The percentage of patients with generalized myasthenia gravis that are AChR antibody positive?
What is 85% of MG patients. 6% have MuSK MG. 1-2% have LRP4 MG, Seronegative 10%
RoPE is an acronym. What does the P stand for?
Risk of Paradoxical Emoblism (RoPE) Score.
"Approximately 20% to 30% of ischemic strokes are cryptogenic, an etiologically heterogeneous class including many possible occult mechanisms. One-half of patients <60 years with cryptogenic stroke (CS) have a patent foramen ovale (PFO), twice the prevalence in the general population.1,2 For these patients, the stroke mechanism may be paradoxical transcardiac embolism (ie, PFO-related) but may still be another occult cause (ie, PFO-unrelated)."
RoPE score 1 through 3--negligible chance stroke is due to PFO, 10 90% probability stroke is due to PFO
The name of the robot at UH, that delivers medications
Who is Pill-Nelope
Name of the involuntary movement that may develop when taking Sinemet
What is a dyskinesia—can include tremors, head bobbing, fidgeting movements
The name of the ability to recognize an object by tactile sensation, with eyes closed, asking a patient to identify objects in their hand
What is stereognosis
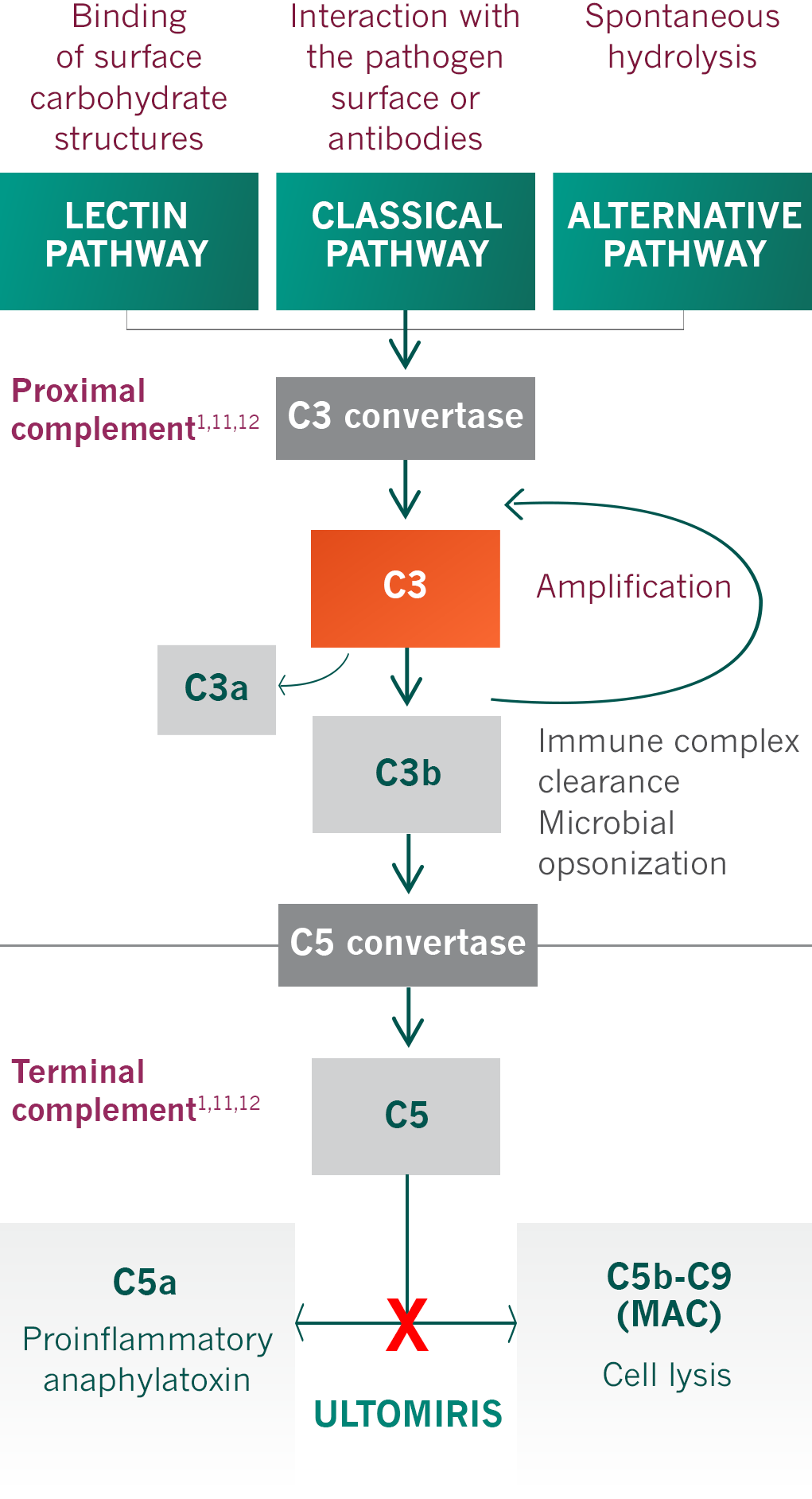
What is the unique inflammatory pathophysiology of AchR positive myasthenia gravis as compared to MuSK myasthenia gravis? In other words what innate system of the body is triggered by the AcHR antibody docking onto the muscle membrane?
