Newton's 3rd
Fnet = ma
What we call a measurement that has both magnitude and direction
Vector
Applied force required to lower a 2kg ball at a downward rate of 4m/s2.
12N
The concept demonstrated this warm-up. One word.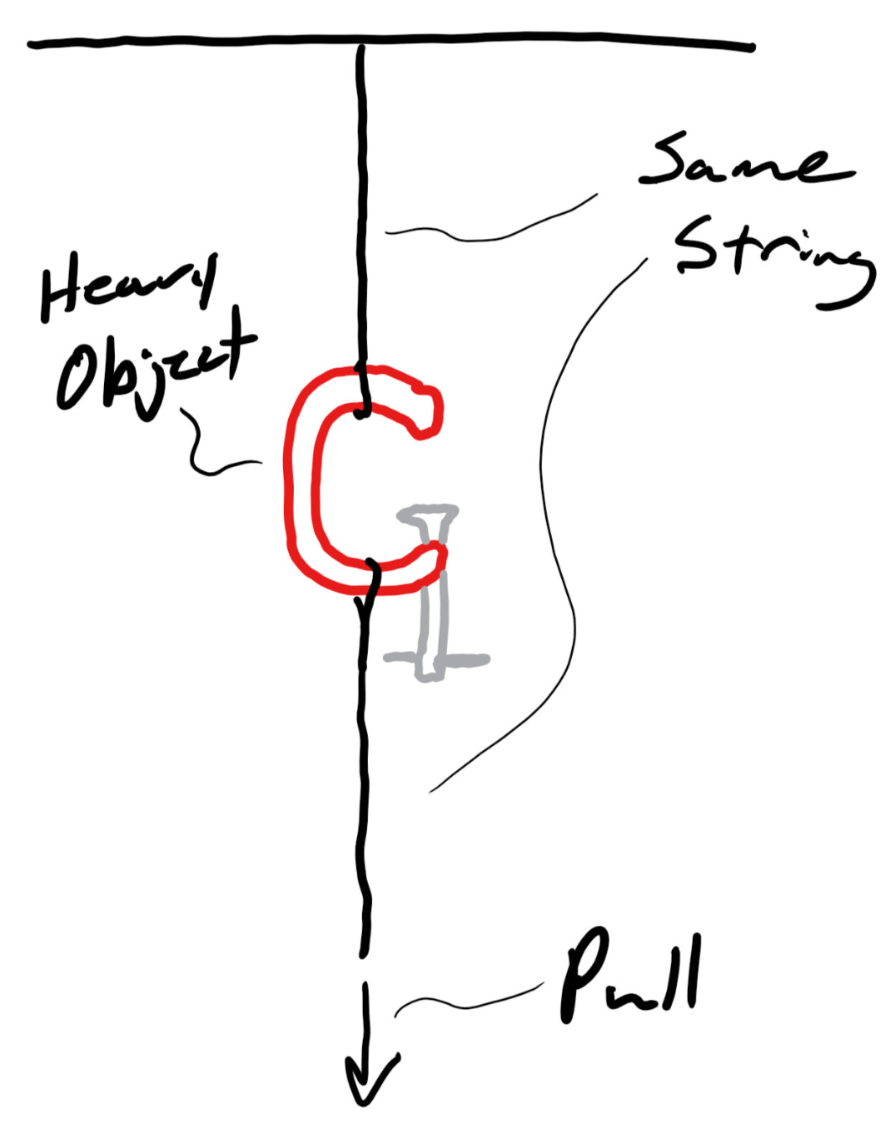
Inertia
Gm1m2/r2 = Fg
Newton's Law of gravitation
All orbits are elliptical, and the object being orbited is at one of the ellipse's foci.
Kepler's 1st
Free-Fall
The string with the most tension...
