The study of weather
What is meteorology?
The study of the Earth's oceans and ocean floor
What is oceanography?
Anything that has mass and takes up space
What is matter?
A push or pull exerted on an object in an effort to change that object's velocity
What is force?
The smallest unit of life in creation
What is a cell?
The study of living organisms
What is biology?
The systematic study of the natural world through observation and experimentation in order to formulate general laws
What is science?
List the 6 Kingdoms
Moisture falling from the atmosphere as rain, snow, or hail
What is precipitation?
The ocean floor is filled with ______ and _______.
Basic states of matter
What are solid, liquid, and gas?
The rate at which an object moves
What is speed?
A method of sorting things according to shared qualities or characteristics
What is classification?
Consisting of more than one cell
What is multicellular?
Early scientist and first to complete a description of planets and stars
Who was Ptolemy?
List the 6 Criterion for Life
1. Contain hereditary info in their DNA 2. Use energy 3. Respond to stimuli/changes in environment 4. Made up of cells 5. Maintain homeostasis 6. Grow
A force exerted onto a surface by the weight of air molecules
What is air pressure?
Large river-like streams of ocean water created by winds, varying water densities, and the rotation of the Earth
What are currents?
The smallest chemical unit of matter
What is an atom?
The scientist who developed the laws of motion
Who is Newton?
An organism that breaks down the dead remains of other organisms
What is a decomposer?
Complex molecules that are involved in nearly every reaction that supports life. Made up of amino acids.
What are proteins?
This scientist developed a picture of what an atom looks like
Who is Neils Bohr?
List the classification divisions in order
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
The boundary where a warm mass of air meets a cold mass of air
What is a front?
A rhythmic back-and-forth motion of water that transfers energy without any overall change in direction of the water mass
What are waves?
A substance that contains different compounds and/or elements
What is a mixture?
The law of inertia - an object in motion (or at rest) will tend to stay in motion (or at rest) until it is acted upon by an outside force
What is Newton's first law?
The process by which green plants and some other organisms use the energy of sunlight and simple chemicals to produce their own food
What is photosynthesis?
One of the main sources of food energy for most animals and are made up of simple sugars
What are carbohydrates?
An explanation of the natural world that has been thoroughly tested and is supported by a significant amount of evidence
What is a scientific theory?
Write out the general formula for cellular respiration
Glucose sugar + oxygen --> energy + carbon dioxide + water
Conditions of the atmosphere in a region over relatively long periods of time
What is climate?
Massive waves created by an underwater earthquake or volcanic explosion
What are tsunamis?
The temperature at which a liquid becomes gas
What is the boiling point?
The speed of an object in a given direction
What is velocity?
How many domains are there in our classification system?
Three (bonus points for naming them)
These are an efficient way to store food energy and are made up of fatty acids
What are lipids?
The variable of part of an experiment to which all other variables will be compared
What is the control?
These two ocean invertebrates are part of the phylum ___________.