What is the complement system. More specifically the classical pathway.
You will recall there are many Cs in the complement pathway including C1r, C1s, C4, C4, C4a, C5 convertase = C3C4b2a3b.
C3a, C4a, 5a are proinflammatory, increases vascular permeability, smooth muscle contraction and leucocyte recruitment.
C5b eventually helps to form Membrane attack complex, (MAC),
MAC lyses the cell via several mechanisms and causes destruction of the neuromuscular junction.
This is why complement inhibitor medications work well for myasthenia gravis. You inhibit the destruction of the neuromuscular junction by lessening the destruction of the neuromuscular junction.
The three complement inhibitors are Ultomiris, Soliris and Zilucoplan that all work on preventing the Cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b

The theory why AChR positive MG does not respond to Rituximab therapy?
What is the B cells that are involved in long term ACHR MG do not have CD20 marker. The Autoantibodies in long term AChR positive MG are thought to be generated from long lived plasma cells.
MuSK positive MG autoantibodies are thought be made continuously from short lived plasmablasts which have the CD20 marker on them and thus MuSK positive MG responds to Rituximab therapy as it is a CD20 B cell inhibitor medication.
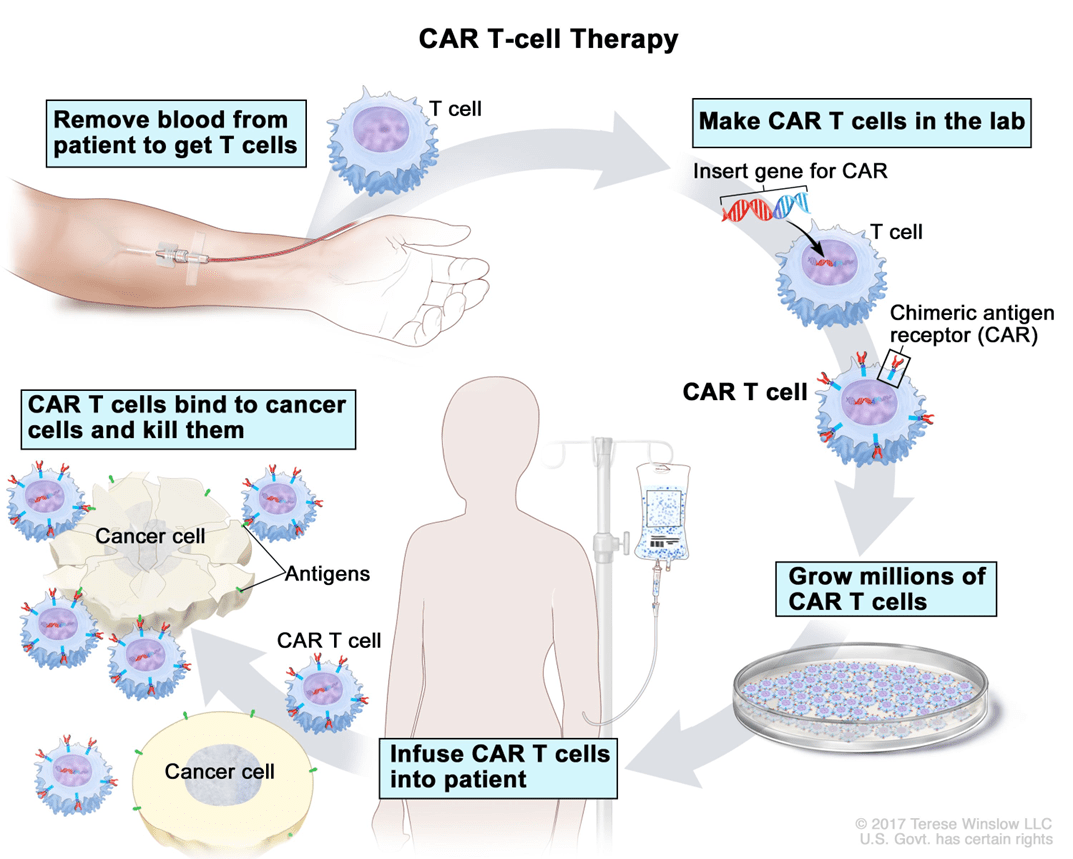
