Consider the Punnett Square below.
In pea plants, Tall(T) is dominant to Short(t).
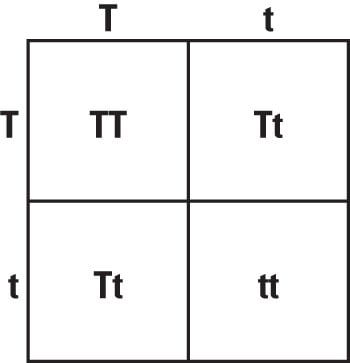
What is the phenotype of the parents?
What is the probability that the offspring will be tall?
Both parents are tall.
75% Tall
If a male has inherited an x-linked recessive trait, which parent did it come from?
Mother
What process has occurred to produce the following abnormal karyotype?

Nondisjunction
List all the possible genotypes for the following blood phenotypes.
A
B
AB
O
A-IAIA, IAi
B-IBIB, IBi
AB-IAIB
O-ii
How many generations are shown in this pedigree.
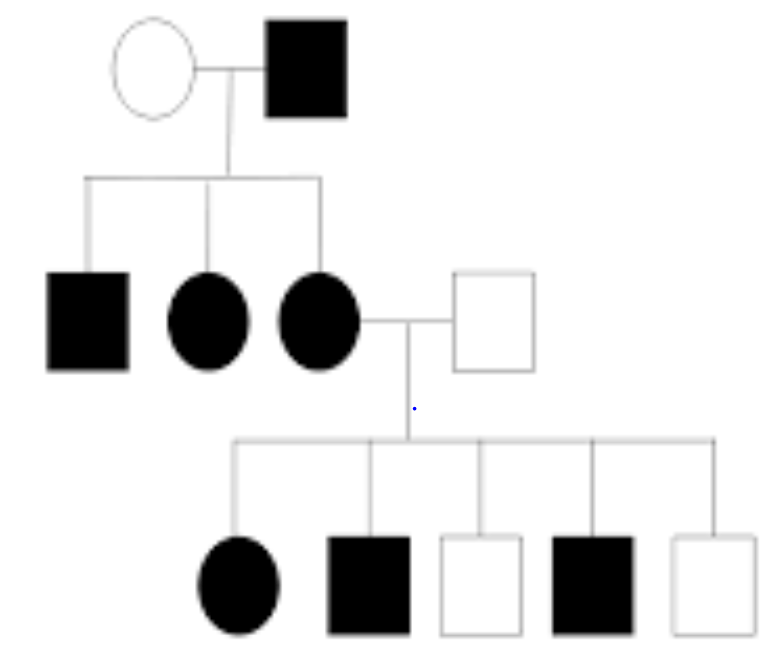
3
In pea plants, Tall(T) is dominant to short(t).
What gametes are produced from a
Homozygous Dominant Individual
Heterozygous Individual
Recessive Individual
Homozygous Dominant Individual-T and T
Heterozygous Individual-T and t
