What principle states that the oldest rock layers are at the bottom and the youngest are at the top?
Principle of Superposition
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called what?
Isotopes
What are the divisions of geologic time in order from largest to smallest?
Eon → Era → Period → Epoch
What is an index fossil?
An index fossil is a fossil of an organism that lived for a short time but was widespread.
In a rock cross-section, what does an intrusion look like?
An intrusion appears as igneous material cutting across existing layers.
Determining whether something is older or younger than something else is called what?
Relative dating
What type of dating compares the amounts of decayed and undecayed radioactive isotopes?
Absolute Dating
Why would the history of the United States be hard to place accurately on the geologic time scale?
U.S. history is extremely short and would be too tiny on the geologic time scale
How can an index fossil be used to determine the age of a rock layer?
If a rock layer contains an index fossil, it must be from the same time period that the fossil organism lived.
What does a fault represent in rock layers?
A fault is a break in Earth’s crust where movement has occurred.
A fault cuts across several rock layers. Which is older—the fault or the layers it cuts?
The fault is younger — a fault must be younger than the rocks it cuts through.
A rock sample contains 50% parent isotope and 50% daughter isotope. How many half-lives have passed?
1
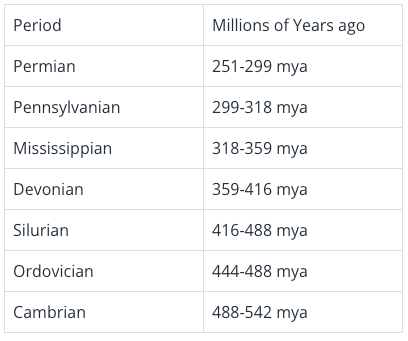
If a rock is 425 million years old, what period is it from?
Silurian
A rock layer contains oyster and snail fossils. Which type of dating method (relative or absolute) is most appropriate?
Relative dating (using fossils)
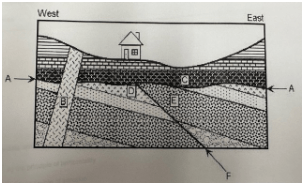 What is the youngest event in a rock sequence where magma cuts across layers?
What is the youngest event in a rock sequence where magma cuts across layers?
The intrusion (letter F in the diagram) is the youngest event if it cuts across all layers.
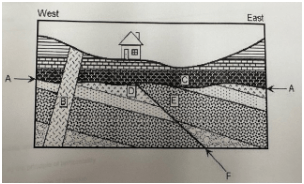 Which is younger, C or D?
Which is younger, C or D?
C because it is higher in the rock.
How much of the original isotope is left after three half-lives?
12.5% of the original isotope remains
What environmental condition does thick tree-ring growth indicate about climate?
The climate was good for growth
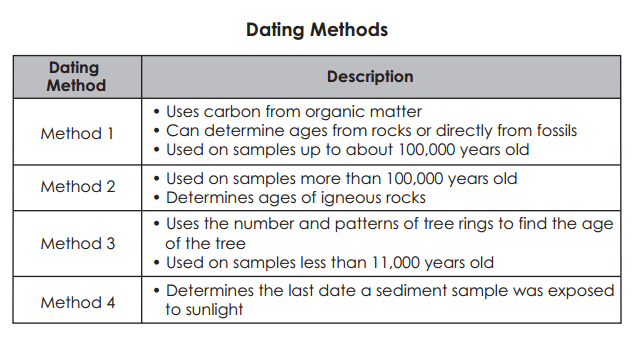
A deeply buried sample of limestone is examined. Which dating method would be the best to use?
4
Explain how a geologist can tell an intrusion is younger than the gravel it cuts through.
The intrusion is younger because it cuts through the gravel; features that cut through other layers are always younger.
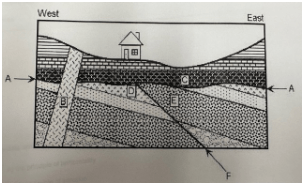
Put this in order from youngest to oldest.
B, C, A, F, D, E
A sample with a half-life of 10,000 years contains 75% daughter isotope. How old is the sample?
20,000 years old
• 25% parent = 2 half-lives → 2 × 10,000 = 20,000 years)
 The Devonian siltstone near Hamilton, NY contains this fossil. What does this reveal about the environment at that time?
The Devonian siltstone near Hamilton, NY contains this fossil. What does this reveal about the environment at that time?
The area had a marine environment during the Devonian Period.
A shallowly buried sample of shale that contains oyster and snail fossils is examined. Which method would work best to date this layer?
1 or 3
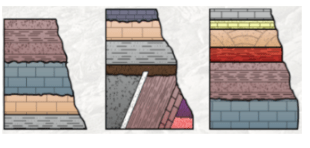
Which of the Rock Columns is in the correct order?
a 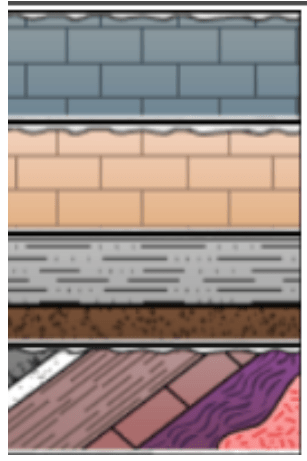
b

A