The full name of CAR as it pertains to CAR T-cell therapy. Bonus 100 points to the team who can explain the process of CAR T-cell therapy.
What is chimeric antigen receptor.
For CJD, there is a recent trial using an investigational molecule called ION717. Explain the mechanism of this molecule.
What is an antisense oligonucleotide designed to inhibit the production of prion protein (PrP).
The specific artery branch that when occluded leads to a "stroke of the eye" aka monocular vision loss.
What is the central retinal artery, which is a branch of the opthlamic artery. When blocked, can lead to sudden, painless vision loss in one eye. Can be described as seeing a curtain drop across vision. A Medical emergency.

Patients with AchR positive generalized myasthenia gravis have different treatment options targeting different parts of the immune system, including thymectomy. Share the answer for the most common histopathological diagnosis of the removed thymus tissue in this patient population?
What is thymic hyperplasia?
About 65%-70% of AchR positive MG patients have thymic follicular hyperplasia.
About 10%-15% of AcHR positive MG patients have a thymoma.
Overall for many patients, they will need less immunosuppression post-thymectomy than without thymectomy. Some will even achieve remission.
There are 3 Identified Acetlycholine Receptor Antibodies, Binding, Blocking and Modulating. Of these three, which is the one activates the complement system?
What is Acetycholine Receptor Binding Antibody.
