This nucleic acid is in the form of a double helix and provides genetic information
What is DNA
The amount of times DNA needs to be copied prior to transcription and translation
What is one time?
The process of creating mRNA using a DNA template
What is transcription?
Disorder shown by the following karyotype
What is Kleinfelder's syndrome.
A change in the genetic code
What is a mutation?
This nitrogenous base, found in RNA, pairs with Adenine
What is Uracil
The nitrogenous base that pairs with Guanine.
What is Cytosine
The type of RNA that carries codons from the nucleus to the cytoplasm.
What is mRNA
The disorder shown by the following chart:
What is Turner's Syndrome
A type of mutation that changes the way an entire DNA sequence is read
What is a frameshift mutation?
This sugar is found in deoxyribonucleic acid
What is deoxyribose
The nitrogen base that pairs with Adenine in DNA
What is Thymine
The RNA that carries an amino acid to the ribosome for protein synthesis
What is tRNA
A laboratory technique used to establish a link between biological evidence and a suspect in a criminal investigation or parentage.
What is DNA fingerprinting
A type of mutation that changes a single amino acid
What is a point mutation
These are the building blocks of a nucleic acid
What is a nucleotide
The enzyme that finds matching nitrogen bases for the new strand of the DNA during DNA replication
What is DNA Polymerase.
This amino acid corresponds with the codon AGC
What is serine?
A type of genetic analysis that checks chromosome size, shape, and number. Can be used to determine chromosomal disorders
What is a karyotype
A mutation that causes a section of a chromosome to detach and reattach on a different chromosome.
What is translocation?
Who are Watson, Crick, and Franklin
After DNA replication a DNA molecule is made up of one strand of _______ DNA and one strand of _______ DNA.
What is old and new
The two processes in the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology (in order).
What are transcription and translation
According to the following chart, who is the most likely father.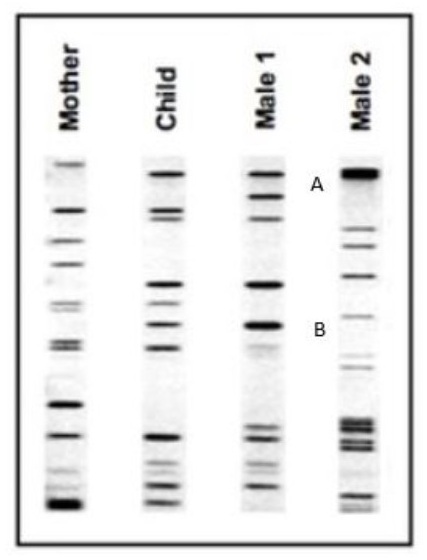
Who is male 1?
The type of mutations that cause Tay-Sachs and Sickle Cell Anemia, respectively.
What is a frameshift mutation and point mutation?