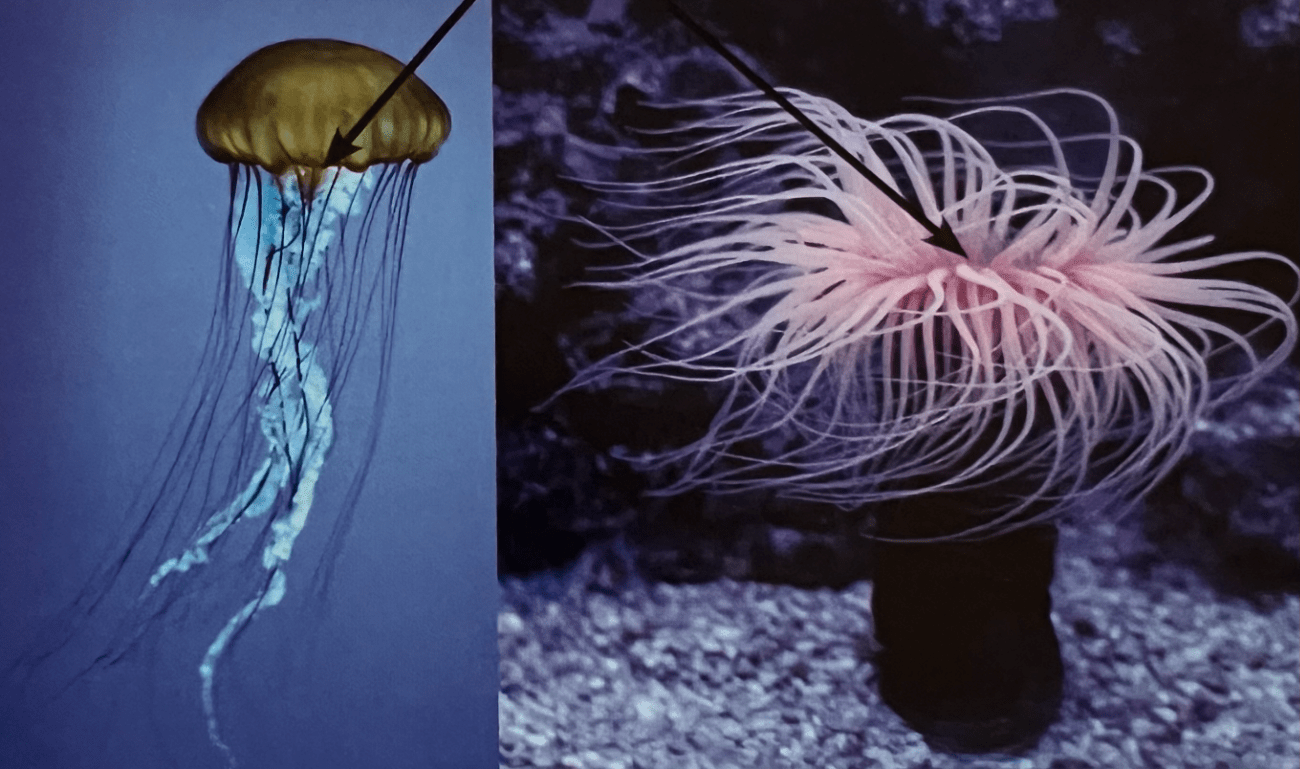

Cnidaria
The three major cloud types
What are cumulus, stratus, and cirrus?
Ocean water movement resulting from the gravitational pull of the Moon and the sun
What are tides?
A change that affects the type of molecules or atoms in a substance
What is a chemical change?
Newton's 3rd law
This cell has no distinct membrane-bound organelles
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Organisms that obtain their nourishment from dead organisms
What are saprophytes?
This test determines the time span between copies and number of copies of a document
What is the bibliographic test?
Name the 4 large ocean basins
Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic
The two main gases in our atmosphere
What are nitrogen and oxygen?
A major physical feature that all mollusks have; a layer of tissue that covers the soft body
What is a mantle?
Identify if physical or chemical change: shredding paper into small pieces
Physical
A device that either multiplies or redirects force
What is a simple machine?
This cell has a membrane-bound nucleus
What is a eukaryotic cell?
These are the most complex molecules of life, involved in the creation, repair, and reproduction of proteins.
When the Earth is between the Moon and the sun so that it casts a complete shadow on the Moon
What is a lunar eclipse?
