m/s. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor is 0.1, how much time will it take for the box to come to a stop?
5.1 s
Consider the following scenario:

A sledder of mass m is at the stop of a sledding hill at height h with a slope of angle a.
The sledder has a mass of 100kg and the hill has a slope of 30o. If the sledder has a velocity of 8m/s when he reaches the bottom of the hill, which becomes flat, and comes to a stop after 20m, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction and the height of the hill? Neglect air resistance and any other frictional forces.
g=10m/s2
μk=0.16, h=4.4m
There are two weights of the same mass of 2.0 kg attached to a string looped over a braked pulley.
The left weight is lying on the floor, the right one is suspended 1.0 m above the floor.
There is another weight of mass 0.5 kg attached to the string 20 cm above the right weight.
The string except the part around the pulley is stretched vertically. We eventually release the pulley.
- What is the speed at which the lower right weight hits the floor?
Neglect the mass of both the string and the pulley, deformation of the string by tension, and friction.

v=1.49 m/s
The system shown is in equilibrium with the string in the center exactly horizontal. Find (a) tension T1, (b) tension T2, (c) tension T3 and (d) angle θ.
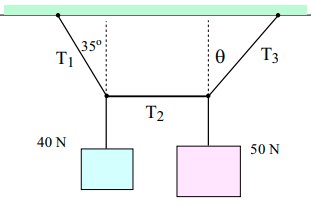
T1 = 48.8 N
T2 = 28.0 N
T3 = 57.3 N
θ = 29.3 o