This receptor is primarily responsible for bronchodilation.
What is the β2-adrenergic receptor?
This device prevents reverse flow of gases in the anesthesia machine.
What is a check valve?
The Mallampati score is assessed with what proper techniques?
Patient sitting upright, mouth open, tongue protruded, no phonation.
Which coronary artery supplies the AV node in most people?
The right coronary artery (RCA).
Which cranial nerve provides sensation to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
CN VII (facial nerve, via chorda tympani).
The fire triad in the OR consists of?
Oxidizer, ignition source, fuel.
The minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of desflurane in a 40-year-old is approximately?
What is 6%?
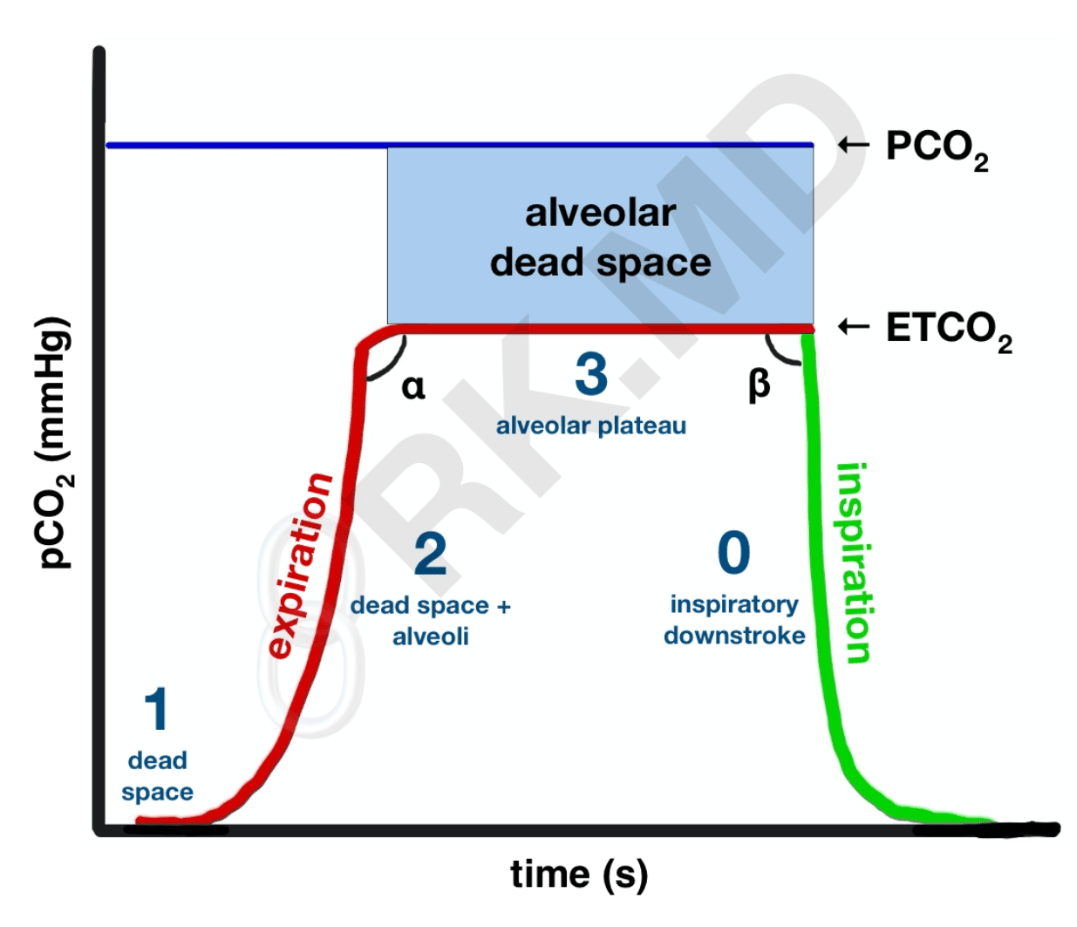
Identify the phase of capnography representing alveolar plateau.
What is Phase III?
What is the most common complication of LMA use?
Sore throat.
What hemodynamic change is most concerning with aortic stenosis?
Tachycardia (reduces diastolic filling & coronary perfusion).
What is the maximum recommended dose of lidocaine without epinephrine?
4.5 mg/kg (max 300 mg).
What is the most common cause of malpractice claims in anesthesia?
Respiratory events.
Which local anesthetic has the highest risk of cardiotoxicity?
What is bupivacaine?
How does a hypoxic guard system work?
It prevents delivery of <21% FiO₂ when nitrous oxide is used.
Describe two changes in pulmonary mechanics with pregnancy.
Decreased FRC, increased tidal volume, increased O₂ consumption.
How does positive pressure ventilation affect venous return and cardiac output?
Decreases both.
What is the most common complication of spinal anesthesia?
Hypotension.
Which inhaled anesthetic is most associated with diffusion hypoxia?
Nitrous oxide.
Explain how hypothermia affects the pharmacokinetics of non-depolarizing neuromuscular blockers.
It prolongs duration due to decreased metabolism and clearance.
What is the most definitive way to detect a CO₂ absorbent exhaustion?
Inspired CO₂ increases.
You see a shark-fin waveform on capnography. What does it indicate?
Bronchospasm/airway obstruction.
This triad of findings is classic for cardiac tamponade—name the triad and its three components.
Beck's triad - jugular venous distention (JVD, hypotension, muffled heart sounds.
What are the hallmark signs of local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST)?
CNS excitation → seizures → CV collapse.
What is the difference between Type I and Type II error in research?
Type I = false positive, Type II = false negative.
Describe the mechanism of action of nitroglycerin at the molecular level.
It releases nitric oxide → increases cGMP → smooth muscle relaxation → venodilation.
Describe the difference between pressure-controlled and volume-controlled ventilation.
Pressure-controlled = set pressure with variable tidal volume; Volume-controlled = set volume with variable pressure.
During one-lung ventilation, what is the single most effective maneuver to improve oxygenation?
Apply CPAP to the non-dependent lung.
Describe the anesthetic management goals in a patient with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM).
Maintain preload, increase afterload, avoid tachycardia and inotropes.
Explain how cerebral blood flow is affected by PaCO₂.
For every 1 mmHg change in PaCO₂, CBF changes by ~2–4% (directly proportional within 20–80 mmHg).
Describe the difference between sensitivity and specificity.
Sensitivity = true positive rate, Specificity = true negative rate.