AChR Binding Antibody--activates complement, Degrades ACh Receptors, Leads to Endocytosis
AChR Blocking Antibody--Binds ACh Receptors, Impairs ACh from docking
AChR Modulating Antibody--Crosslinks ACh Receptors, Endocystosis of the Receptor
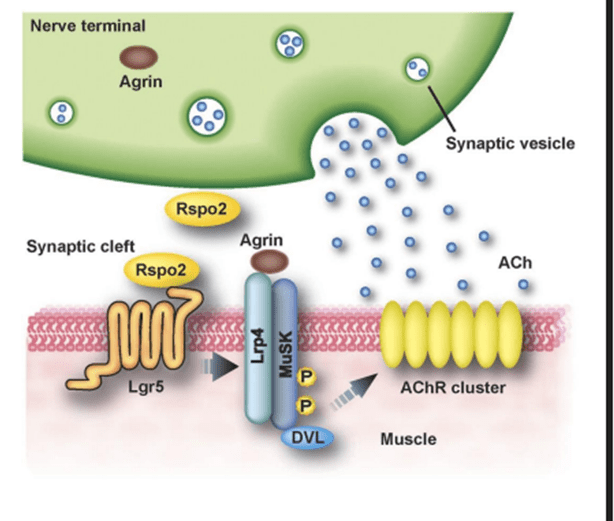
Of note MuSK Antibody (Muscle-Specific Kinase) Ab, reduces the clustering of ACh receptors
The name of the fluid-filled spaces that surround blood vessels in the brain. Origin is from German and French.
What is a Virchow-Robin spaces named after German pathologist Rudolf Virchow and French anatomist Charles Phillppe Robin
The essential vitamin that has a half-life of 18 days. Its deficiency is associated with beriberi.
What is thiamine? Needed for thiamine pyrophosphate, cofactor of citric acid cycle and needed for sugar breakdown. Citric acid cycle is necessary for carbohydrate, lipid, amino acid metabolism. Thus if thiamine deficient, one would inhibit many molecules including neurotransmitters glutamic acid and GABA. Thiamine is also involved in neuromodulation. Thiamine deficiency is thought to be major contributor to Wernickes in those with poor nutrition including ETOH abuse.
In contrast, the half-life of B12 is years (2-5 years in some studies). One area that B12 is stored is in the liver.
The percent range of those with GCA have PMR?
What is about 60% (58%). PMR affects proximal, axial joints, with elevated ESR as well. Responds to low dose steroids. PMR prevalence is 1 in 133. ~ 15-20% with PMR develop GCA. ~ 60% of individuals with GCA, have PMR.
The Greek/Latin translation of the condition myasthenia gravis?
mys--muscle
Asthenia--weakness
Gravis--severe
What is Grave muscle weakness or severe muscle weakness?
What type of brain cell is the target of the condition that is most likely represented by the below images? 
What are astrocytes. Inflammation in NMO spectrum disorders primarily seem to target astrocytes. AQP4 is a water channel that is present in the foot processes of astrocytes. It is concentrated in the spinal cord gray mater, periaqueductal and periventrical areas.
The specific name of the variant of CJD that presents with cortical blindness.
What is the Heidenhain variant of CJD. Vision disturbance is seen in 10-20% of cases of sCJD at presentation and up to 30-50% during the course of the illness. In 1928, Heidenhain described cortical blindness as an initial symptom of spongiform encephalopathy.
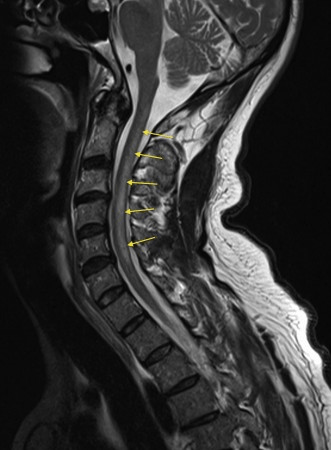
The most common vitamin deficiency associated with the MRI Findings in this picture
What is B12 deficiency? Leading to subacute combined degeneration of the dorsal columns and lateral columns due to demyelination. Symptoms can include sensory deficits, paresthesias, weakness, ataxia, gait changes. Can lead to spasticity and plegia in severe cases.
We get cobalamin from meat, fish, dairy and eggs and fortified cereals. Richest sources are clams and animal liver. History taking should focus on diet, GI symptoms and history, autoimmune disease, and drug-induced causes including gastric acid suppressants, metformin, and nitrous oxide abuse. Lesser causes in the US are tapeworm infections and genetic causes.
The condition that leads to sudden-onset eye pain, red eye, nausea, vision loss, headache that is an opthamologic emergency.
