What psychological concept refers to the phenomenon where retrieval of information is most effective when the conditions of encoding and retrieval are the same or highly similar?
Encoding Specificity is when memory recall is optimized when the conditions present during encoding match those during retrieval.
For example, if you studied for a test in a quiet room with soft music playing, you may perform better on the test if you're in a similar environment.
What psychological concept refers to the phenomenon where memory retrieval is most efficient when an individual's internal state at the time of encoding matches their state at the time of retrieval?
State-Dependent Learning
Information learned or encoded in a particular state, such as being happy, sad, intoxicated, or sober, is better recalled when the individual is in the same state during retrieval.
State-dependent learning highlights the role of internal cues or context in memory retrieval processes, emphasizing the interconnectedness between mood states and memory performance.
What is anterograde amnesia
Type of memory impairment characterized by the inability to form new memories after the onset of amnesia.
Individuals with anterograde amnesia may have intact memories of events that occurred before the onset of amnesia, but they struggle to encode and retain new information or experiences.
A seemingly sly criminal plots to murder a rival gang leader and "get away" with the crime by pleading insanity. Apart from the low probability of success when pleading insanity, why did this sly criminal’s plan fail?
A. He did not have a prior record of psychological disorders.
B. The court could determine that he did not meet the criteria for insanity.
A. He did not have a prior record of psychological disorders.
What is the criteria for a psychological disorder?
1. Statistical Rarity
2. Disrupts daily life
What book do psychologists typically use to diagnose patients?"
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) 5
As the night falls, Sally starts feeling sleepy, and her body begins to wind down for rest. What hormone is likely to be secreted by her pineal gland to regulate her sleep-wake cycle?
Melatonin
True or False - Insomnia is a sleep disorder characterized by persistent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, leading to inadequate sleep quality and daytime impairment.
True
What is the "magic number" that represents the typical capacity of working memory?
7
What cognitive strategy involves improving memory and increase working memory capacity?
Chunking
Particularly effective for remembering long lists, sequences, or complex information by breaking it down into smaller, more easily remembered units.
What is the name for 'classic amnesia,' and what type of amnesia does it refer to?
Retrograde amnesia is a type of amnesia characterized by the loss of memories for events or information that occurred before the onset of amnesia.
Individuals with retrograde amnesia may have difficulty recalling past experiences, knowledge, or personal information.
Andrea Yates was accused of killing her five children. Her defense attorney contended that she suffered from which psychological disorder?
Postpartum depression
Despite having a strong desire to attend social gatherings and events, Sarah finds herself avoiding them at all costs. She experiences intense fear and anxiety when thinking about leaving her home and being in situations where escape might be difficult or embarrassing. What psychological disorder might Sarah be experiencing?
Agoraphobia
What is a common treatment for most psychological disorders?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Jerry works night shifts regularly and struggles to adjust to his sleep-wake schedule. What is the term for the internal biological clock that regulates his sleep patterns and makes it difficult to adapt to this shift?
Circadian Rhythm
In your deep slumber, you're in a stage of sleep where your brain produces slow delta waves, and it's tough to wake you up. If someone does wake you, you'll likely feel disoriented. What stage are you in?
Stage 3 or Stage 4
Slow-Wave Sleep
What are the three components of the Information Processing System in psychology?
Encoding: Encoding involves the initial processing of sensory information into a form that can be stored in memory.
Storage: Storage refers to the retention of encoded information over time. Once information has been encoded, it is stored in memory for later retrieval.
Retrieval: Retrieval is the process of accessing and bringing stored information back into conscious awareness when needed.
What are the two types of rehearsal, and which one is better for long-term memory retention, and why?
Maintenance rehearsal involves simple repetition of information to keep it in short-term memory, while elaborative rehearsal involves deeper processing by making meaningful connections between new information and existing knowledge.
Elaborative rehearsal is better for long-term memory retention because it encourages semantic encoding, which facilitates deeper understanding and integration of information into existing memory networks.
Elaborative rehearsal enhances memory durability by creating multiple retrieval paths and associations, making the information more readily accessible for future recall.
Explain when the serial effect would be advantageous in situations such as voting or memorable performances.
What are the two types of effects associated with it?
