The amount of heat required to raise 1 kilogram of water by 1 degree Celsius
kilocalorie
The class of chemicals that contain carbon
Organic chemicals
The 2 subatomic particles found in the nucleus
Protons, neutrons
This property of water, due to H bonding, allows bugs walk across its surface.
Surface tension
When a blood vessel is damaged, chemicals are released that summon platelets to the scene of the damage. When they arrive, they secrete more of the same chemicals, which calls more platelets, until the blood vessel is clogged. What type of mechanism is this?
Positive feedback
Why does 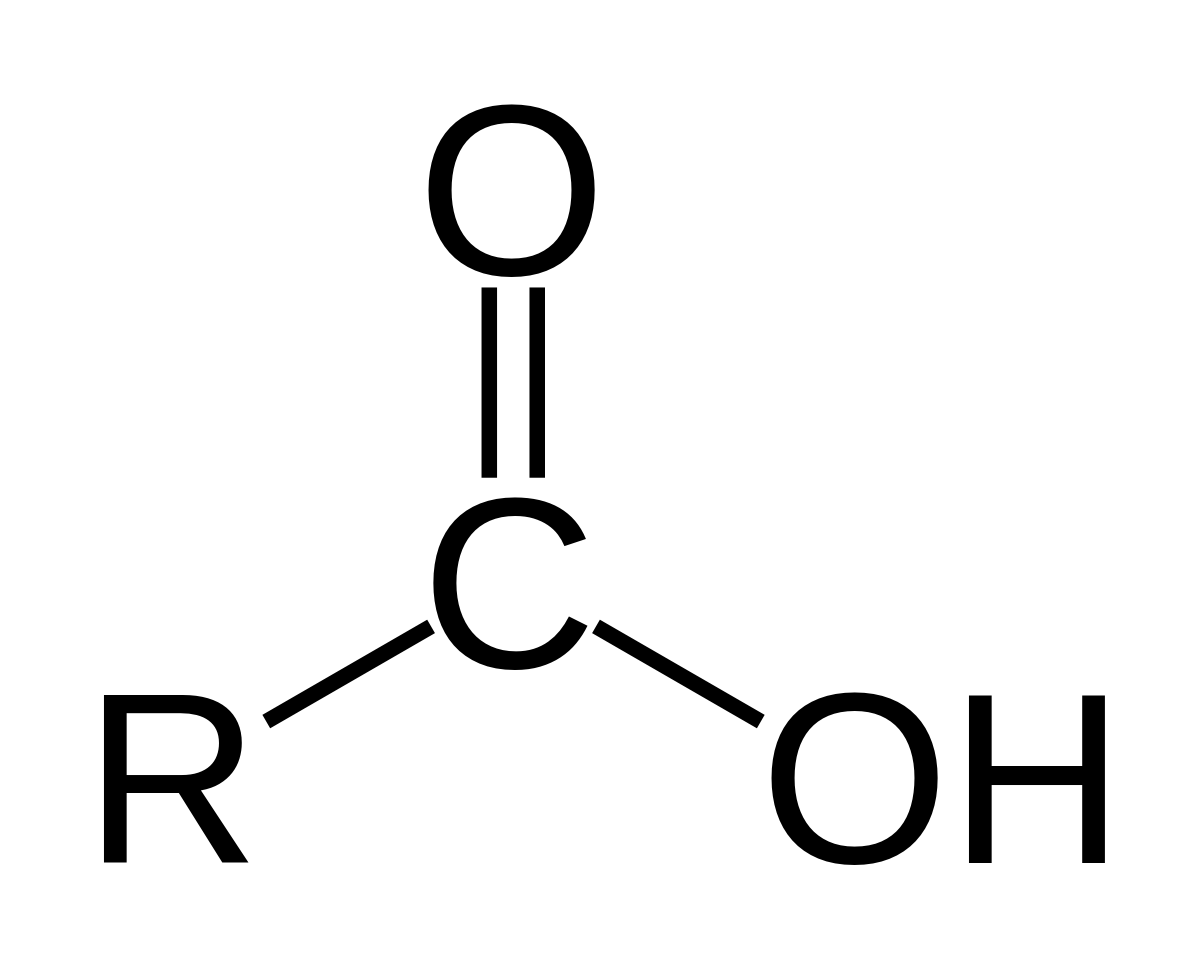 act as an acid?
act as an acid?
Carboxylic acid can (and usually does at physiological pH) release a H+ ion into solution.
Atomic mass of an atom with 11 protons, 13 neutrons, and 11 electrons.
24 daltons
Number of double covalent bonds that each carbon can form
2
This type of chemical bond results in a transfer of 1 or more valence electrons, resulting in 2 oppositely charged atoms that are attracted to each other.
Ionic bond
6.02 X 1023 of anything
1 mole
The most basic structural and functional unit that constitutes life.
A cell
Name this functional group
Amine group. Acts a weak base.
Molecular mass of HNO3
H = 1, N = 14, O = 16
31 daltons
A chemical group, attached to an organic molecule, directly involved in chemical reactions.
Functional group
This group is common in monosaccharides:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hydroxylfunctional-56a129e05f9b58b7d0bca5df.jpg)
hydroxyl group
Double down for double points: These groups form weak bonds called _________.