Recessive Individual- t and t

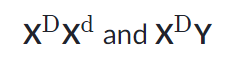
How many chromosomes are in a normal human karyotype?
46
Blood type in humans is controlled by which 3 types of inheritance?
Codominance
Simple Dominance
Multiple Alleles
In a dihybrid cross, where both parents are heterozygous for both traits, what is the probability of producing a homozygous recessive offspring for both traits.
1/16

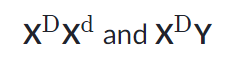
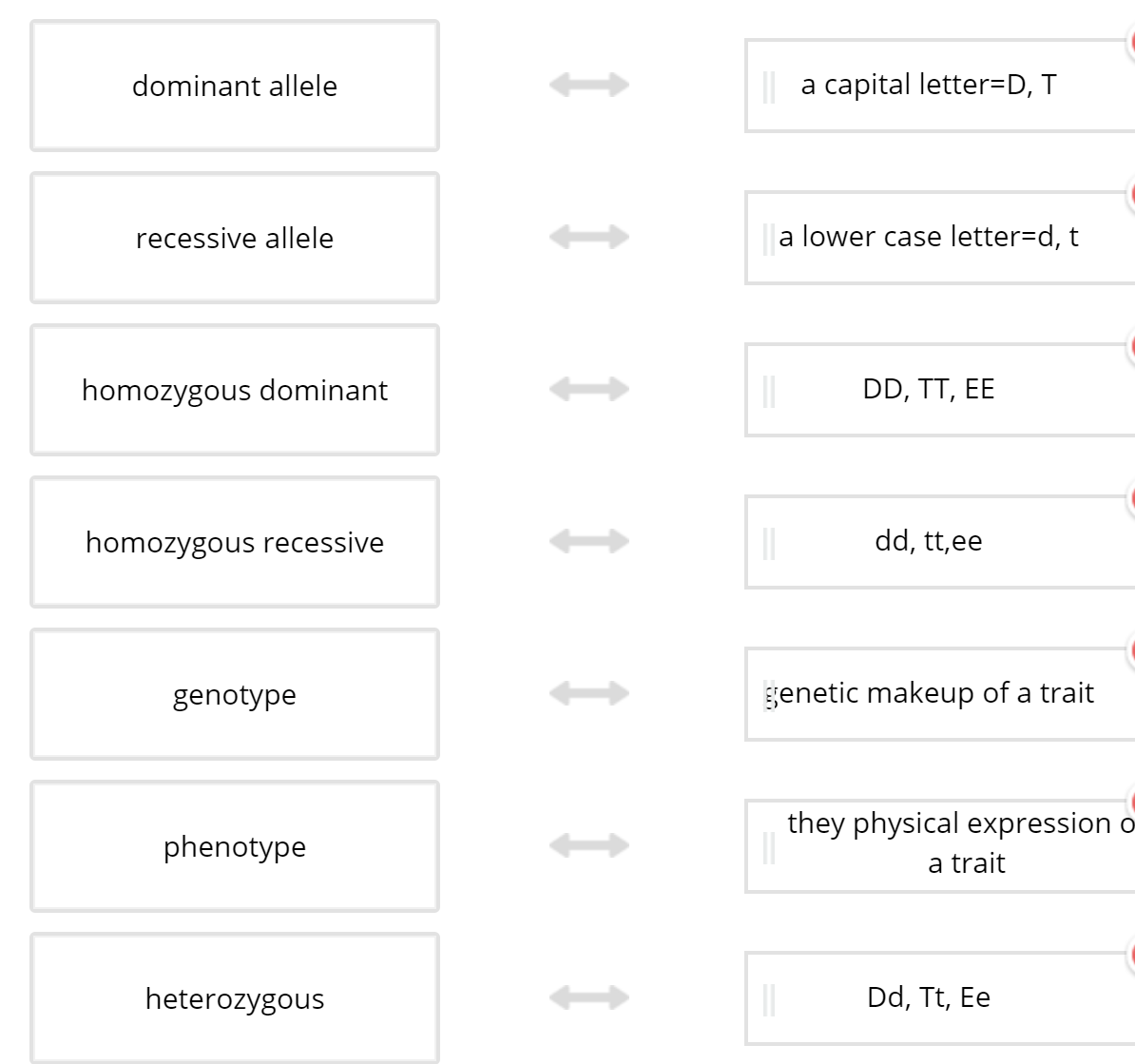
What are the possible genotypes of the offspring?
XDXD
XDXd
XDY
XdY
How are 2 recessive alleles inherited?
Each parent had at least 1 copy of a recessive allele and it was passed on to the offspring.
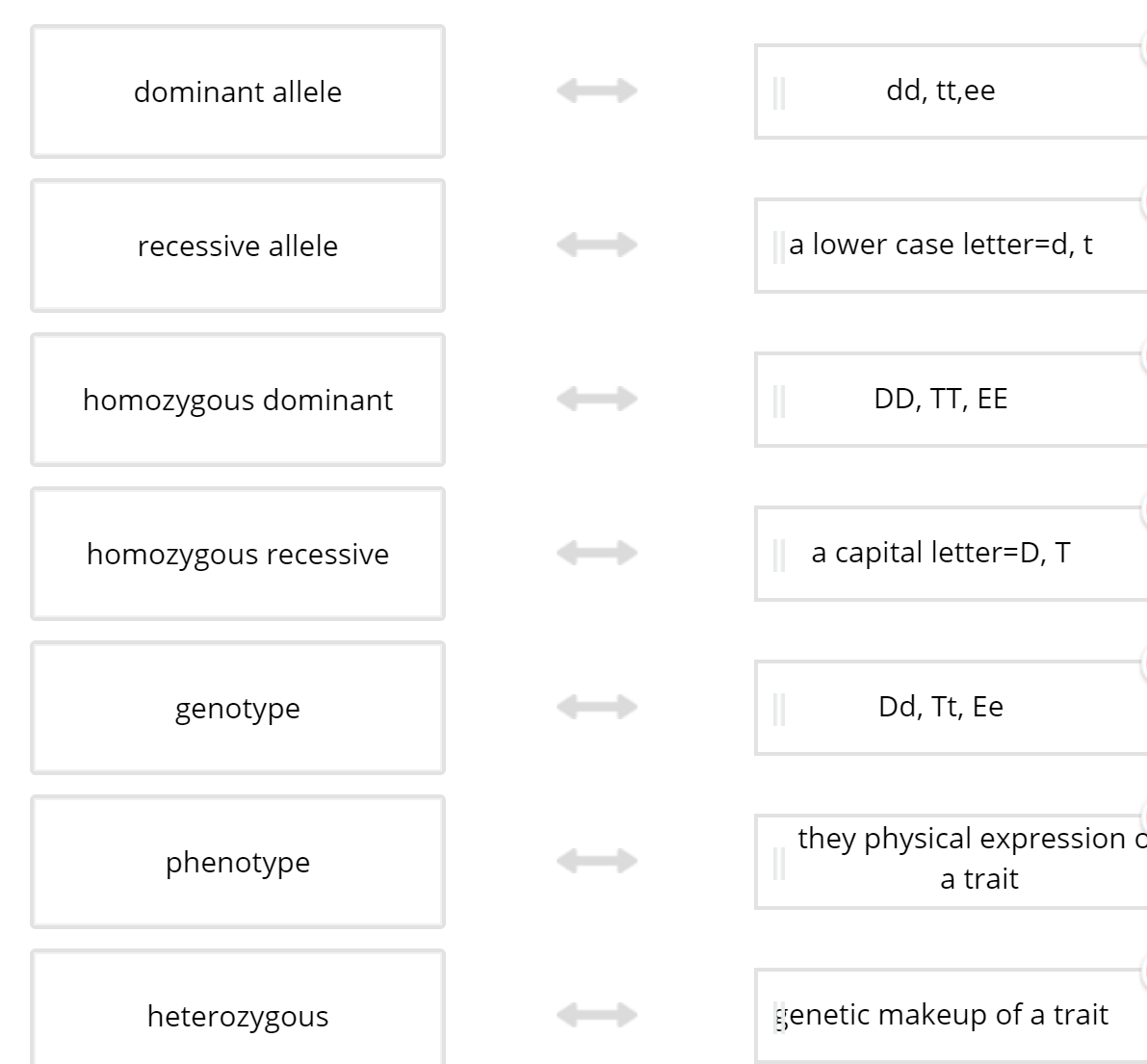
Assuming the chart above is tracing the dominant trait of "White Forelock (F)" through the family. F is a tuft of white hair on the forehead.