Label the marked organelles of this eukaryotic cell
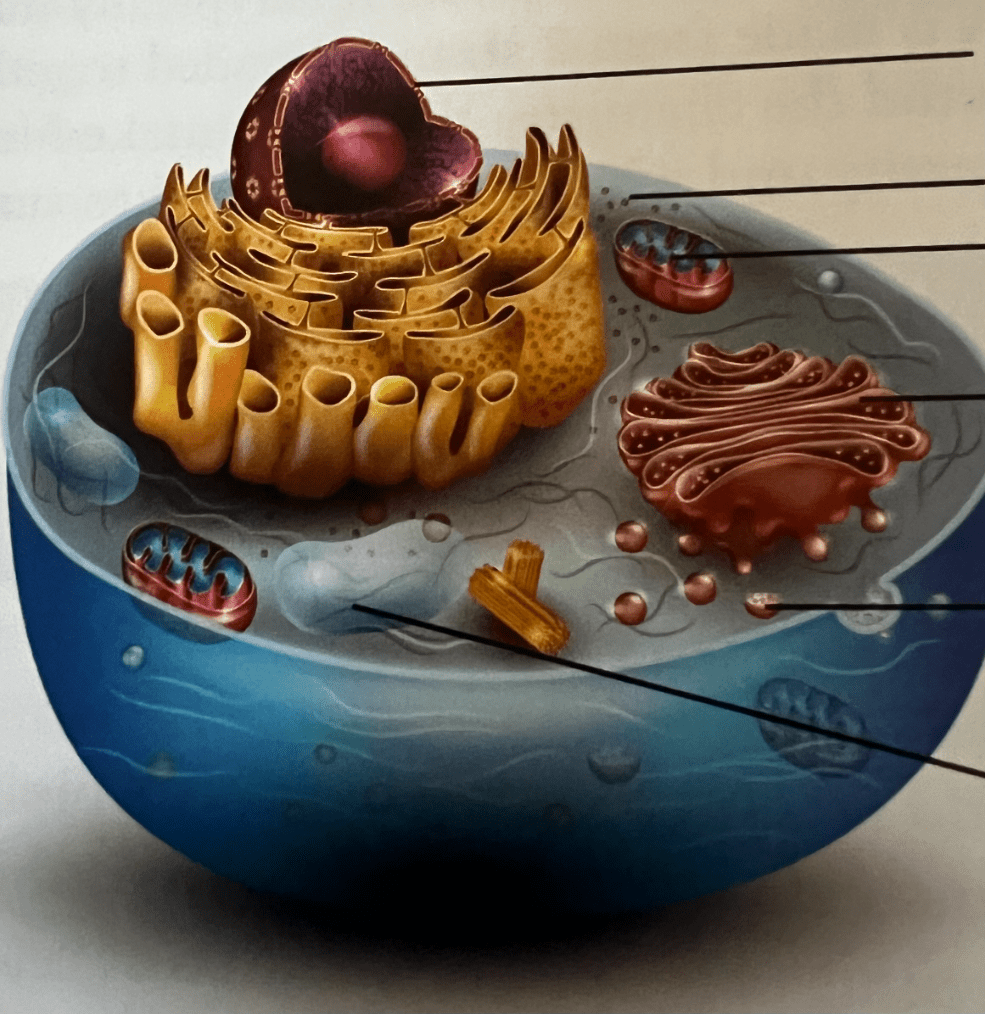
Nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondrian, Golgi body, lysosome, vacuole
Which of the following is NOT one of the air properties meteorologists use to help predict weather?
temperature, pressure, humidity, wind direction, radiation
Radiation
This organism is designed with a base of 5 radiating parts
What is an echinoderm?
When atoms share electrons
What is a covalent bond?
F = m x a
What is Newton's 2nd Law?
A Latin-based naming system
What is binomial nomenclature?
Carries water and dissolved material throughout plants
What is vascular tissue?
Name the major layers of Earth
crust, inner core, outer core, mantle
Name the function of the previous organelles of the Eukaryotic cell
Ribosomes - make proteins; Mitochondria - make energy; Vacuoles - storage; Golgi bodies - store and alter proteins and lipids; Lysosomes - hold enzymes; Nucleus - control center, DNA
The term ENSO stands for:
El Nino-Southern Oscillation
An example of a cartilaginous fish
What is a shark?
A bond formed when ions are attracted to each other
What is an ionic bond?
