What is this Position called?
What is Semi-Fowlers?
Bonus: Why are patients put in this position?
What is the difference between Fowlers and Semi-Fowlers
A patient is preparing for preoperative surgery and the surgeon ordered the patient must have NPO for 12 hours. What does NPO mean?
What is "Nothing by Mouth"?
Bonus: The patient asks if they can have some water. Would you be able to give this patient water? Why or why not?
The patient is done with surgery and now is placed on a clear liquid diet. What foods are an example of this?
What are all the vital signs?
What is blood pressure, temperature, oxygen saturation, respirations, pain and pulse?
Bonus: What is the apical pulse and how is it measure? Where is it measured?
What are the normal values of vitals in adults?
What is DNR?
What is DO NOT RESUSCITATE
Bonus: What are you violating if you resuscitate a DNR patient?
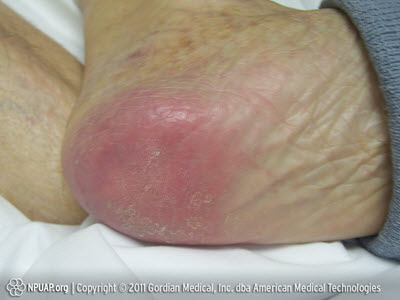 A patient has been imobile for some time and started developing a pressure wound. What stage is this wound in?
A patient has been imobile for some time and started developing a pressure wound. What stage is this wound in?
What is stage 1?
Bonus: How would you care for this type of pressure wound?
 What is this position called?
What is this position called?
What is lateral?
Bonus: What are the benefits of this position?
Why would you lay someone on their left side?
What about their right side?
What is it mean to be right lateral recumbent?
A pregnant woman begins to develop gestational diabetes. She is urinating more frequently and has excessive thirst. What are some diet and health modifications the patient should make?
What is monitoring blood sugar, safe exercise, monitoring the baby, eating healthier foods and/or regular visits with her OB/GYN
Bonus: How does gestational diabetes affect the unborn fetus?
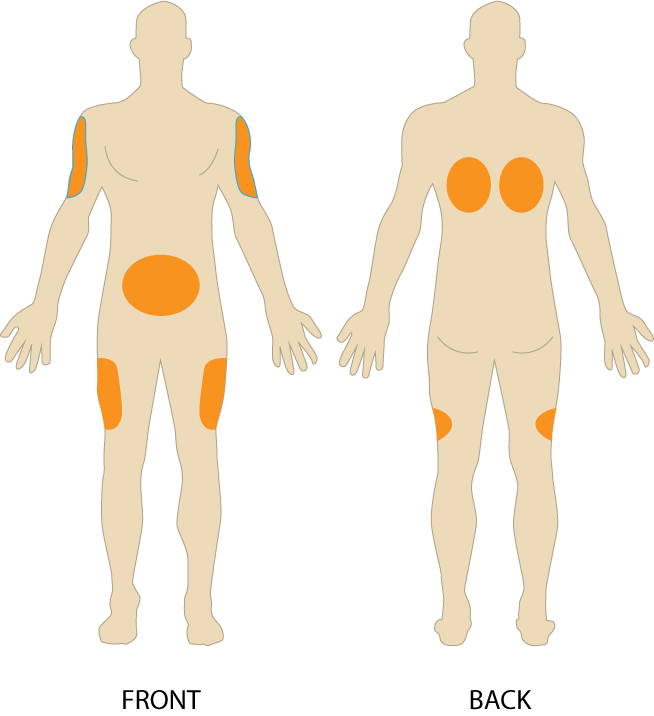 A diabetic patient needs their SC injection of insulin because it is a slow absorbing medication. What layer of the skin does this injection go below?
A diabetic patient needs their SC injection of insulin because it is a slow absorbing medication. What layer of the skin does this injection go below?
What is dermal layer?
Bonus: Where is the vastus lateralis?
At what angle can should you inject an Intramuscular injection?
A nurse talks about a patient she is caring for to a colleague. She states she is excited to care for this patient, as he is a well known celebrity. The colleague then looks at the patient's chart and begins to look the reason for why the patient is being seen. What violation is this?
What is HIPAA?
BONUS: What does HIPAA stand for?
What is PHI?
A localized protective response brought on by injury or destruction of tissues.
What is inflammation?
Bonus: What are the signs of inflammation?
What are the phases of wound care?
The Brain is ________ from the Heart, feet are _______ from the abdomen.
What is Superior and What is Inferior?
Bonus: What is the difference between Cranial and Frontal?
What is Proximal and Distal?