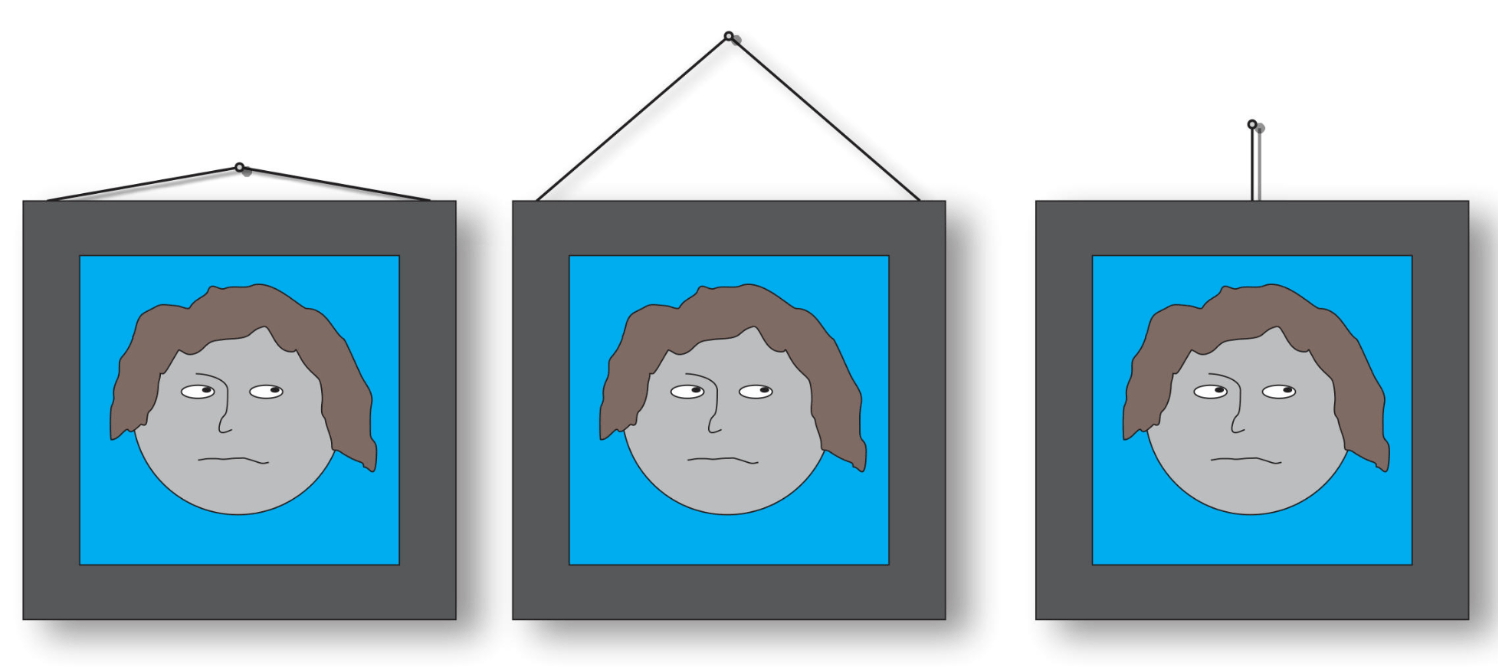
Left
Without this force, this demo won't work [something other than gravity]

Friction
Regardless of its distance from the planet being orbited, a satellite "sweeps out" equal areas in equal times.
Kepler's 2nd Law
The law that tells us that planets move more slowly when they are farther from the Sun.
Kepler's 2nd.
A force that exerts itself equally, in both directions, at every point within a string.
Tension
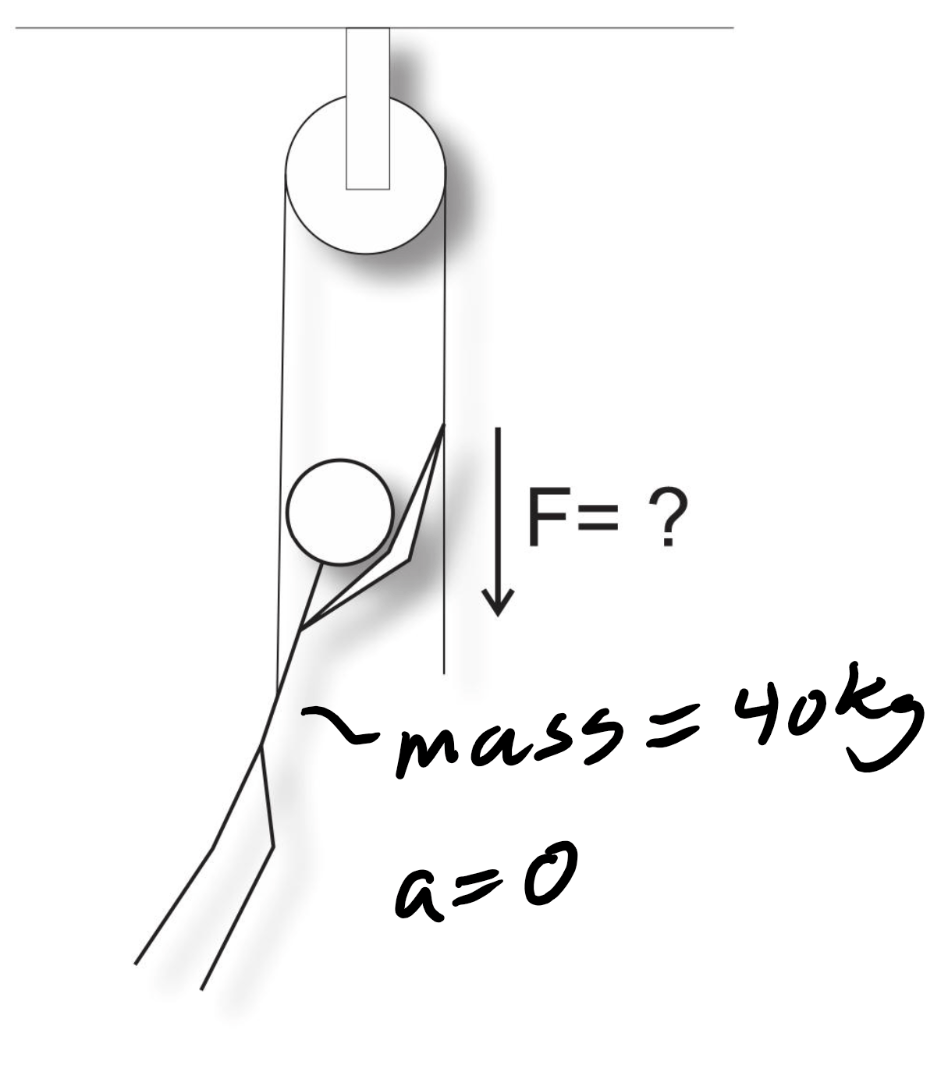
200N
The velocity of the O.

