What is meiosis?
A type of cell division where it includes sexual reproduction, creates four daughter cells, daughter cells have 23 chromosomes, produces reproductive cells, and replicates DNA.
Solve the punnet square below:
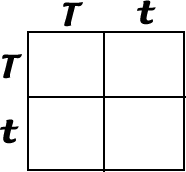
Offspring will have:
Dominant trait (T)= 75%
Recessive traits (t)= 25%
What is the definition of ADAPTATION?
An adaptation is a change or the process of change by which an organism or other species becomes better suited for its environment. (Behavioral or structural).
What is cloning?
Cloning is when individuals with identical or virtually identical DNA reproduce; Can create a copy of itself to create more of it. To make more of a specific thing.
What is the law of Superposition?
The law of Superposition is that the layers of rock on top are the youngest while the ones on the bottom are the oldest. (Unless there are other disturbances).
What does the nucleus do in a cell?
The nucleus directs all the cells activities, stores DNA, and is the control center of the cell.
What is heterozygous?
Heterozygous is when traits or genes of an organism have two different alleles.
What is NATURAL SELECTION?
Natural Selection is when organisms have better genes or traits adapted to their environment. These will be passed down over time and become the new normal and majority.
What is a GMO?
A GMO is a genetically modified organism, usually made to make a more desirable product, mostly in food. Examples: Canola, apples, sweet corn, cotton, papaya, summer squash, sugar beets, soy beans, potatoes, and alfalfa.
What is relative age of rocks?
Relative age of rocks is the rocks age compared to other rocks around it.
What is the definition of the MITOCHONDRIA in a cell?
The mitochondria is turns nutrients into energy and is the powerhouse of the cell.
What is homozygous?
Homozygous is when an organism have the same alleles in their genes; (can be recessive or dominant).
What is Genetic Drift?
Genetic Drift is when events or random occurrences affect the fluctuations of alleles inside of a small population, therefore it effects the population drastically.
What is selective breeding?
Selective breeding is changing a population all the time by selecting the wanted traits and combining them into other things. (Example: Dog breeding).
What is the absolute age of rocks?
The absolute age of rocks is when scientists use the decay of radioactive materials to find the absolute age. Half-life is also used by the predictable amount of time that it takes for an element to decay.
What is Mitosis?
Mitosis is the creation of two daughter cells via one parent cell.
What is a phenotype?
A physical trait that an organism has. (Blue eyes, colored hair, etc.)
What is a mutation?
A mutation is an alteration made in one organism that could become the new normal if it is better for survival via reproduction. (Positive or negative mutations).
What is gene therapy?
Gene therapy is an experimental way of using genes to treat or prevent diseases.
What are the types of fossilization?
Petrification, replacement, perminalization, molds and casts, carbonization, fossil resin (amber), tar and ice, and trace fossils.
What is the difference between plant cells and animal cells?
Plant cells have chloroplast and a cell wall while animal cells do not.
What is a genotype?
A genotype is the genes of an organism that are determined by the alleles; (TT, Tt, tt).
What is migration?
Migration is when a percentage of a spices or environment moves in or moves away for their survival when their original ecosystem can't supply their basic needs.
What are some advantages and disadvantages of artificial selection?
Advantages:
-insect resistance
-weed resistance
-less chemicals (pesticides and insecticides)
-soil preserved
-drought resistant
-faster growth
-more purchases
-increasing nutrition
Disadvantages:
-Unsure of long term effects (allergies could develop)
-could decrease crop diversity
-could have effects on soil, long term
-could be prone to more mutations
What are the three fossil record time periods in order from oldest to youngest?
They are: Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic.