______ consisting of living organisms and products of organism.
Biotic
Based on this food web, what is the snake eaten by?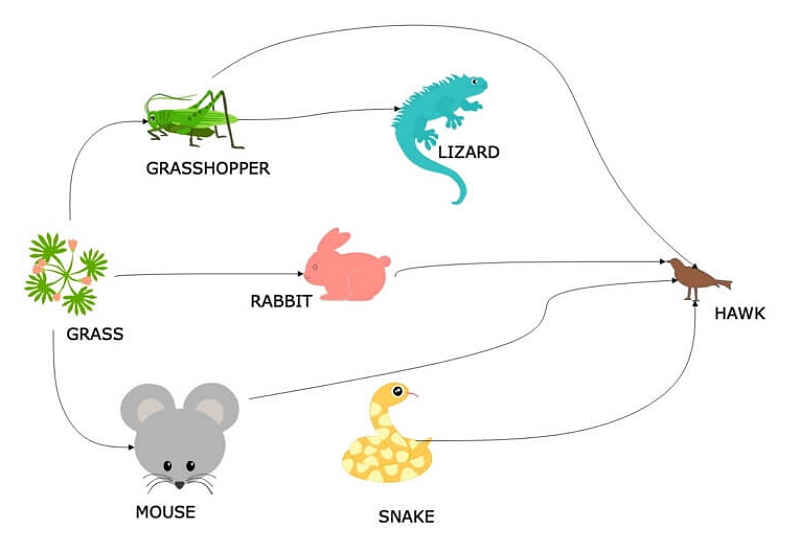
Hawk
True or False: Limiting factors can only be Abiotic things?
False
What would be an example of an abiotic factor in an ecosystem?
Sunlight, temp/climate, water, soil, rocks, air, sand, man-made structures.
How do the Deer and Rabbits interact with on another based off this food web?
The Deer and Rabbit would be in competition for the same kind of food.
Autotroph or producer
What happens to an ecosystem if you remove ALL producers?
Everything would die! There would be nothing to eat.
Name two types of limiting factors.
Predations, Disease, Competition, Resources (food water) Seasons, Climate change, Habitat size etc.
True or False: Ecosystems can be as small as the area under a rock, or as large as the Sahara Desert.
True (Ecosystems vary in size. Ecosystems can even exist within other ecosystems.)
Explain how a change in one population can affect other populations in an ecosystem.
There is a direct casue and effect for changes in an ecosystem. May cause fluctuations in resources, or food webs resulting in an organism inability to grow and reproduce.
What do you call a species that introduced to an ecosystem and has a negative impact on it?
Invasive Species
Food chains and food webs show the flow of ____.
Energy
Daily Double: Why is the availability of food an important limiting factor in ecosystems?
Organisms need food as a source of energy to survive and reproduce.
Name three types of consumers within an ecosystem.
Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores
Name two ways humans can have a negative impact on an ecosystem?
Answers may vary...
_______ is all the same kinds of individuals in a specific area at the same time.
Population
Describe the rule of 10%.
As energy is passed from one trophic level to the next, 90% of the energy will be used by the organism and only 10% will get passed to the next level.
What might be a limiting factors that producers in a forest might experience?
Resources: Competition for sunlight, competition for nutrients.
Where does all energy with an ecosystem come from?
Sunlight
How does the introduction of a new predator impact the population of prey species in an ecosystem?
It can lead to a decrease in the population size of the prey species due to predation.
A word meaning "reliant on each other."
Interdependent
How are food chains and food webs different?
Food chains show one level of energy being transferred while food webs show a variety of competing consumers.
How do limiting factors help keep an ecosystem sustainable?
They prevent a population from getting to large and requiring more resources than the ecosystem can provide.
What are the 5 labels for this trophic level pyramid? You must start at the bottom of the pyramid.

Producers, Primary Consumer, Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer/Apex Predator with Decomposers on the side.
Explain how energy and simple chemicals are returned to the Ecosystem.
Decomposers break down these dead organisms and release the compounds back into the soil. Producers then use them for nutrients during their process of photosynthesis. The compounds reenter the ecosystem.