A 29-year-old man is evaluated for fatigue and difficulty concentrating. He finds himself worrying frequently and reports that he loses energy easily during the week, worries about being evaluated negatively at work, and sometimes snaps at his coworkers when he is particularly tense. These symptoms have been present most days of the week for the past year. Family and personal medical history is otherwise noncontributory, and he takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs and other findings are normal.
Results of laboratory studies show normal thyroid function. A urine drug screen is negative.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
GAD
Panic attacks
ADHD
Social anx
An 89-year-old woman is evaluated in follow-up after discharge from a rehabilitation facility. Two weeks ago, she fractured her right hip after falling in her home when she tripped rushing to the bathroom to urinate during the night. Urinary urgency continues to be a problem. She has a history of hypertension, coronary artery disease, and insomnia. Her home medications are amlodipine, aspirin, lisinopril, metoprolol, and diphenhydramine as needed for sleep.
On physical examination, vital signs and other findings are normal. The incision at the right hip is healing well with no signs of infection.
Which of the following is the most appropriate medication management to reduce this patient's risk for falls?
no more benadryl
Ca
oxybutinin
d/c metoprolol
A 45-year-old man is evaluated during a routine examination. He does not exercise. He has never smoked and drinks one to two beers, 4 nights per week. There is no family history of premature atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. For the purpose of calculating the patient's risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the patient reports that he is Black.
On physical examination, blood pressure is 124/78 mm Hg. BMI is 28, and waist circumference is 106 cm (42 in).
Laboratory studies:
Fasting blood glucose : 106 mg/dL (5.9 mmol/L)
LDL cholesterol: 148 mg/dL (3.83 mmol/L)
HDL cholesterol: 38 mg/dL (0.98 mmol/L)
Triglycerides: 160 mg/dL (1.81 mmol/L)
His calculated 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) is 4.3%.
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Diet and exercise
A 72-year-old man is evaluated during an annual physical examination. The patient is a widower and has one daughter, from whom he is estranged. He has not completed an advance directive. His father died of complications of stroke after a prolonged hospital stay.
The patient mentions that he does not want to die like his father did, “hooked up to machines.” He is worried that he will receive aggressive care at the end of life, which he does not want.
The physician engages the patient in a discussion of health care preferences and goals for future care.
Which of the following best describes this interaction between the patient and his physician?
Advanced care planning
Creation of living will
Execution of advanced directive
Identification of healthcare proxy
A 32-year-old man is evaluated in the emergency department for low back pain of several weeks' duration. The pain is in the lumbar area and does not radiate. He has no other symptoms. Medical history is significant for injection drug use.
On physical examination, temperature is 37.4 °C (99.4 °F); other vital signs are normal. Pain is present with gentle palpation of L3 and L4. The pain worsens with hyperextension or flexion of the spine. Marks from injection drug use are seen on the forearms. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Interferon-γ release assay, HIV test results, and blood and urine cultures are pending.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
MRI spine
CT spine
Xray spine
Empiric Abx
A 42-year-old man is seen for a routine evaluation. Medical history is unremarkable. He takes no medications.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 35. The remainder of the physical examination is normal.
Laboratory studies reveal an LDL cholesterol level of 128 mg/dL (3.32 mmol/L) and triglyceride level of 348 mg/dL (3.93 mmol/L).
His 10-year risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease based on the Pooled Cohort Equations is 2.4%.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
recommend lifestyle interventions
fibrate
statin
omega 3 FA
A 29-year-old woman requests advice after receipt of a direct-to-consumer genetic test result that included BRCA gene analysis. She has no breast symptoms and has not undergone any previous breast cancer screening. Her mother was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 48 years and ovarian cancer at age 60 years; she died at age 62 years. The patient's sister was recently diagnosed with breast cancer at age 41 years and is still living. The genetic test report is negative for BRCA1 and BRCA2variants. Family members have not undergone genetic testing.
On physical examination, vital signs, breast examination, and other findings are normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Genetic counseling
BRCA test
MRI breast
Reassurance
A 79-year-old woman is evaluated for weight loss. She is brought to the office by her niece, with whom she moved in 3 months ago. There are several adult family members in the home. The patient is able to ambulate short distances in the home with a walker. She does not toilet independently and requires assistance with feeding, bathing, and dressing. Current medical problems include type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. Medications are metformin, losartan, atorvastatin, and acetaminophen.
On physical examination, vital signs are normal. BMI is 22. The patient is disheveled. She speaks very little and only to answer yes-or-no questions. Dry mucous membranes are noted. The perineum is soiled with caked feces and urine, and skin in the area is erythematous. An early stage 2 sacral decubitus ulcer is noted. There is bruising on the right upper arm. The remainder of the examination is normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Adult Protective Services
Feeding tube
Hydrocolloid wound dressing
Hwalek-Sengstock Elder Abuse Screening Test
A 47-year-old man is evaluated in the hospital after treatment for acute alcoholic pancreatitis. During the hospitalization, he is diagnosed with moderately severe alcohol use disorder. Medical history includes hypertension. He has been prescribed antihypertensives in the past but struggled with medication adherence; he recognizes this as a potential problem. Medical history is otherwise unremarkable, and screens for depression, other mood disorders, and additional substance use disorders are negative. He takes no medications at the present time.