Primacy & Recency effects, are advantageous in situations where the order of presentation influences memory retention, such as voting or memorable performances.
In voting scenarios, candidates listed first or last on the ballot often benefit from the primacy and recency effects, respectively. Similarly, in memorable performances, the order of acts can impact audience recall.
By strategically arranging the order of presentation, organizers can capitalize on these effects to enhance audience memory and engagement.
Your father was admitted to a mental hospital where a team of professionals meets with you and your family. According to the team leader, your father suffers from one of the most commonly diagnosed disorders and is also comorbid.
Your father has at least two disorders
Sarah and Jake both exhibit symptoms of ADHD, but their experiences differ.
Sarah is often described as talkative and daydreamy in class, while Jake is frequently disruptive and impulsive.
What might account for these differences, particularly considering gender?
ADHD symptoms in females are often underdiagnosed or overlooked due to differences in how they present. Females with ADHD may exhibit internalizing symptoms, such as inattention and daydreaming, which can be mistaken for other conditions like anxiety or depression.
Males with ADHD may display more externalizing symptoms, such as hyperactivity and impulsivity, which are more readily recognized.
These gender differences in symptom presentation can influence diagnosis and treatment approaches for individuals with ADHD.
Samantha feels intense anxiety whenever she has to speak in front of a group of people. Even the thought of giving a presentation makes her feel physically sick.
What psychological disorder might Samantha be experiencing?
Social Phobia
A person's body temperature gradually rises during the day, reaching its peak in the late afternoon. What aspect of the Circadian rhythm is responsible for this temperature pattern?
Sleep-Wake Cycle
Picture yourself in the middle of a fascinating, action-packed dream. You're likely experiencing this stage of sleep, marked by vivid, intense dreaming. What is the name of this stage?
REM
What is the consolidation hypothesis in the context of memory?
The consolidation hypothesis is a theory in cognitive psychology that explains how memories are initially fragile and susceptible to disruption but become more stable and resistant to interference over time. According to this hypothesis, newly formed memories undergo a process of consolidation, during which they are strengthened and integrated into existing neural networks within the brain.
This is the duration that information can last in short-term memory if it is not rehearsed.
What is 20-30 seconds?
Why is the cognitive interview better for recall than a traditional police interview?
The cognitive interview employs techniques such as open-ended questioning, mental reinstatement of context, and encouraging witnesses to report everything they remember, even if seemingly trivial.
These techniques help to maximize the retrieval of accurate information from memory by facilitating a more comprehensive and detailed recall of events.
Which anxiety disorder is characterized by intense physiological reactions in the absence of any specific stimulus?
Panic disorder
What are three inattentive symptoms of ADHD?
1. Struggles with task attention
2. Difficulty Organizing
3. Avoid tasks involving mental effort
4. Easily distracted
Provide an example of Dissociative Fugue and explain its occurrence
John suddenly leaving his home and traveling to another city without any memory of his past identity or purpose for doing so.
Dissociative Fugue occurs when an individual experiences a sudden and unexpected departure from their usual environment, accompanied by amnesia for their past identity and life circumstances.
This can happen due to severe stress, trauma, or psychological conflict, which overwhelms the individual's ability to cope, leading to a dissociative state.
During the fugue state, the individual may assume a new identity and engage in unfamiliar behaviors, often without awareness of their previous life.
You've just completed a long-haul flight that took you from New York to London, and you're feeling quite disoriented. Despite the local time showing morning, your body is convinced it's still the middle of the night. What term describes this phenomenon when your body's internal clock lags behind the local time after eastward travel?
Phase Delay
Imagine you've been sleep-deprived for several nights, and when you finally get a full night's rest, you experience more dreams than normal. What phenomenon are you likely encountering?
REM Rebound
What is the difference between retroactive and proactive interference in memory?
Retroactive Interference:When newly learned information disrupts the recall of previously learned information. For example, if you learn a new password for a website and then later have trouble remembering the old password, retroactive interference may be at play.
Proactive Interference: When previously learned information interferes with the encoding and retrieval of new information. For instance, if you've previously learned how to ride a bike using a particular technique and then try to learn a new, different technique, the old technique may interfere with your ability to master the new one.
