Name 5 weather elements and their units of measurement.
E.g. temperature (degrees Celcius), pressure (mbars, mmHg), wind speed (m/s), wind direction (NSEW), cloudiness (oktas), precipitation (mm/h).
What is the main greenhouse gas on Earth?
Water vapour

Globalisation time! Sing a song that is known worldwide.

Great job!
What is natural increase?
Difference between birth rate and death rate.
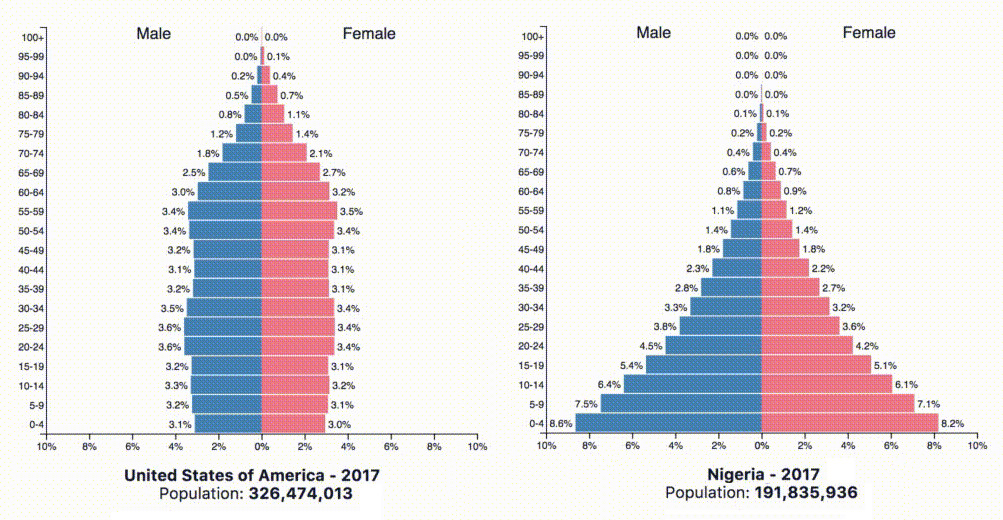
What kind of information can we get from a population pyramid?
• the proportion of males and females,
• the proportion of people in different age groups.

Show a cyclone, an anticyclone and regions with higer and lower wind speed in the synoptic chart below.
Cyclone - low pressure - L.
Anticyclone - high pressure - H.
Wind speed is higher when isobars are closer to each other.
Not your day... Paint your nails with a marker.

What is Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)?

Cost of the same goods in different countries OR what you can buy for the same amount in different countries.


Great Job!
Which pyramid is typical for LEDC and MEDC? Explain why.

The left one is for USA (MEDC): lower birth rate, low infant mortality, higher life expectancy. The right one is for Nigeria (LEDC): very high birth rate, high mortality and low life expectancy.
Perform an anticyclonic dance: show rotation in the Northern hemisphere and vertical air movement in anticyclones.

Rotation clockwise, vertical movement downwards.
What is Carbon Footprint? Which human activities produce the most part of carbon dioxide?

Transportation, goods, heating and cooling, other energy use, food.

What do GNI and HDI stand for? Explain the difference between them.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/wealthypoor-58b9e0225f9b58af5cbd064b.jpg)
Gross National Income and Human Development Index. GNI is an economic index, while HDI includes GNI and social factors (life expectancy at birth and average education level).

Explain how access to clean water affects country's population.

Good water quality and better sanitation lead to decreased death rate (especially to infant mortality), so the population will increase.
Say the colours, NOT the words! 2 slips allowed.