Zero
Newton's 1st
If mass of an object decreases, but it continues to experience the same net force, this is what happens to its acceleration.
The horizontal distance that a projectile travels during a symmetric flight.
Range
Push the Earth harder than the other team pushes the Earth.
It's the main reason why clouds don't fall.
Their tiny particles have very slow terminal velocities.
For every object in a solar system, the ratio of the square of its orbital period to the cube of its orbital radius is the same.
Kepler's 3rd Law
This is the action that causes the reaction of a rocket ship to accelerate in the vacuum of space.
Rocket's exhaust is pushed out.
The name for the acceleration of an object in uniform circular motion.
Centripetal
Three motionless ships of varying mass (100kg, 1,000kg, and 10,000kg), but otherwise identical characteristics, are shot with cannonballs of identical mass that embed in the ships, causing them to float backward. If the impact time is the same, which ball exerts the most force on its target?
The one that hits the 10,000kg ship
The name of the force that is most directly responsible for the person's acceleration.
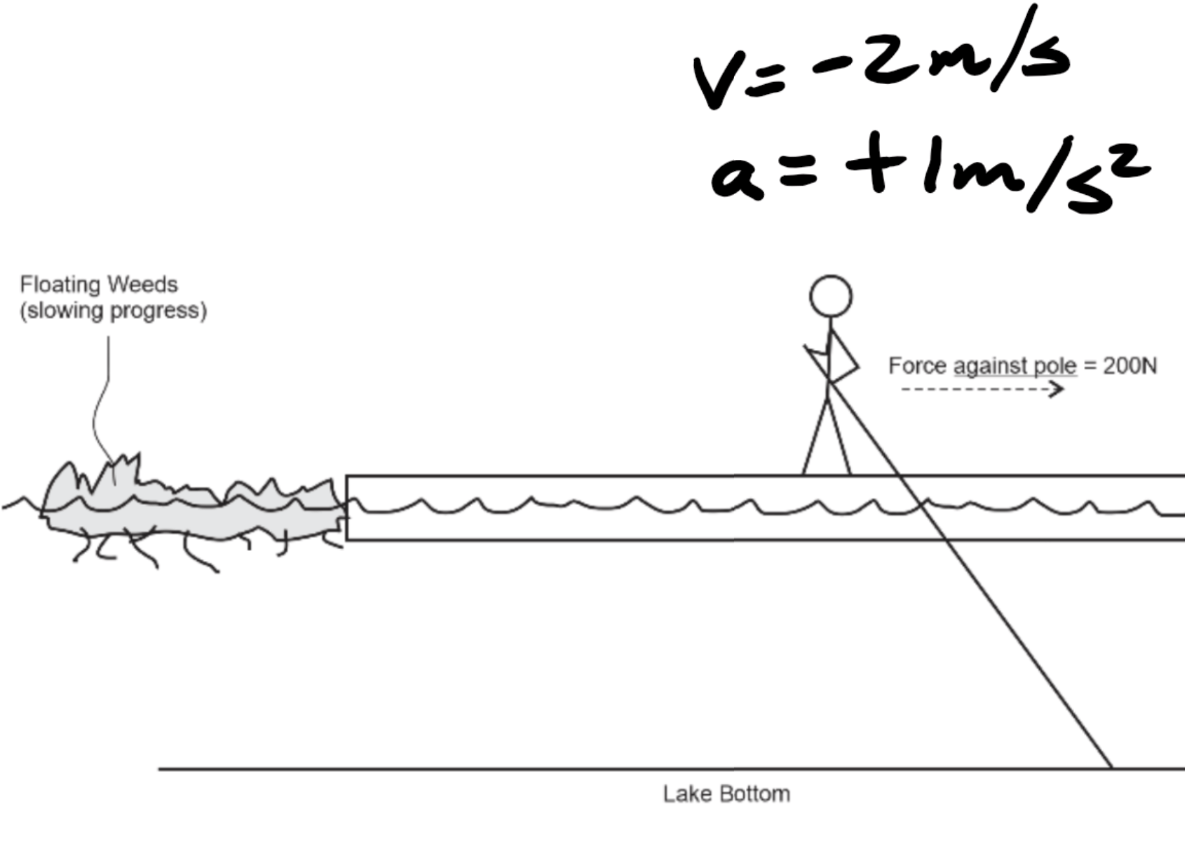
Friction