The curve of forgetting shows that this type of review can help reduce the amount of forgotten information.
Spaced Effect
Provide an example of an episodic and a semantic memory.
Can either of these be a flashbulb memory?
Why or why not?
Episodic memory could be recalling your high school graduation ceremony, including details such as who attended, what you wore, and how you felt during the event.
Semantic memory could be knowing that Paris is the capital of France, without any personal context or recollection attached to the information.
Episodic memories are typically personal experiences tied to specific events and contexts, whereas semantic memories are factual knowledge independent of personal experience.
Flashbulb memories are typically vivid, detailed recollections of significant and emotionally charged events, such as the assassination of a prominent figure or a major historical event.
While both episodic and semantic memories can contribute to flashbulb memories, the episodic component is more dominant. Flashbulb memories often involve a strong emotional response and are characterized by their perceived clarity and accuracy.
Brad and Sheila have been dating for several months. Sheila, a graduate student in psychology, is studying to be a clinical psychologist. Over the months, she’s become concerned that Brad may suffer from______ . Because Brad seeks additional information before making even minor decisions.
GAD
Why is Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) sometimes thought to be fake or not believable?
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) is sometimes thought to be fake or not believable due to misconceptions and stigmatization surrounding the disorder. Media portrayals and sensationalized accounts have contributed to skepticism about the validity of DID.
DID is often underreported or underdiagnosed due to factors such as lack of awareness among clinicians, stigma associated with mental illness, and challenges in accurately diagnosing the disorder.
Who are the group of people who experience little to no Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)?
Why is this the case?
The Amish community is often cited as a group of people who experience relatively low rates of MDD.
The Amish prioritize strong family bonds, communal support, and a simple way of life that emphasizes traditional values and close-knit relationships.
Additionally, their lifestyle typically involves regular physical activity, meaningful work, and a lack of exposure to modern stressors such as technology and urbanization.
These factors, along with a collective approach to problem-solving and coping, contribute to the lower prevalence of MDD within the Amish community.
What two factors tend to increase the severity of the symptoms of jet lag?
Crossing many time zones & west to east travel
Imagine you're in the middle of a cozy nap. As you begin to relax, your brain enters a stage of sleep with sleep spindles and K complexes.
What stage is this? Explain how sleep spindles and K complexes work together and their purpose.
Stage 2
Sleep spindles & response to unexpected or significant sensory events, potentially protecting your sleep by enhancing arousal if needed.
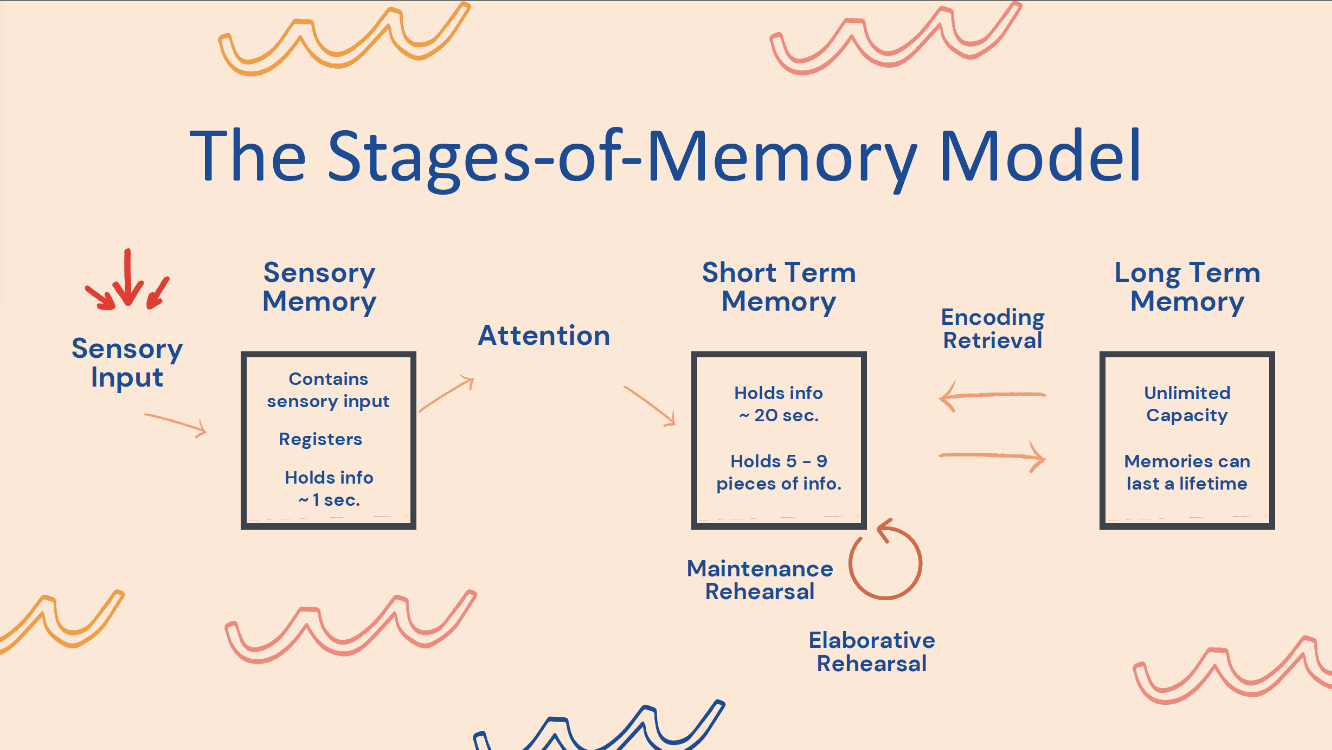
Draw the typical memory model, including its components and stages