What is acute angle glaucoma. Occurs when aqueous humor in the eye cannot flow in and out normally. This leads to a build up of intraocular pressure which damages the optic nerve. With angle-closure glaucoma, natural lens thickens and pushes against the iris, blocking drainage.
The below is a picture of repetitive stimulation. This is an EMG test commonly used to evaluate for neuromuscular junction disorders such as myasthenia gravis. What is the reason for the classic "U" shaped seen as is the case below? In other words, why does the amplitude increase again at the 4th or 5th shock in a particular train?
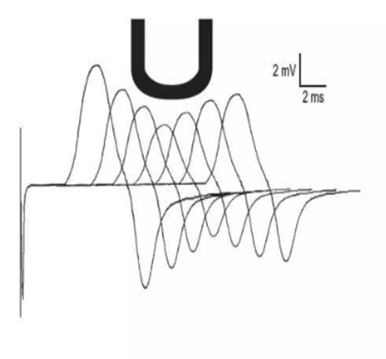
What is the axon utilizing the secondary or mobilization store of Acetycholine?
Acetylcholine is stored as a primary, secondary and tertiary storage in the nerve.
Primary--beneath the pre-synpatic nerve terminal membrane
Secondary--located toward the axon, starts to replenish the immediately available store after 1-2 seconds of rep stim and is responsible for the classic U-shaped of rep stim where the amplitude increased again after the 4th or 5th shock.
Tertiary store--also available in the axon and cell body.
The above is a pictorial of IgG. It is the only Ig that has the ability to exchange its arms as shown above. We talked about IgG. This question is
1.) What is the half-life of all IgG?
1.) Half life of IgG is 21 days. This is due to the FcRn system which essentially helps to recycle IgG. When IgG is bound to FcRn, it is protected from being degraded by lysosomes.
IgG4 -- Musk Myasthenia Gravis. This is important to know because an IgG4 mediated disease can be treated with medications such as Rituximab.
Further, in AchR positive MG, this is an IGG1 and IgG3 disease with pathophysiology including the destruction caused by activating the complement cascade.
In MUSK MG, the destruction is not caused by the complement cascade. MUSK MG is caused by blocking assembly of agrin-LRP4-Musk complex, results in decreased AChR clusters--leads to less miniature endplate potential and EPP, leads to failed muscle action potential and weakness.
For comparison, the half-life of
IgA and IgM- 4 to 6 days
IgE - 2 to 3 days (can be up to 9 to 12 weeks if bound to a particular receptor)
The neurologist who coined the term asterixis with colleague Raymond Adams in the 1940s.
Who is Joseph Foley. Dr. Foley is the father and founder of the neurological division at University Hospitals; under Dr. Foley he built a division of neurology within the Department of Medicine. Story goes that he consulted a Jesuit Scholar from Boston College. Dr. Foley and Father Cadigan drank metaxa (Greek spirit, a wine with botanicals) and came up with the term an (negative) - iso (equal), and sterixis (solidity of firmness). Anisoterixis was too many syllables, and thus shortened it to asterixis.
What is the other name for Mad Cow Disease, aka Bovine Spingiform Encephalopathy (BSE)?
What is variant CJD. This is linked to the consumption of contaminated beef. Variant CJD in humans can cause memory loss, early death, psychiatric symptoms. The incubation period in cattle can be 2-8 years and cattle can develop a fatal disease that can include symptoms of nervousness, aggression, lack of coordination, affects appetite and motor system. Time to death is 2 to 6 months.
vCJD should not be confused with sporadic CJD which is what we see in the human patient population. Median survival time for sporadic CJD in humans is 4 to 6 months after diagnosis, can vary with some living longer than 1 year and rare cases even longer.
The most common opthalmic manifestation of systemic sarcoidosis?
What is anterior uveitis. The exact incidence is widely variable depending on studies, some citing 10-50%.