A patient is experiencing dysphagia and needs assistance while being fed. He was able to sip thickened fluids with your assistance. He may start eating solid foods at level 1 with no other restrictions to his diet.
The kitchen is serving these kinds of foods for breakfast. The patient has NKA to food. What can this patient eat from these choices?
A.Vanilla shake with Pureed Blueberries
B. Cream of Wheat with Mashed Bananas
C. Souffee with Onion and Bacon bits.
D. Ham and Cheese Croissant
E. Yogurt Parfait with Honey Granola
F. Fine-milled Grits
What is A, B or F?
Bonus: If the patient begins to aspirate, what should you do?
Before being able to eat Level 1 foods, the patient was on a full liquid diet. What does this mean?
Assessment, Nursing Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation and Evaluation are these
What is the nursing process?
Bonus: What the correlation in the nursing process that is within your scope of practice as an LVN?
How does critical thinking help you in setting up a care plan?
A nurse fails to document the patient's vital signs and check on the patient as the physician ordered. The patient later suffers a myocardial infarction. It was found his heart rate was tachycardic with a low, shallow deep respiration rate. This is a violation of ________
What is breach of duty?
Bonus: Is this malpractice?
What are the elements of Malpractice?
What is surgical asepsis?
Bonus: What is septic shock and how can it be fatal?
What are the 4 rules of surgical asepsis?
An elderly female patient is preparing to go through catheterization because of incontinence due her decreased mobility, weak urinary sphincter muscles, helplessness, and lower back pain. What position would you put this patient in to prepare for catheterization?
What is Lateral Recumbent?
Bonus: Why would you not put this patient in Lithotomy position for catheterization?
At what angle should you bend your patient's knee for positioning?
A patient has been eating a high-sodium fad diet that is increasing his blood pressure up to 160/94. He is experiencing diarrhea, dehydration, oliguria and lethargy. This patient has an electrolyte imbalance called ____
What is Hypernatremia?
Bonus: What is the normal blood sodium level?
How much is the average sodium intake in a day?
What are some nursing interventions?
A patient has some discomfort while breathing, her oxygen saturation is at 92% and she is coughing up clear mucus. You are ordered to suction the patient to remove the excess secretions. What should the suction pressure be set at?
What is 80 and 120 mm Hg?
Bonus: You try oral suctioning first, yet her oxygen level is still at 92%. Can you try nasopharyngeal suctioning?
Can you use the same catheter that you did for the mouth for nasopharyngeal suctioning? Why or Why not? How about vice versa?
Your patient comes in with a fractured rib, a bruised left eye and many scratches on her face. She is sobbing to you stating her husband has been abusing her. As she is sobbing, she begs you not to tell anyone, as she is worried he is going to her kill.
What is the appropriate thing to do in this situation?
What is contacting the authorities?
Bonus: Under what law is the nurse protected under?
A patient's complains of her pain score being at a 6/10 after her hysterectomy surgery. She describes the pain as achy, and throbbing at the site. The patient is restless, agitated and the site is painful when the patient moves around. With a doctor's order, you are able to give this patient some pain medication PRN every 4-6 hours for relief. What is the alternative name for pain medication?
What is an analgesic?
Bonus: What are some types of this medication?
What type of pain is this?
During ambulation, your patient(has a gait belt on) begins to fall forward. What do you do?
What is grasping the patient by the gait belt at the waist OR under the axilla, with your feet slightly behind the patient.
Bonus: You were not able to catch the patient and the patient is now injured at the ankle. What should you do?
Water intake is very important for several of the body's functions as it is the most important nutrient. If a female patient weighs 135lbs and is 5'6" tall , how much water intake should the patient take in a day?
(Hint: 1kg=2.2lbs, 35mL of water per kg.
You may round up to the first tenth)
What is 2148 mL or 2147.7 mL?
Bonus: Would this be a normal BMI for this patient?
What happens if you take in too much water?
What are the four stages of Anesthesia?
Stage 2. Excitement phase
Stage 3. Surgical anesthesia state
Stage 4. Complete Respiratory depression
Bonus: What is the role of a scrub person and a circulating nurse?
What are the rights of a patient in healthcare?
What is the right to access, safety, respect, privacy, partnership and giving feedback.
Bonus: What are the medication rights of the patient?
A nurse places an IV in a patient. Immediately the patient yelps in pain and begins his arm is feeling numb. Soon the arm begins to swell, feel tender and cool to the touch. What is this called?
What is infiltration?
Bonus: Should the nurse continue the IV? If so, how would he do that?
How often must you monitor an IV site?