Provide an example of something that starts off as explicit memory and then moves on to implicit memory.
Explain what this transition means.
Learning to ride a bicycle.
Initially, when someone is learning to ride a bike, they rely on explicit memory to remember the instructions, techniques, and rules involved, such as how to balance, pedal, and steer.
With practice and repetition, these skills become automatized, and the process of riding a bike becomes more automatic and effortless.
At this stage, the memory of how to ride a bike transitions from explicit to implicit memory. Implicit memory is non-conscious and involves the recall of information without conscious effort or awareness.
Explain how semantic and episodic memories differ in their entry into Long-Term Memory
They differ in their entry into LTM in terms of their encoding processes and the types of information they store.
Episodic memories involve the encoding of personal experiences
Semantic memories involve the encoding of general knowledge, facts, and concepts that are independent of personal experience or context.
Episodic memories, involving personal experiences and events, often have a strong emotional or contextual component that inherently facilitates their encoding and storage without explicit rehearsal. The vividness and richness of episodic memories, along with their autobiographical significance, contribute to their durability in LTM without the need for extensive rehearsal.
Semantic memories, typically require some form of rehearsal or elaboration to ensure their retention in LTM. Because semantic memories lack the personal context, they may be more susceptible to forgetting without deliberate rehearsal or association with existing knowledge.
Therefore, while both types of memories contribute to LTM, episodic memories often enter LTM more readily and robustly, whereas semantic memories may require additional cognitive effort to establish and maintain
Amy has been collecting baseball cards for years. At the drop of a hat, she will launch into a lengthy discussion of her collection, the price of cards, and her plans for purchasing more cards. Her friends say that she must be suffering from obsessive-compulsive disorder. You disagree. What do you say to her friends when they ask you why you disagree?
Unlike an obsessive-compulsive, Amy derives pleasure from this activity.
In Prolonged Exposure Therapy, individuals are gradually exposed to traumatic memories and situations to reduce their symptoms.
This therapy is typically beneficial for which group of people?
Who are individuals with PTSD who have experienced specific traumatic events, such as combat veterans, survivors of sexual assault, or individuals who have been involved in accidents or natural disasters?
List and describe three positive and three negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Positive Symptoms:
- Hallucinations: Sensory experiences that occur in the absence of external stimuli.
- Delusions: False beliefs that are firmly held despite evidence to the contrary.
- Thought Disorder: Fragmented or illogical thoughts, making it difficult for individuals to communicate coherently.
- Disorganized behavior: Unusual behaviors that disrupt normal activities.
- Disorganized Speech: Speech that is incoherent or incomprehensible.
