In patients with COPD and hypoxemia, this cutoff of SpO2 is recommended to improve quality of life and mortality when recommending supplemental oxygen, correlating to an arterial PO2 of 55mmg or lower.
88%
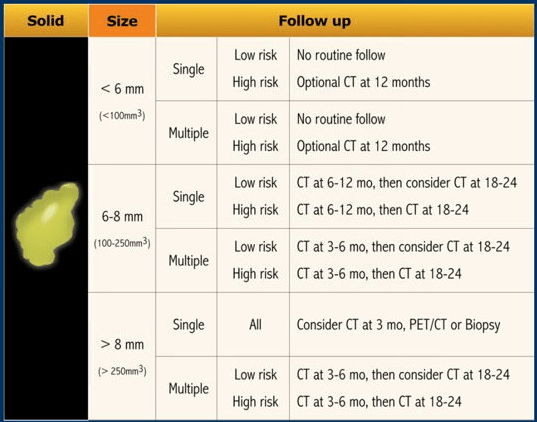
These guidelines help to direct when incidental nodules should be followed up based on radiological criteria.
Fleischner 2017 Guidelines
Give one indication for why a patient cannot manage his/her own CGM.
Multiple answers: but anything that limits patient's mental status/ability, lack of supplies, confusion/AMS, suicidality, etc.
This is the gold standard for diagnosing and classifying Pulmonary Hypertension.
Right Heart Catheterization; cutoffs of mPAP >20mmHG
This finding (Depicted here) in cirrhosis will first develop bilaterally involving first the hypothenar and then thenar eminences, then fingers, then palmar surface.
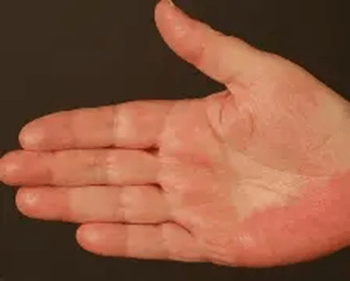
Palmar Erythema
23% of patients with cirrhosis present with palmar erythema, frequently due to higher density of AV shunts and an increase in the dilation of capillaries and increased superficial arterial and venous plexi. Likely secondary to estradiol stimulation of NO via nitric oxide synthase.
This additional diagnostic test, in conjunction with spirometry, can be suggestive of bronchospastic disease or asthma if the FEV1 is decreased by at least 20%.
Methacholine Challenge Testing
The diagnosis of asthma requires demonstrating reversible airflow obstruction; for a patient with symptoms of asthma and normal spirometry, methacholine challenge testing to evaluate for bronchial hyperresponsiveness is indicated.
This should be on the differential for asthma and includes mediastinal lymphadenopathy, noncaseating granulomas and batwings on xray.
Sarcoidosis
Can present with cough, dyspnea, fatigue, chest pain.
Pulmonary symptoms are frequently accompanied by systemic manifestations such as fatigue, malaise, fever, and weight loss, particularly in the elderly [18,19]. Systemic inflammation may also contribute to muscle weakness and exercise intolerance [20-22].
This is the terminology for when an insulin pump system shuts off insulin delivery when the CGM values drop below a given level.
Low Glucose Suspend
This Group of Pulmonary Hypertension is associated with CTEPH.
Group 4
This complication (depicted here) of cirrhosis can occur in excess of 500ml of ascitic fluid and typically accumulates around the posterior lobe in CTs due to porous or ‘bare’ nature of the right posterior diaphragm.
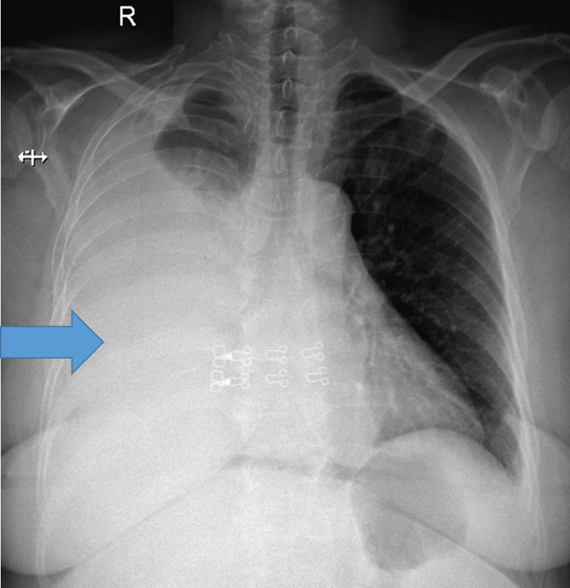
Hepatic Hydrothorax
Typically occurs on the right posterior lobe/right hemidiaphragm as the left is thicker and more muscular. 73-85% on the right.
