The helpful gene extracted from a donor organism in genetic engineering. Such as the gene for insulin.
What is the gene of interest? Or the desired gene?
The study of how ethically different some biological processes are is called this.
What is bioethics?
The number of strands human DNA has.
What are two?
An absent or faulty gene is replaced by a working gene.
What is Gene Therapy?
 46
46
C
The matching ends of DNA sequences created by restriction enzymes
What are sticky ends?
DNA that has other genes inserted into it.
What is recombinant DNA?
A, C, T, and G are examples of these.
What are nitrogenous bases?
The clear suspect who committed the crime... 
Who is John?
 54
54
A
A circular, single-stranded piece of DNA.
What is a plasmid?
These are used for cutting pieces of DNA and plasmids open, creating sticky ends.
What are restriction enzymes?
If you accidentally used two different ones of these, genetic engineering would not work because the sticky ends won't match.
What are restrictions enzymes?
1.) take a somatic cell from the desired animal 2.) take an unfertilized egg from the egg donor 3.) enucleate (remove the nucleus) from the egg 4.) put the somatic nucleus from the animal to be cloned to the empty egg cell 5.) allow the egg cell to undergo mitosis 6.) insert the embryo into the surrogate 7.) surrogate produces the baby
What are the steps in cloning?
 57
57
B
E-coli + AmpR vs. E-coli - AmpR
What is bacteria transformation?
Something that delivers genetic information to the cell.
What is a cloning vector?
Plasmids occur naturally in certain types of this.
What are bacteria?
More unique and valuable than fingerprint, this is key evidence to differentiate key suspects in a crime scene.
What is a DNA fingerprint?
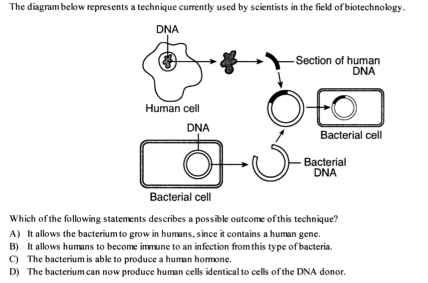 106
106
C
The receiving organism after it's its DNA has been changed/manipulated.
What is a transgenic organism? Or what is a genetically modified organism (GMO) ?
The "glue" that puts sticky ends back together
What is DNA ligase?
Nuclear Transplantation is the key technique to this genetic engineering process
What is cloning an organism?
1. cut the DNA with a restriction enzyme, 2. plug the DNA into the wells, 3. apply a positive charge at one end and a negative charge at the other end, 4. the DNA bands fragment and travel toward the negative charge, separating according to size
What are the steps in performing a gel electrophoresis?
 39
39
A