___ are responsible for the isolating function of membranes
___ are responsible for selectively exchanging substances
Phospholipids; Proteins
Most animal cells secrete a fiber composite outside of the cell called the ___. One of the most important functions is structural support.
extracellular matrix (ECM)
The units of inheritance.
genes
Meiosis is a specialized cell division process that produces haploid ___.
gametes
In an organism that has 14 pairs of chromosomes, how many possible chromosome combinations can be created in its gametes?
214 = 16,384
Describe the orientation of phospholipids in a phospholipid bilayer.
Heads of the outer layer orient outward toward the watery exterior, while heads of the inner layer face the watery interior; tails face inside the membrane.
Plant cells are connected by ___.
plasmodesmata
Correct order of mitotic phases.
In this phase, homologous chromosomes pair up.
prophase I
Substances that cannot easily cross phospholipid bilayer. Substances that can.
Water-soluble substances such as salts, amino acids, and sugars.
Water-insoluble substances: very small molecules (water, oxygen, CO2, larger, lipid-soluble molecules)
___ connect adjacent cells by forming channels. These channels allow the flow of small molecules between cells.
Gap junctions
Sexual reproduction in eukaryotic organisms occurs when offspring are produced by the fusion of ___ (sperm and eggs) from two adults.
gametes
___ is a mutual exchange of DNA) between maternal and paternal homologues.
Crossing over
These membrane proteins are glycoproteins that serve as identification tags on the surface of a cell.
Recognition proteins
These are usually small molecules, typically present in minute concentrations, having a large impact on the condition of the organism as a whole.
Hormones
Most of the time, the DNA in each chromosome is wound around proteins called___.
histones
Fusion of the gametes (fertilization) combines the two haploid chromosome sets to produce a diploid (2n) ___.
zygote
___ are membrane proteins with pores that can be opened or closed to allow specific substances to pass across the membrane.
Channel proteins
___ hormones usually diffuse across the plasma membrane and go into their target cells’ cytoplasm.
___ hormones are large or hydrophilic, do not cross the plasma membrane instead bind to a receptor on the cell’s plasma membrane.
Lipid-soluble; Lipid-insoluble
Chromosomes that contain the same genes are called ___ chromosomes.
homologous
Paired homologous chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell in this phase.
metaphase I
A ___ solution is one with a greater solute concentration; a ___ solution has a lower solute concentration.
hypertonic; hypotonic
The four steps of cell–cell signaling.
1. Signal reception
2. Signal processing
3. Signal response
4. Signal deactivation
A ___ cell has half the number of chromosomes of a ___ cell.
haploid, diploid
The random combination of maternal and paternal homologues (and, therefore, alleles) during metaphase I is called
independent assortment
Name the tonicity for a, b, and c.
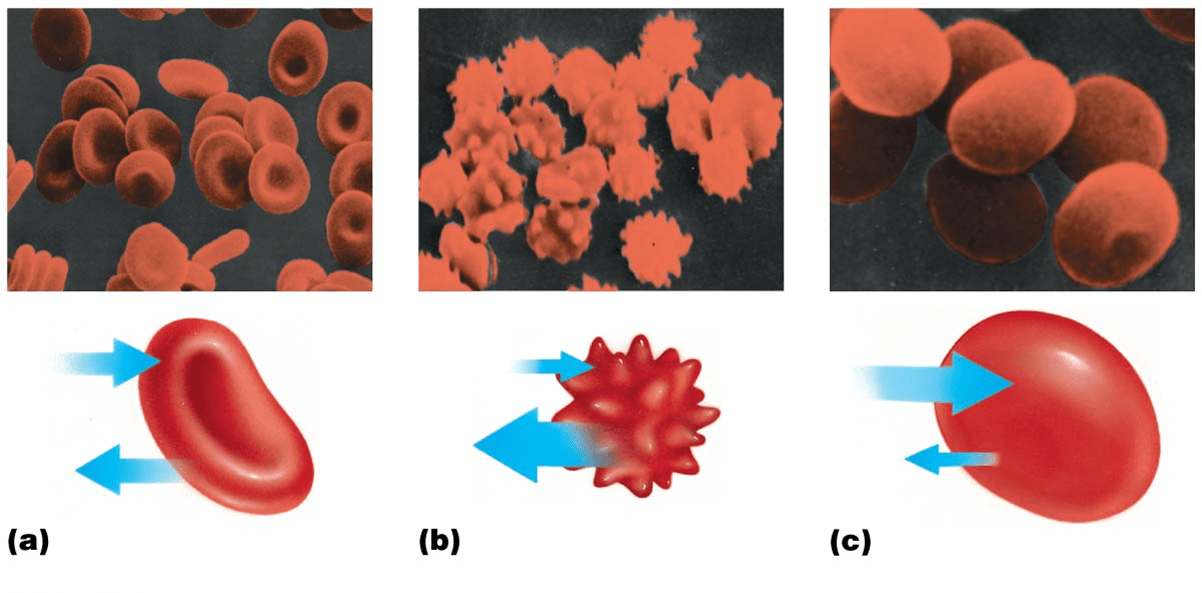
a) isotonic, b) hypertonic, c) hypotonic
When a signal binds at the cell surface, it triggers a complex series of events collectively called a ___ which converts the extracellular hormone signal to an intracellular signal.
signal transduction pathway
This phase is characterized by DNA synthesis, during which every chromosome is replicated.
S (synthesis phase)
In this phase, whole duplicated chromosomes of each homologous pair separate.
Sister chromatids remain attached and move as a homologue unit.
anaphase I
Water pressure within the central vacuole is called ___.
turgor pressure
___ proteins trigger the production of an intracellular messenger.
They are intracellular peripheral membrane proteins that are closely associated with transmembrane signal receptors.
G
The region from which the spindle microtubules originate contains a pair of microtubule-containing structures called ___.
centrioles
During ___, the sister chromatids of each duplicated chromosome separate, in a process that is virtually identical with mitosis.
meiosis II
___ are found between cells where tubes and sacs must hold contents without leaking.
Tight junctions
Several second messengers work by activating protein ___ which are enzymes that add a phosphate group to other proteins, a process called phosphorylation.
kinases
In this phase, polar microtubules from opposite poles attach to one another where they overlap at the equator. These microtubules simultaneously lengthen and push on one another, forcing the poles of the cell apart, so that the cell assumes an oval shape
anaphase
___ occurs from one generation to the next as a result almost entirely from meiosis and sexual reproduction.
genetic variability