Mind tricks work ;)
Explain what happens with air and moisture in a depression, give reasons.
Pressure is lower in the center, that means air rises up, cools down with altitude, moisture condenses, forming clouds and leading to precipitation.
Name the main sources for air pollution with: methane (NH4), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon monoxide (CO).
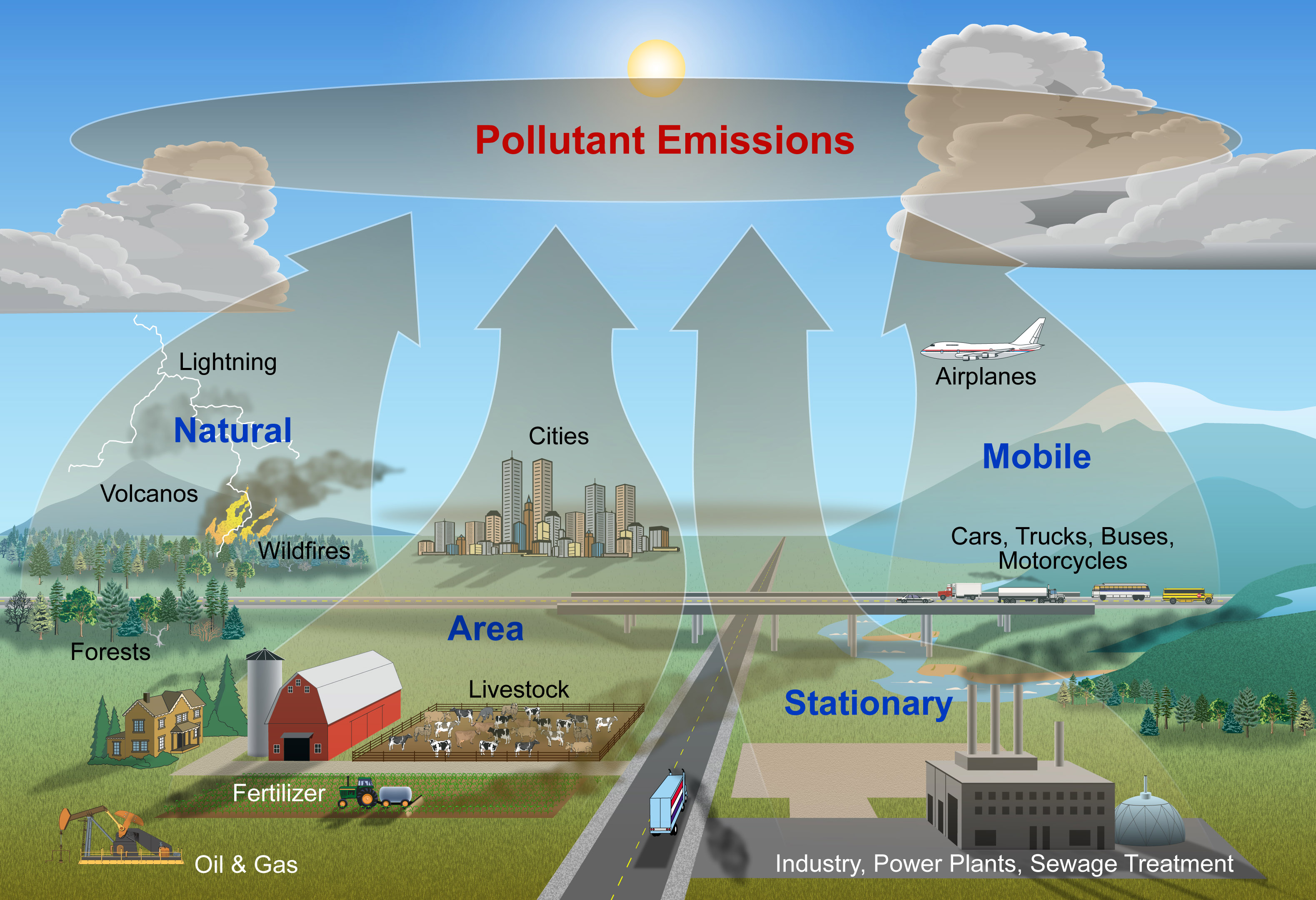
Methane (NH4) - agriculture, sulfur dioxide (SO2) - electricity genegation, carbon monoxide (CO) - road vehicles.
Name four main causes that make globalisation possible.

Communications, transport, trade, global marketing, international investment, TNCs, travel and migrations.
Which way is the dancer spinning?

It is impossible to say! Our brain does not have enough information.

How can emancipation of women lead to population change? (increase/decrease, why?)
For example, more girls are educated at school or enter universities and have a career instead of raising children. The birth rate is decreasing, so the total population is decreasing as well.
Describe the weather for the South of the UK. Give at least 4 weather elements. Explain.
Cyclonic weather, cold front in place. Fast pressure change, increasing wind speed, fast forming clouds, heavy rain and storm possible.
Name each type of radiation and describe what happens on each stage on the greenhouse effect scheme.

Sun radiation, including UV, IFR and visible light. Infrared radiation from the ground and from the greenhouse layer.

Name two advantages and two disadvantages of TNCs (one for the source country, one for the host country).

A source country is the one where the headquarters of TNC is located. A host country is where the TNCs' facilities are moved.
Name three social factors that influnce country's population change. Give an example for one of them.
Traditions, family size, birth control, women rights, contraception, healthcare, hygiene and sanitation habits, education, religion, lifestyle.
Describe transition from stage 2 to stage 3 of DTM. Give reasons of birth and death rate changes.

Stage 2: birth rate is still high (traditionally, plus limited access to contraception), death rate decreases (improved medicine, healthcare and sanitation), very high natural increase due to these.
Stage 3: birth rate decreases (contraception, family planning, women choose career), death rate decreases slowly (good medicine, very low infant mortality, better standards of living, higher life expectancy). Natural increase is not so high.