He agrees to attend a 12-step facilitation program after hospital discharge, but he is concerned that it will not help sufficiently.
Which of the following is the most appropriate additional treatment?
Injectable naltrexone
PO naltrexone
Bupropion
Lorazepam
A 74-year-old man undergoes follow-up evaluation 4 weeks after an urgent care visit for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. He is concerned about an upcoming trip and the possibility of falling. He has had no recent falls but did have a near fall. Medical history is significant for atrial fibrillation. Current medications are metoprolol, apixaban, and meclizine.
On physical examination, blood pressure and pulse rate are normal and without orthostatic changes. Cardiac examination reveals an irregular rhythm. Screening neurologic examination is normal.
The Timed Up and Go Test result is prolonged (16 seconds).
The patient undergoes canalith repositioning with the Epley maneuver.
Which of the following is the most appropriate additional management to reduce this patient's risk for falls?
Stop meclizine
Stop metoprolol
Rx for four prong cane
Prescribe vit D
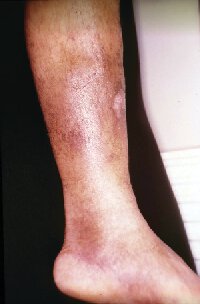
A 76-year-old man is evaluated for a several-year history of bilateral lower extremity edema and hyperpigmentation. He has also noticed that his legs are tired by the end of the day and feel heavy. He has hypertension and obesity. His only medication is lisinopril.
Management?
Compression stockings
LE duplex
Lasix
Cefadroxil
A 28-year-old man is evaluated in follow-up after a visit for multiple fluctuating somatic symptoms, including paresthesia, nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, dizziness, muscle spasms, and fatigue. An extensive evaluation, including subspecialty consultation, laboratory testing, imaging, and diagnostic procedures, showed no clear diagnosis. He is frustrated at the lack of diagnosis and is concerned that “something is being missed.”
On physical examination, vital signs and other findings are normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Acknowledge the patient's feelings
Assess for malingering
Cure him
Follow up only if symptomatic
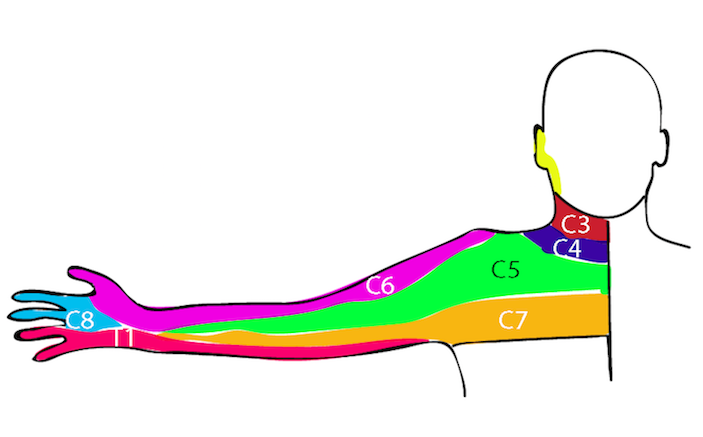
A 28-year-old woman is evaluated for a 2-month history of left-sided neck and shoulder pain and paresthesia in her left arm from her fingers to her shoulder. Her symptoms worsen with overhead arm activity. She takes no medications.
On physical examination, she has full range of motion in her left neck, shoulder, elbow, and wrist. Muscle bulk, tone, and strength in the upper extremities are normal bilaterally. Neurologic examination reveals normal reflexes and sensation in the upper extremities bilaterally. Upper extremity pulses are full and equal. There is no cyanosis, swelling, or edema.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome
Arterial thoracic outlet syndrome
Venous thoracic outlet syndrome
Cervical radiculopathy
A 58-year-old woman is evaluated for follow-up of chronic insomnia. She has participated in cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia; however, she continues to have difficulties maintaining sleep. After a discussion of risks and benefits and shared decision making, the patient has opted for a limited course of pharmacologic therapy for her insomnia. She has no other medical problems and takes no medications.
Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Doxepin
Trazodone
Nothing
Benadryl
A 34-year-old woman is evaluated for a 3-month history of dry cough. She does not use tobacco. A chest radiograph obtained 1 month ago was normal. The patient has a history of seasonal rhinitis. Since the onset of the cough, she has used fluticasone nasal spray daily without improvement. She has no other symptoms.
Vital signs and physical examination are normal.
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Spirometry
Omeprazole
Sputum eosinophil count
Chest CT
Ambuatory pH monitoring
An 80-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with fever, confusion, and productive cough. He has COPD. A chest radiograph shows left lower lobe consolidation. The emergency department has been simultaneously involved in caring for several patients critically injured in a motor vehicle accident. The emergency department team provides nebulizer treatment and intravenous glucocorticoids to the patient. Admission to the hospital for COPD exacerbation is recommended. The hospitalist team is notified of the admission but is interrupted by the activation of a rapid response team for another patient. The inpatient nurse team is not notified of this patient admission. Several hours later, the patient is found in his hospital room unresponsive with agonal breathing and hypotension.
Which of the following is the fundamental basis for this diagnostic error?
Systems factors
Deductive reasoning
Time management
Estimation of pre-test probability