What is agriculture?
The process of raising products from the soil .
What is a mixed farm? Give an advantage for a mixed farm.
The use of a single farm for multiple purposes.
Give an example for how a farmer would reduce the amount of soil erosion.`
Wind brakes; Traps, zero tillage;
Define Food Security.
When people can consume enough nutritious food in order to stay healthy and active.
What is irrigation?
Farmland that becomes artificially.
What are the two broad categories for agriculture?
Commercial Farms and Subsistence Farms
What is required for a farm to be considered 'Intensive'?
Production that is characterized by high inputs of capital, fertilizers, labor or technologies.
Give one advantage and one disadvantages to Adminstered Marketing.
Advantage: Security, profits are exepected
Disadvantage: Little opportunity for profit making, Quota system, Difficult for export.
What are the four variables for determing a country has food security.
Availability
Access
Utilization
Stability
What are three main types of irrigation.
Sprinklers
Gravity Flow
Drip Systems
A commercial farmer needs to consider these four factors when choosing a crop to grow.
Type of Crop
Soil Condition
Climate
Growing Season
In Manitoba what types of farms will you see between 55N and 50N?
Wheat, grain, cattle farms.
Give an example of a technology that has impacted farming production.
GPS; LIDAR; Satellite Imagery; Databases
Rising population; Economic Development
What three major factors in Industrial Agriculture.
•Utilises approximately 70% of the worlds freshwater supply
•Dependent on chemical pesticides and artificial fertilisers
•Permanently removes nutrients from soils.
Soil is a combination of these four factors.
Parent Material
Organic Material
Air
Water
DAILY DOUBLE: What types of farms would you find in Nova Scotia? (Need 3 of 4).
Cattle, fruits, vegetables and dairy
How have GMO's affected food production?
Withstand pests --> less pesticides
Hardy to various climates.
Climate; Water Stress; Pests and disease.
Define either aeroponics or hydroponics.
•Hydroponic Food production: Plants are growing in a nutrient solution.
•Aeroponic Food Production: plants are suspended in the air. Water containing nutrients is sprayed onto the roots and the water drips off the roots and is recycled.
Describe the A horizon of this soil profile. 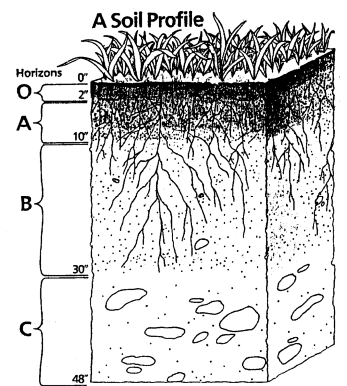
Topsoil, mostly mineral matter, but humus is present and biological activity is high.
This is a dominant forming of farming in Asia. What is it and how does it work?
Organic Farming
Food supply is impacted by human factors. What ae two human facotrs that relate to food accessbility and production.
Poverty; Technology; War and conflict
The process of producing food in a way that recreates natural ecosystems to protect soil, insects and other wildlife.
Permaculture.