Draw the Lewis structure for BeF2. What is the molecular geometry?
Linear
![]()
Rank the following from strongest to weakest.
London Dispersion Forces, ion/ion, dipole/dipole, ion/dipole, dipole/induced dipole
ion/ion
ion/dipole
dipole/dipole
dipole/induced dipole
London Dispersion Forces
Define viscosity and give an everyday example of one fluid that is more viscous than another.
Viscosity: resistance of a liquid to flow
Ex. Syrup is more viscous than water.
Convert 18 grams of water to moles.
1
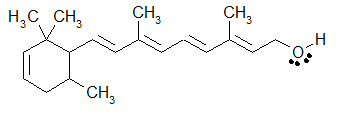
Write the chemical formula.
C20H30O
Write the Lewis structure for CCl4. What is the molecular geometry?
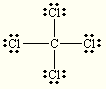
tetrahedral
What is the difference between an intramolecular force and an intermolecular force? Which one is an "IMF"?
intramolecular: between different molecules
intermolecular (IMFs): within the same molecule
Ex. INTERstate, INTERnational, etc.
Name and define the 6 phase transitions that we have gone over.
sublimation: solid to gas
deposition:gas to solid
vaporization: liquid to gas
condensation: gas to liquid
melting/fusion: solid to liquid
freezing: liquid to solid
How many grams are in 0.7 moles of H2O2?
23.8g
Which phase transitions have a negative ∆H? Which have a positive ∆H? What does this tell us about the processes?
Endothermic (positive ∆H), absorb heat:
vaporization, melting/fusion, sublimation
Exothermic (negative ∆H), release heat:
condensation, freezing, deposition
Draw the Lewis structure for BH2–. What is the molecular geometry?
![]()
bent
Define Hydrogen Bond.
Hydrogen - (N, O, F)
Define the critical point on a phase diagram.
- at Critical Point, gas and liquid states form supercritical fluid
Is carbon tetrachloride polar or non polar? What is its molecular geometry?
non polar, tetrahedral
Name 3 factors that affect viscosity.
IMFs, molecular structure, temperature
Write the Lewis structure for NI3. What is the molecular geometry?
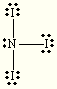
trigonal pyramidal
Rank the following from greatest to smallest boiling point. What is the dominant IMF in each?
CH4, NaCl, C5H12
NaCl, C5H12, CH4
ion-ion; dispersion; dispersion
Define normal boiling point? How is boiling point affected by altitude?
Normal BP is at 1atm of pressure. At higher altitudes (less pressure) the boiling point decreases.
Is SeF6 polar or non polar? what is its molecular geometry?
How does temperature affect IMFs?
Greater temperature = weaker IMFs
Write the Lewis structure for SI6 .What is the molecular geometry?
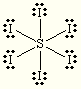
octahedral
Rank the following from weakest to strongest:
H-bond, London dispersion, dipole-dipole
H-bond>dipole-dipole>London
polar; trigonal pyramidal
Write the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation.
LnP2/P1= Hvap/R(1/T1-1/T2)