Donates a hydrogen to a solution
Acid
6.02 X 1023 of anything, but usually atoms or molecules
Mole
Molecules that sport one of these groups 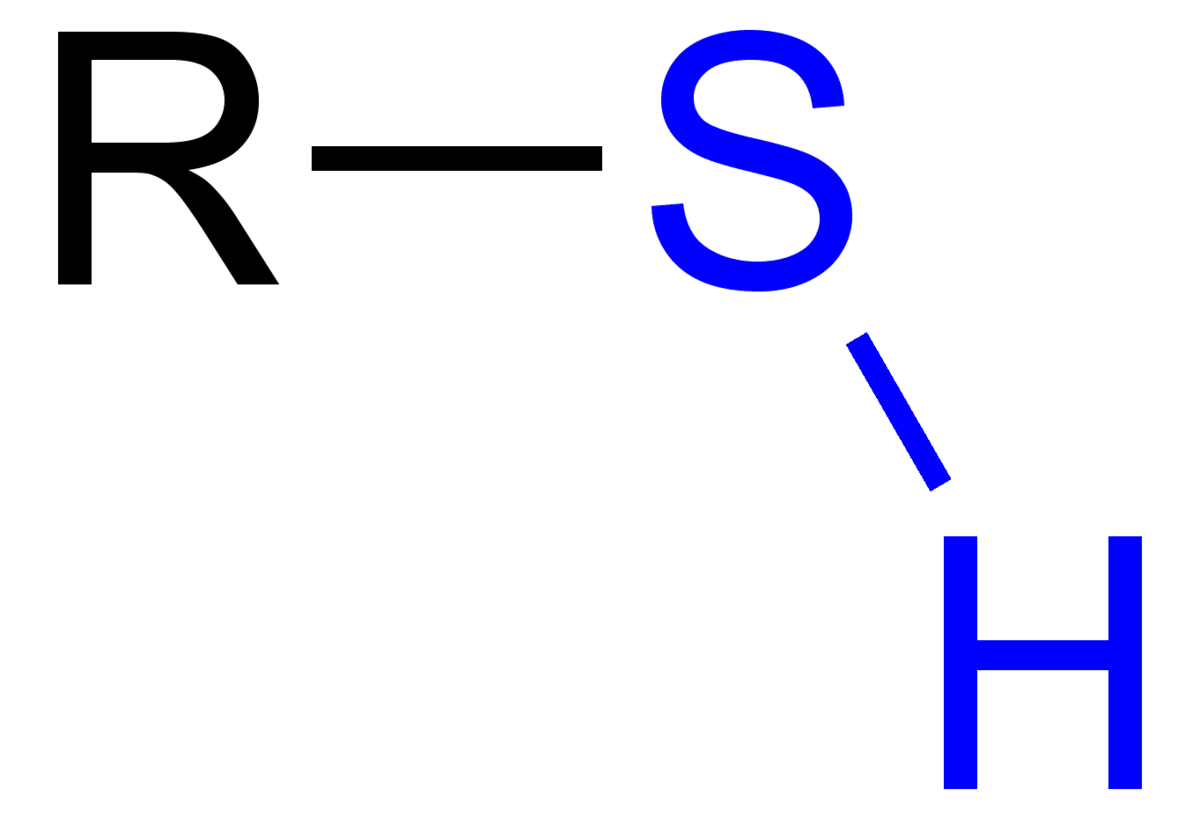 are called
are called
Thiols (sulfhydryl group)
Double down for double points: Which amino acid has a sulfhydryl group?
Molar mass of methane, CH4
C = 12, H = 1
16 grams
Organic molecule consisting of only Carbon and Hydrogen
Hydrocarbon
This group is nonpolar and is often used to regulate gene expression.
and is often used to regulate gene expression.
Methyl group
Will pick up H+ ions if pH decreases, can also donate them if pH increases. Prevents wild pH swings.
Buffer
Ice floats on water because
Its solid form is less dense than its liquid form.
An important group for cellular energy
Phosphate group. Found in ATP and nucleotides, for a start. Weak acid, very polar.
How much NaCl would you weigh out to make 1 liter of .25M NaCl solution?
Na = 11
Cl = 17
7 grams
Both of these molecules have the same molecular formula - C6H12O6, they are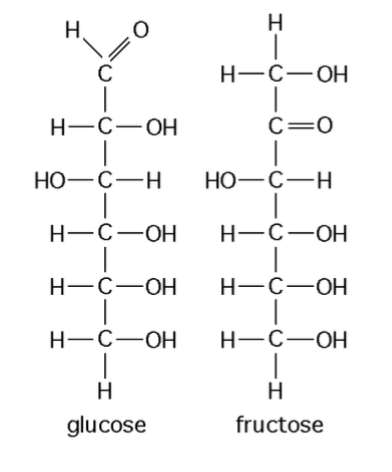
Structural isomers
In this type of chemical bond, an electronegative atom "hogs" the shared electrons.
Polar covalent bond
The property of a substance that is defined as the amount of heat required to raise 1g of that substance by 1 degree Celsius.
Specific heat
If the pOH of a solution is 2, this is the pH.
pH 12
Carbonyl groups are split into 2 categories. Name them and what makes them different from each other.
Aldehydes: double bond to oxygen is on the terminal carbon.
Ketones: double bond to oxygen is to a carbon that is not bonded to hydrogen.
