What is the Arrhenius theory?
- Acids produce hydrogen ions in solution
- Bases produce hydroxide ions in solution
What does it mean for a substance to be amphoteric? Name three compounds that are amphoteric.
A compound that can act as an acid and a base.
Name the six strong acids.
HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO4, H2SO4
How do weak acids differ from strong acids?
Weak acids dissociate partially in solution, while strong acids dissociate completely in solution.
What is the Brønsted-Lowry theory?
– Acid is a proton donor
– Base is a proton acceptor
What are the conjugate bases of H3PO4, H2PO4-, HPO42-?
H2PO4-, HPO42-, and PO43-
Name the strong bases.
Group 1 hydroxides and Ca, Ba, Sr hydroxides.
A weak acid HA is diluted until the pH is 5.43. What is the concentration of H+?
3.72*10-6 M
What is the Lewis theory?
- Lewis acids accept an electron pair to form
coordinate covalent bonds
- Lewis bases donate lone pairs of electrons to
form coordinate covalent bonds
As acid strength increases, conjugate base strength ______.
decreases
What is [H+] of a 0.01 M solution of HClO4
0.01 M
A weak base is diluted until the pH is 9.22. What is the concentration of OH-?
1.66*10-5 M

Which theory best explains this acid?
Lewis theory
Conjugate acid of a base is obtained by:
Addition of a proton to the base.
What is the pH of a 1.34*10-4 M solution of HBr?
3.87
Hydrocyanic acid (HCN) has a Ka of 6.2*10-10. What is the pH of a 0.100 M solution of HCN?
5.10
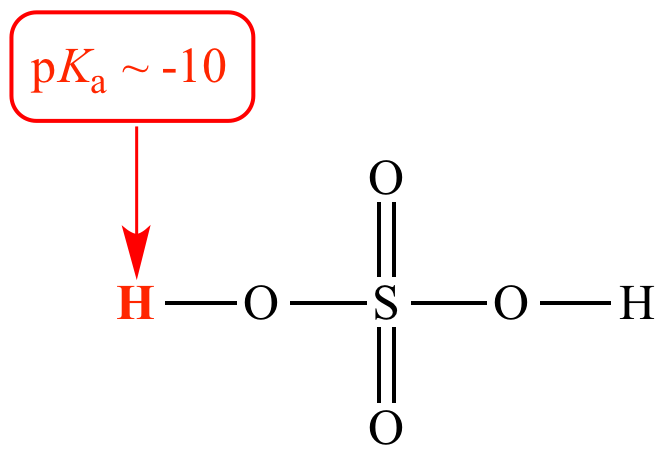 Which theory best explains the behavior of this acid?
Which theory best explains the behavior of this acid?
Bronsted theory
What are the conjugate pairs in this reaction:
and
Is the Ka of a strong acid <1 or >1?
>1
What is the pH of a 0.300 M solution of aniline? (Kb = 3.8*10-10)
9.03