List 5 signs and symptoms of ESLD
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to a buildup of bilirubin.
- Ascites: Fluid buildup in the abdomen, causing swelling.
- Edema: Swelling in the legs and ankles.
- Easy bruising and bleeding: Due to the liver's inability to produce clotting factors.
- Fatigue and weakness
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and loss of appetite
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating
- Itchy skin
Crohn's disease is an example of this type of condition that causes inflammation of the digestive tract and which part of the tract is most effected.
What is IBS inflammatory bowel disease and the Ileum
What are the two classifications of GIB
What is Upper and Lower
This is the common purpose of a nasogastric tube (NGT) and the highest risk of having one.
What is to drain stomach contents or provide nutritional support and prevent aspiration pneumonia?
What does a biliary drain do?
It allows bile to flow out of a blocked bile duct, into a drain bag or directly into the small intestine.
Name the condition, often associated with ESLD, is characterized by a buildup of toxins in the brain, leading to confusion and cognitive dysfunction, its treatment and Goal.
What is hepatic encephalopathy
Lactulose and 3-4 Bowel Movements/day
This treatment is often used to control inflammation in Crohn's disease, and it can be delivered through an infusion or injection.
What is biologic therapy example, TNF inhibitors
Remicade (infliximab)
What is the most common cause of upper GI bleed and Lower GIB
What is a Peptic Ulcer and Diverticular disease
Where should a Small Bore feeding tube terminate to prevent aspiration ?
post-pyloric
Who is allowed to flush and change the dressings on the biliary drains
Nursing!!
-Viral hepatitis: Hepatitis B and C
-Alcohol-related liver disease
-Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
-Autoimmune liver diseases
-Biliary diseases
-Total parenteral nutrition-related liver disease
This term refers to inflammation of the colon, which can have various causes, including infection, ischemia, and autoimmune diseases.
What is Colitis
Name three Preps used for Colonoscopy's
Golytely
Miralax
Enemas
What does PEG Tube stand for?
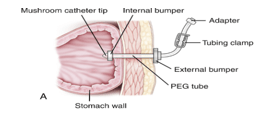
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Tube
This is a common complication is associated with biliary drains.
What is infection, or cholangitis?
What blood vessel is often implicated in ESLD when portal hypertension causes a dangerous increase in pressure, leading to varices in the esophagus or stomach
What is the portal vein?
A complication of severe colitis, this procedure involves the removal of the colon and is sometimes performed when other treatments fail.
What is a colectomy?
These two tests are used to identify the source of a GI bleed, especially when endoscopy is inconclusive.
What is a CT angiogram and tagged red blood cell scan?
How does a G-J tube work?
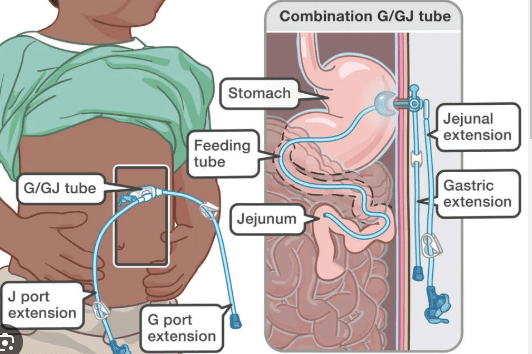
G-J tube is a tube that is placed into your child's stomach and small intestine. The “G” portion of this tube is used to vent your patients stomach for air and or drainage, as well as give your patient an alternate way for feeding. The “J” portion is used primarily to feed your patient.
Biliary drains are commonly used to treat this condition, where the bile duct becomes blocked, often due to a gallstone or tumor
What is cholestasis or choledocholithiasis?
What is the name of and describe the procedure to treat portal hypertension?
A TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt) procedure is a minimally invasive procedure, a procedure that involves inserting a stent (tube) to connect the portal veins to adjacent blood vessels that have lower pressure. This relieves the pressure of blood flowing through the diseased liver and can help stop bleeding and fluid back up.
This complication of Crohn’s disease can result in blockages, abscesses, or fistulas in the intestines.
What is a stricture or fistula formation?
This is a potential risk or complication of a colonoscopy, particularly if the procedure involves removing polyps.
What is perforation or bleeding?
Name two Nursing consideration when caring for a Pt with NGT or DHT
•Ensure the type and size of tube inserted in LDA
•check and document length of the tube that is external to the patient, measured from nose to the end of the tube Q 8 hrs and before any instillation of liquid into the tube
•X ray to confirmation of the tube position. Must have nurse communication order from MD order “OK to Use” This is also true for tube present prior to admission
Give three reasons your patient should seek medical attention for when providing discharge education.
-If you experience pain, swelling, or bleeding around the drain site.
-If you have trouble flushing the tube.
- If you notice any bile leaking around the drain site.
-Fever or other signs of infection
-If the tube falls out