 1) What is the most likely genotype of individual “A”? (FF, Ff or ff?)
1) What is the most likely genotype of individual “A”? (FF, Ff or ff?)
2) What is the most likely genotype of individual “C”? (FF, Ff or ff?)
3) What is the probability of the couple A and C having a child with white forelock?
1) Ff
2) ff
3) 50%
When 2 parents who are heterozygous for 2 traits, what is the expected phenotypic ratio?
9:3:3:1
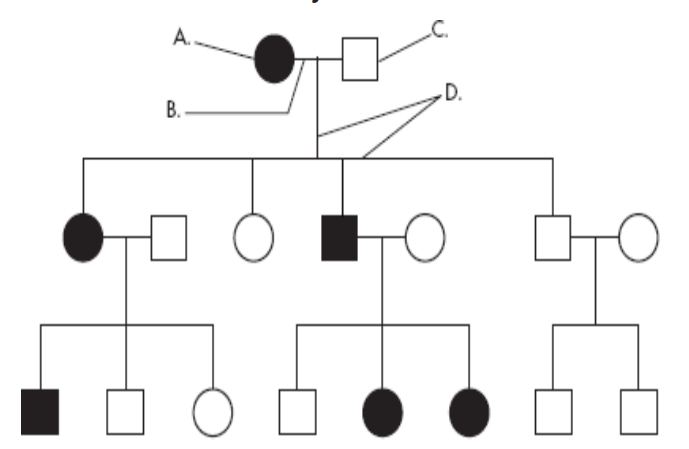
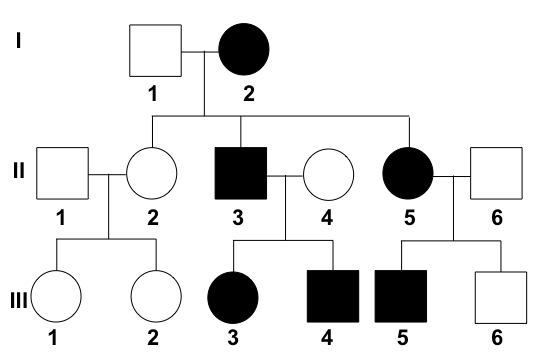 Is this trait dominant or recessive?
Is this trait dominant or recessive?
How many individuals have this trait?
What is the genotype for individual II-2 (homzygous dominant, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive)?
What is the genotype for individual III-5 (homzygous dominant, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive)?
Dominant
6
Homozygous recessive
Heterozygous


1) How many of the offspring out of 16 are right-handed, tongue rollers?
2) How many of the offspring out of 16 are left-handed, non-tongue rollers?
1) 4/16 or 1/4
2) 4/16 or 1/4
In snapdragons, there are 3 flower color varieties (red, white, and pink). When red flowering plants are crossed with white flowering plants, the offspring are all pink.
1) What type of inheritance does this show?
2) Show a cross of 2 pink flowering plants. What percent of the offspring are pink?
3) What percent of the offspring are white?
4) What percent of the offspring are red?
1) Incomplete Dominance
2) 50%
3) 25%
4) 25%
In fruit flies, the gene for eye color is on the X chromosome.
The allele for red eyes is dominant to the allele for white eyes. A researcher crosses a heterozygous red-eyed female fly with a white-eyed male fly?
1) What percent of females have red eyes?
2) What percent of males have red eyes?
1) 50%
2) 50%
There are 2 size variations in pea plants, tall and short. When 2 pure-breeding tall plants are crossed all offspring are tall. When 2 short plants are crossed, all offspring are short.When a true breeding tall plant is crossed with a short plant, all offspring are tall.
What type of inheritance is exhibited for this trait (incomplete dominance, complete dominance, or codomiance)?
Complete dominance