Physical characteristics/ traits of an organism.
phenotype
This gene always shows is self over a recessive gene
Dominant Gene
All human cells contain _________ chromosomes
46
Organized display of all the chromosomes an organism has arranged from biggest to smallest
karyotype
a capital letter represents ______ type of trait
Dominant
The passing of traits from parent to offspring is called.
Heredity
genotype that has two of the same alleles
homozygous
type of non-mendelian genetics where both alleles show.
ex. red and white flowers
co-dominance
Term used for DNA replication that describes the process of separating and using the old strands as templates for the new nucleotides to pair with, so that both copies are identical. Half old and half new
Semi-Conservative
type of non-mendelian genetics that have an in-between phenotype.
ex. Red + white flowers = pink offspring
Incomplete dominance
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Genotype characterized by two different alleles for the same trait.
heterozygous
The process by which DNA is duplicated
Replication
Where are chromosomes located?
nucleus
What percent of the offspring of heterozygous parent will be homozygous?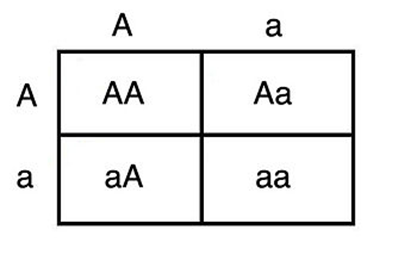
50%
Chromosomes are made up of _______.
DNA
Tool that shows possible gene combinations
Punnett square
Phase of cell cycle that does replication
s-phase
genes of a trait that is hidden when the dominant gene is present
recessive
What percent of the offspring of heterozygous parents will be heterozygous?
50%
Sequence of nucleotides in DNA.
Gene
Enzyme that "unzips" the DNA for DNA replication
helicase
One of two or more forms of a particular gene
allele
What percentage of two homozygous dominant parents will be heterozygous?
0%
The phenotypic ratio for a dihybrid cross of two heterozygous parents for both traits.
9:3:3:1
The flow of information in genetics
DNA -> RNA -> Protein
Carries instructions for making a protein to a ribosome
term for the group of three nucleotides of mRNA that will code for an amino acid
codon
genes/ alleles
ex. AA or Aa or aa
genotype
The four nitrogen bases found in RNA.
adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil
The production of mRNA from the code of DNA
Transcription
Location of:
A. Transcription
B. Translation
A. Nucleus
B. Ribosome
The "r" in rRNA
ribosomal
The group of three complimentary nucleotides found on tRNA.
Anti-Codon
The RNA molecule that brings the correct amino acid to the site of translation
tRNA
