
Constitutional (structural) isomer
What functional groups do you see?

phosphate group
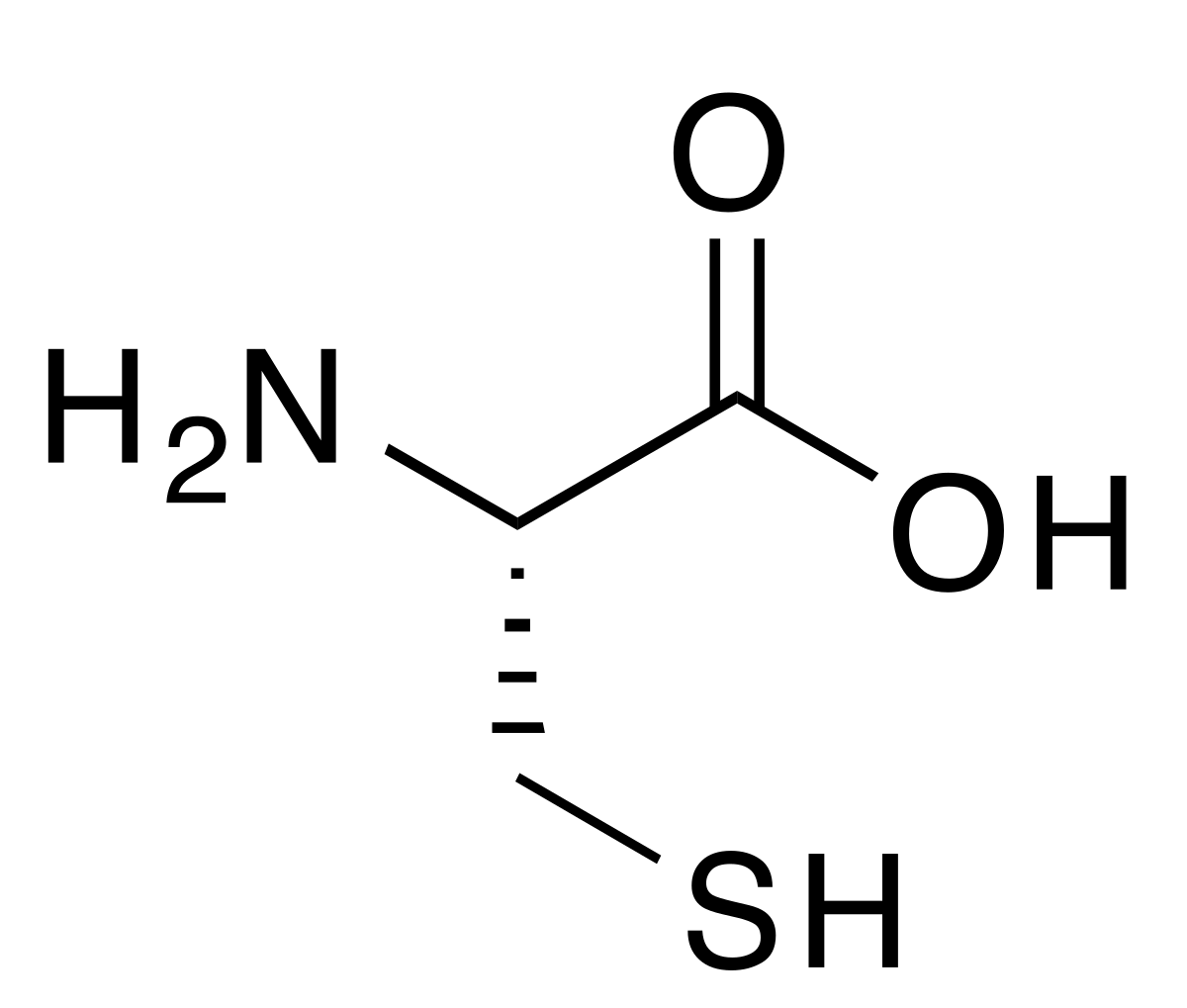
amino group
hydroxyl group
Unsaturated triglycerides require at least one-
double bond
Are there any chiral centers?
Yes! Look at the bottom of the 4-carbon ring.

alpha-1,2 glycosidic bond
between: glucose and fructose (Sucrose)

enantiomer- they are mirror images of one another
disulfide group
carboxyl group (think carboxylic acid)
amino group
Enantiomers require-
a chiral center!
same chemical structure!
same chemical bonds!
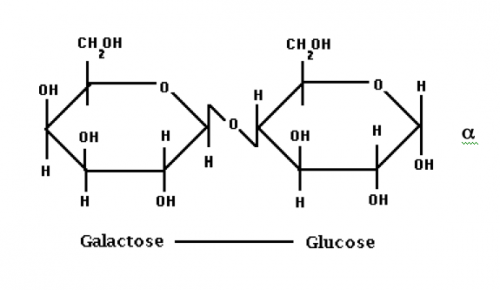
beta-1,4 glycosidic
between: galactose and glucose (lactose)