Current ATS (American Thoracic Society) cutoff for bronchodilator responsiveness in clinical practice is an increase in FEV1 or FVC from baseline by this number (% or mL accepted).
12% or 200mL
Some patients with longer asthma duration may experience decreased BD responsiveness.
A FeNO of this number suggests eosinophilic inflammation and responsiveness to corticosteroids is likely.
>50ppb
FeNO is higher in patients with T2-high asthma (IL-13 pathways) but it is also elevated in non-asthma conditions with T2 inflammation (eosinophilic bronchitis, atopy, allergic rhinitis, eczema). May be falsely low during bronchoconstriction; or smokers.
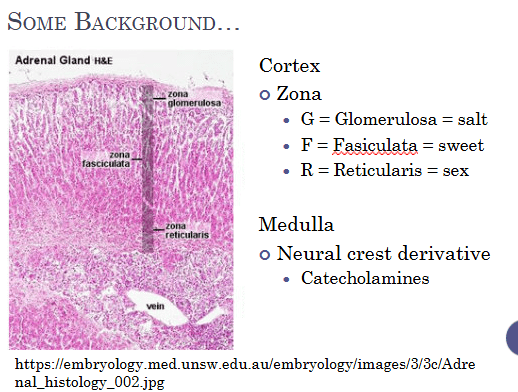
This part of the adrenal gland produces cortisol from 17-OH-progesterone.
Fasiculata.
This can be a cause of pulmonary hypertension that may also have the following blood smear:
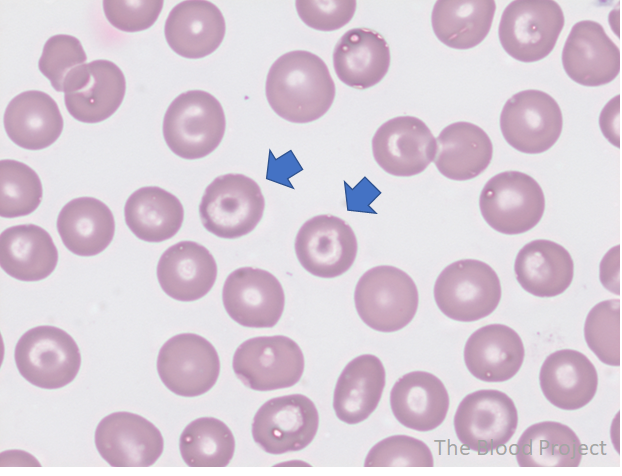
B-Thalassemia can be associated with group 5 Pulmonary Hypertension
(Will also accept IDA as can rarely be related)
This range of Houndsfield units may suggest simple ascites without complications (will accept any number in the range as well). Depicted below.
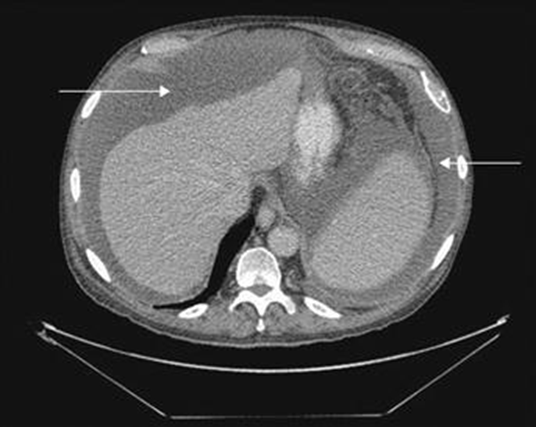
-10 to 10 HU
Can be found on CT at only 50-75mL of fluid present in the peritoneal space, but at this levels may be “free fluid” or physiological. May represent any cause of exudative fluid but is typically seen surrounding the anterior lobe of the liver as well at more advanced stages. This would NOT include fluid that is loculated or exudative fluid.