Negative Symptoms:
- Avolition: Lack of motivation or goal-directed behavior, leading to difficulty initiating and sustaining activities.
- Alogia: Poverty of speech, characterized by reduced speech output or content.
- Flat affect: Reduction in the display of emotional expression, leading to a lack of facial expressions, vocal intonation, and gestures.
- Anhedonia: Inability to experience pleasure or enjoyment from activities that were previously rewarding.
- Social withdrawal: Avoidance of social interactions and a preference for solitude, often due to discomfort or apathy toward social situations.
- Cognitive deficits: Impairments in cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and executive functioning, which can impact daily functioning and social relationships.
Imagine you're about to fall asleep, and suddenly, you feel a sensation of being held down with an inability to move or scream. What sleep phenomenon is this and when is it most commonly to take place?
Sleep Paralysis
Entering or Exiting REM
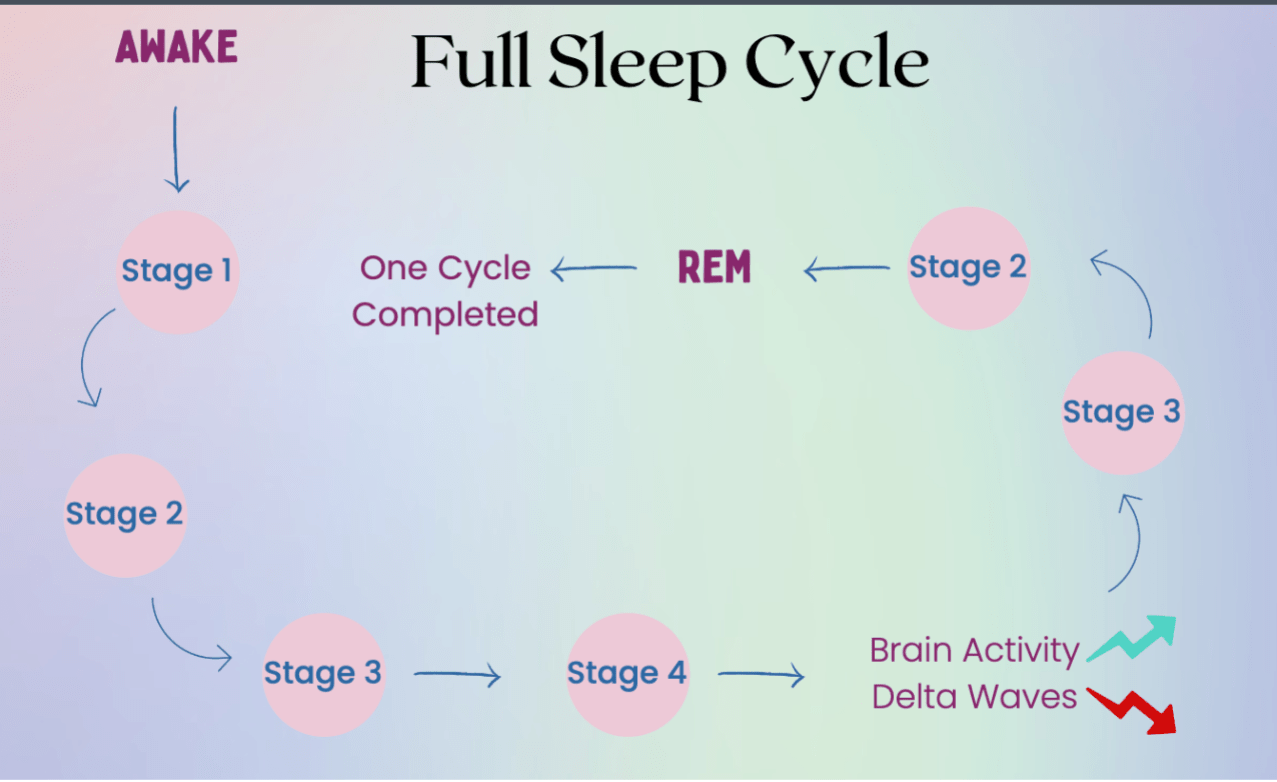
Draw the entire sleep cycle.