This is also known as the study of heredity.
Genetics
The passing on of traits from parents to offspring.
heredity

Many farmers prefer cattle without horns because it is safer for their herds. The allele for no horns (N) is dominant to the allele for the presence of horns (n).
A farmer mates a male with horns to a heterozygous female without horns.
What is the chance that the offspring will have horns?
1/2 or 2/4 or 50%
This grid is used to show all the possible combinations of genes in offspring
Punnett Square
Part 1: Who is considered the father of genetics?
Part 2:Use the image below to create a Punnett square for the crossing of two heterozygous parents. Give the PHENOTYPIC and GENOTYPIC ratios
Gregor Mendel

Someone who is heterozygous would have the genes BB.
False
Bb
In most cases, this vocabulary term has a dominant and recessive form.
Allele

The physical feature resulting from a combination of alleles.
Phenotype
In lizards, brown coloring (B) is dominant, and blue coloring (b) is recessive.
A homozygous brown mussel crosses with a blue mussel.
What percentage of offspring are expected to be blue?
0% or 0/4
Using the dichotomous key classify an organism that has the following:
small or no wings, shorter rear legs, not a horned head and small eyes.


Humans use selective breeding to increase improve plants and animals for farming.
True.

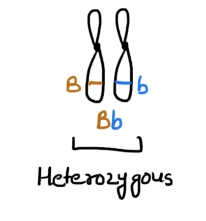
When two alleles that make up a genotype are different.
Heterozygous.
When two alleles that make up a genotype are identical.
Homozygous
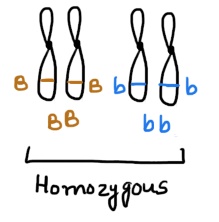
In horses, the allele for straight hair (H) is dominant, and the allele for curly hair (h) is recessive.
A horse breeder mates a homozygous dominant mother with a heterozygous male.
What is the chance that the offspring will have straight hair?
4/4 or 100%
Unlike the lizard, the salamander lacks this feature or trait. Use the cladogram to answer


A recessive trait prevents another trait from being expressed.
False.

The gene combination for a trait.
Genotype.
When alleles are neither dominant or recessive so a mix of both traits is seen in the offspring. This is referred to as __________.
Codominance

In humans, right handedness, R, is dominant to left handedness, r. Two heterozygous parents are having their first child. What chance does that child have of being right handed?
3/4 or 75%
Make a proper key, tree, or cladogram for the creatures below.


Orange hair is an example of a recessive genotype.
False.
Recessive PHENOTYPE
Someone that does not show a disease, but can pass it to their offspring.
A Carrier.

A segment of DNA responsible for expressing a trait
A gene.
In humans, a widow's peak, T, is dominant over a straight hairline, t. A woman homozygous dominant marries a man with a straight hairline. What chance do their kids have of getting a widow's peak?
4/4 or 100%
Which of these trees depicts a different evolutionary history than the others?


According to the tree below, Species A and C are more closely related.

False. B and C are more closely related.