This genetic cause of recurrent pneumothoraxes is linked to positive folliculin (FLCN) gene mutations.
Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome
Sniff Test
Another test of diaphragmatic weakness can be done on seated vs supine spirometry.
Seated vs supine spirometry
A drop in FVC <10% of the sitting value is considered normal
If FVC drops by >30%, bilateral diaphragmatic paralysis is suspected
Name one type of lipid POOR cortical tumors that can be found on CT imaging.
Lipid-poor adenoma, ganglioneuroma, myelolipoma, adrenocortical carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, or adrenal metastases.
Lipid rich include: Benign non-functioning adenoma, conn's tumor (aldosterone), cushing's disease (cortisol), virilizing tumor (DHEA).
The 2023 European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology/ACR guidelines created guidelines for this condition associated with pulmonary hypertension and includes this pictured physical exam finding. Name condition and physical exam finding.
APA: Livedoid vasculopathy (will accept livedo racemosa as well)

This radiological sign (depicted here) represents the presence of fluid or blood in the pelvic peritoneal recess on supine abdominal radiography.
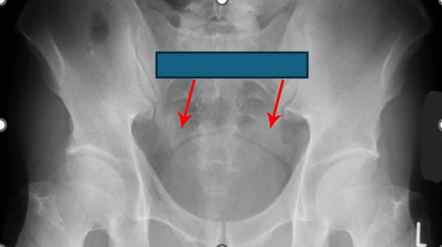
Dog’s Ear Sign
The appearance of the sign comes from a convex soft-tissue density representing fluid or blood in the lateral pelvic peritoneal recess separated from the bladder by a thin hyperlucent strip of extraperitoneal fat which is reminiscent of dog ears.
In patients with severe COPD and frequent exacerbations, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) would recommend this additional medication (or mechanism) in addition to the long-acting bronchodilator treatment (with or without inhaled glucocorticoid) after failing maximal inhaled therapy.
PDE4 Inhibitors, Roflumilast
PDE4 inhibitors are anti-inflammatory agents that inhibit breakdown of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate for chronic bronchitis, severe to very severe COPD, and history of exacerbations. PDE4 inhibitors improve lung function and reduce moderate to severe exacerbations in patients on a fixed-dose long-acting bronchodilator–inhaled glucocorticoid combination. Given this patient's clinical picture, she would likely benefit from the addition of roflumilast.
2R on the IASLC Lymph Node Map is considered which lymph node location.
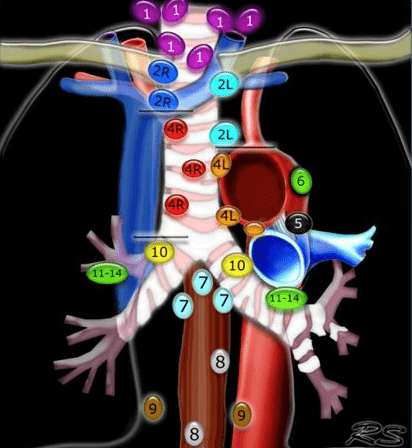
Upper paratracheal (will also accept superior mediastinal).
This confirmatory test for primary hyperaldosteronism, after screening with aldo:renin >20, is considered positive if the aldosterone suppression is <30% from initial level.
Captopril Challenge

Of the complications of pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (arrhythmias, atelectasis, wound infection, pericardial effusions, delirium, etc) this fear complication can lead to bilateral infiltrates, hypoxemic respiratory failure and occasionally severe hemorrhage.
Reperfusion pulmonary edema.
Will not accept ards or pulmonary edema.
: This endoscopic finding (depicted here) is suggestive portal gastropathy. Pup’s beware.
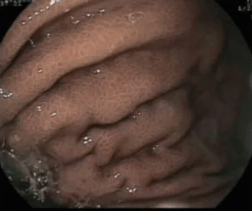
Snake’s Skin Appearance (also described as mosaic-like mucosal pattern).
Comments: May also see nodularity or varices, which if found in the gastric body similar to this picture would not be amendable to banding.