landform regions
- Western Cordillera Region.
- Interior Plains.
- Canadian Shield.
- Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Lowlands.
- Appalachian Region.
- Arctic Lowlands.
- Innuitian Mountains.
Push/pull factors (give examples)
push factor: something that makes people want to leave a place (ex. war, unemployment)
pull factor: something that attracts people to a place or an activity (ex. education, healthcare)
waste diversion
process of diverting waste from landfills (reduce, reuse, recycle
sustainability
the quality of not being harmful to the environment or depleting natural resources, and thereby supporting long-term ecological balance
plate techtonics
the lithosphere of the earth is divided into a small number of plates which float on and travel independently over the mantle and much of the earth's seismic activity occurs at the boundaries of these plates
define refugee
refugee is someone who has been forced to flee his or her country because of persecution, war, or violence.
renewable vs. non-renewable resources
renewable resource: any resource, that can or will be replenished naturally in the course of time (ex. trees)
non-renewable resource: a resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means on a level equal to its consumption (ex. coal)
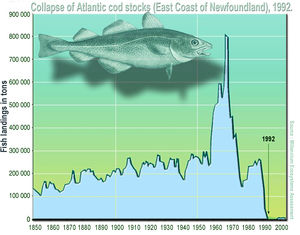
one reason for the collapse of east coast fisheries
Overfishing
LOWERN
L- latitude
O- ocean currents
W- wind and air pressure
E- elevation
R- relief
N- nearness to water
immigrant classes
economic: this category includes immigrants who have been selected for their ability to contribute to Canada's economy
family: immigrants who were sponsored by a Canadian citizen or permanent resident and were granted permanent resident status on the basis of their relationship either as the spouse, partner, parent, grand-parent, child or other relative of this sponsor.
refugee: immigrants who were granted permanent resident status on the basis of a well-founded fear of returning to their home country.
intensive vs. extensive farmimg
Intensive Farming: farming method that uses higher inputs and advanced agricultural techniques to increase the overall yield
extensive farming: an agricultural production system that uses small inputs of labor, fertilizers, and capital, relative to the land area being farmed
suburban vs. suburbia
suburban: A suburb is a residential district located on the outskirts of a city.
suburbia: the suburbs or their inhabitants viewed collectively.
maritime climate
generally features warm summers and cool winters
doubling time
the period of time required for a quantity to double in a size or value.
aquaculture
the fishing of aquatic creatures
consequences of urban sprawl
consequences of urban sprawl: increased air pollution, increased water pollution, increased water consumption, decreases human health, wasted tax money and crowded schools, increases traffic congestion and loss of open space.
how are metamorphic rock created
Metamorphic rocks can be formed by pressure deep under the Earth's surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic plates.
how do you calculate birth and death rate
birth rate= (number of births) + (total population) X 1,000
death rate= (number of deaths) + (total population) X 1,000
One reason for the collapse of east coast fisheries
over fishing
lower vs high order goods
low order goods: a good or service, usually inexpensive, that people buy on a regular, often daily daily basis. (ex. bread)
high order goods:a good or service, usually expensive, that people buy only occasionally. (ex jewelry)