Geometric Isomers
- which is cis? trans?
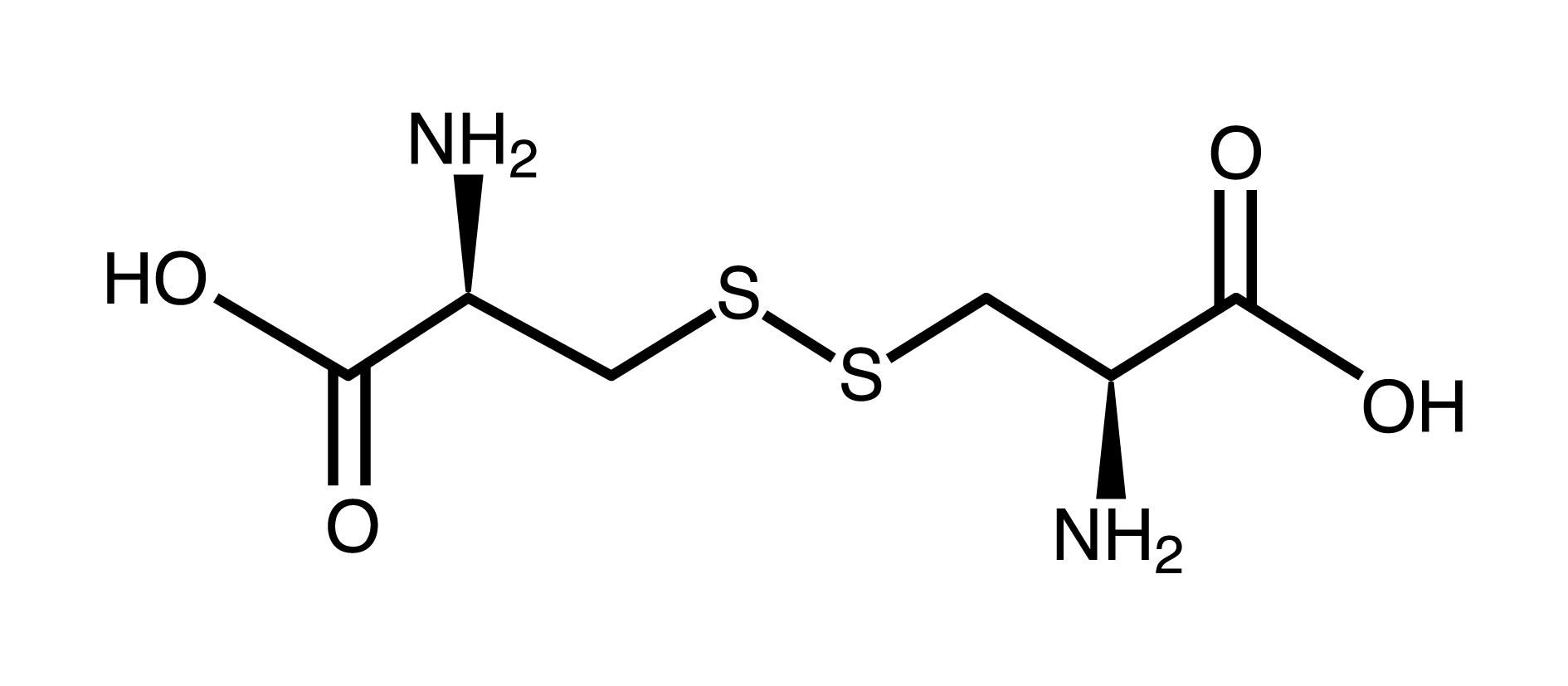
hydrolysis reaction? what would we produce?
carboxyl group
amino group
A hydrocarbon molecule is _____ but can be made _____ with _______ which allows it to interact with water.
nonpolar; polar; functional groups
substituted hydrocarbons-
hydrogen in the backbone of a hydrocarbon can be replaced with an element such as O or N

alpha- 1,4 glycosidic bond
between: glucose and glucose (maltose)
starch is -
polymer made up of glucose monomers
composed of:
- amylose: unbranched
- amylopectin: branched
to link up two monosaccharides, we must-
extract a water molecules through dehydration synthesis
glycogen is-
composed of glucose monomers
similar in structure to amylopectin but more highly branched
major storage form of glucose in animals
to unlink two monosaccharides, we must-
add in a water molecules through hydrolysis
- hydro = water & lysis = breaking