List 2 forces from your text
Gravitational force, strong force, electromagnetic force
Give an example of how the body regulates itself
Sweating, adjusting breathing rate, or adjusting heart rate
The trees that lose their leaves in the fall
What are deciduous trees?
The study of Earth's physical structure, its history, the processes acting on it, and the rocks of which it is compared
What is geology?
What is this cycle called? Label the phases.
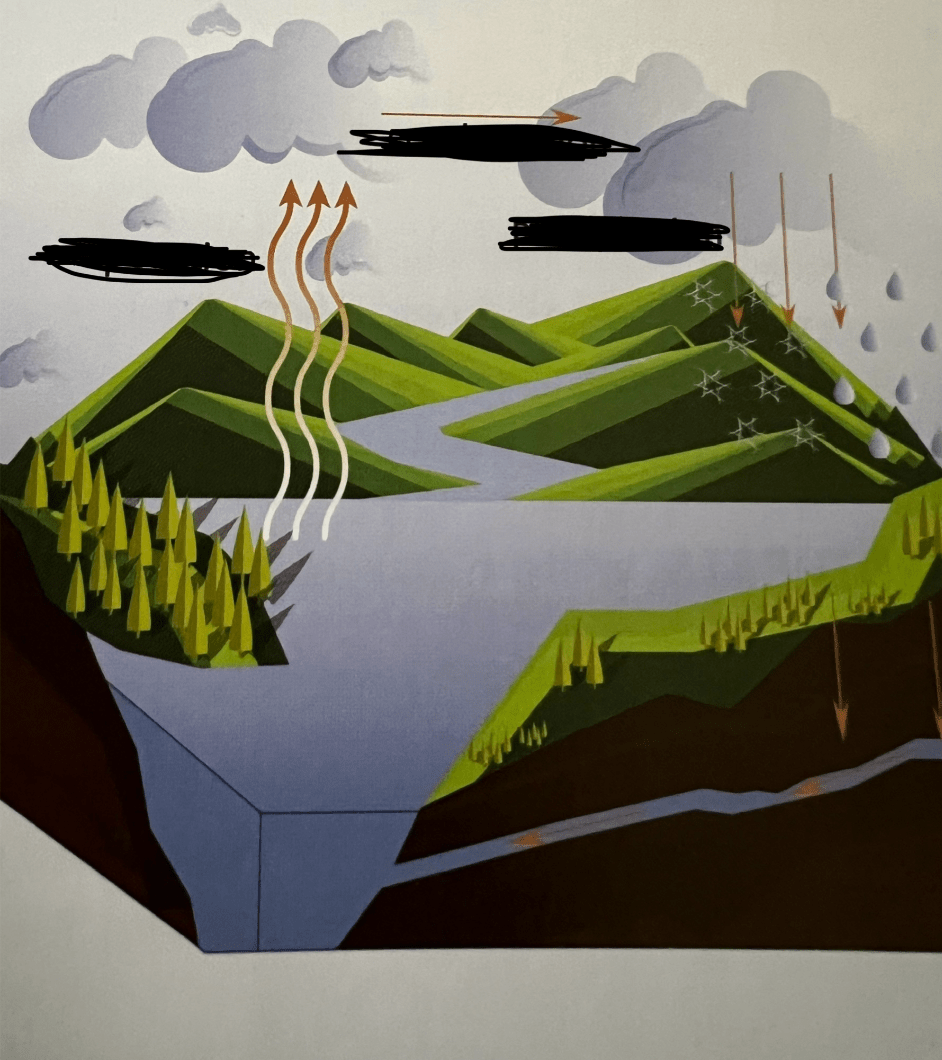

The hydrologic cycle
evaporation, condensation, precipitation
List the 5 layers of the atmosphere, in order from closest to earth up to outer space
What are: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, exosphere
The gas-filled sac in bony fishes that allows them to remain at a certain depth without moving
What is an air bladder?
Atoms with an overall charge
Which beam of reflected light is correct?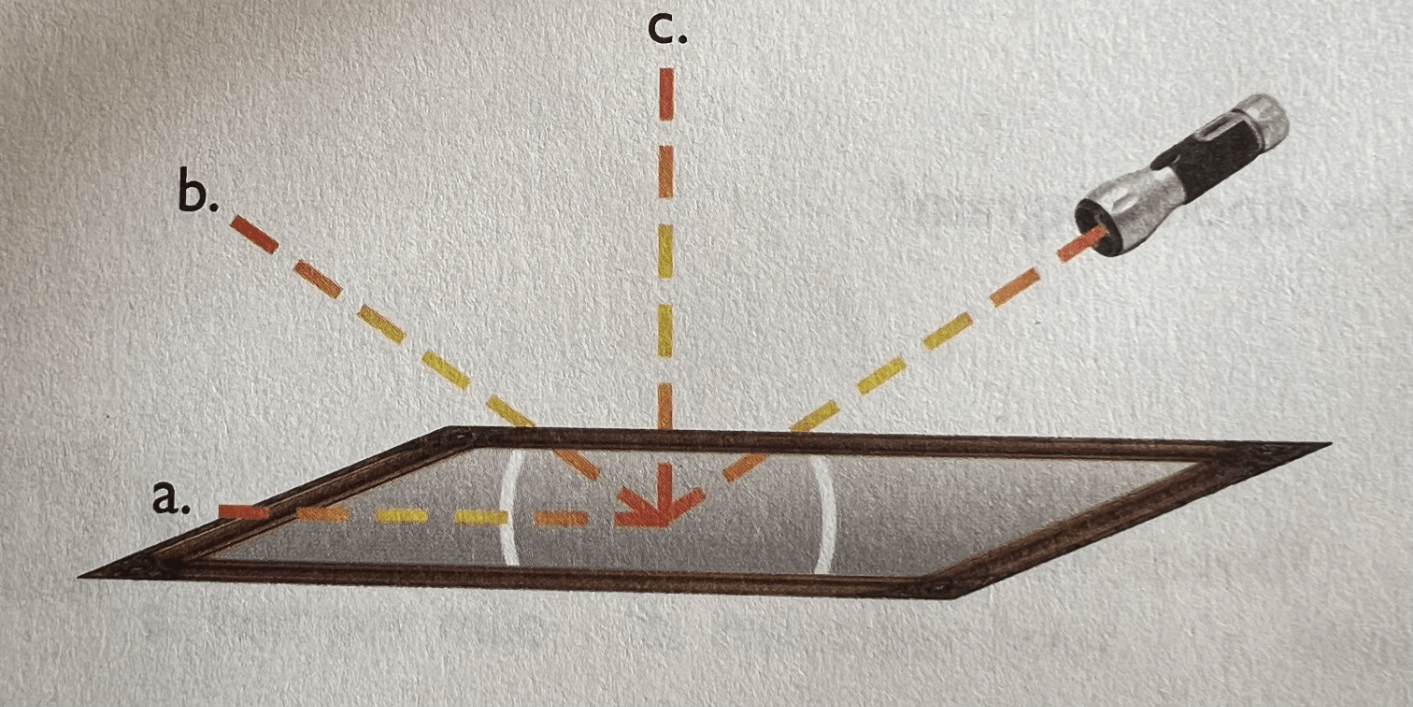
B
List the 6 criterion for life
1. Contain hereditary info in their DNA
2. Use energy
3. Respond to stimuli/changes in environment
4. Made up of cells
5. Maintain homeostasis
6. Grow
The major location where photosynthesis occurs in plants
What are the leaves?
The boundary line between two plates
What is a fault?
How do clouds form?
As a result of warm air cooling off. Bonus - name the 4 ways: fog (moist air cools down by the ground at night); convection (warm air rises, cools, and the water vapor condenses); frontal (wind blows warm, moist air on top of cooler, drier air; mountain (moves along ground up the side of a mountain)