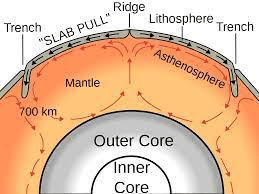
The thickest layer of the Earth
Mantle
What causes the plates to move?
A. They just do
B. The Earth's rotation
C. Convection currents in the mantle
D. The tilt and revolution of the Earth
C. Convection currents in the mantle
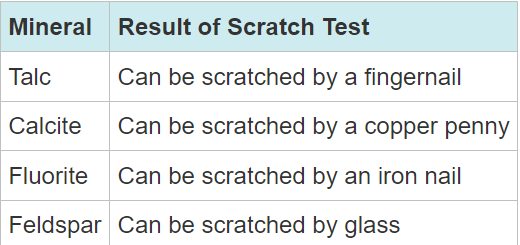
This chart shows four minerals and the hardness of each. Which mineral from the chart would be the softest of the four?
Talc (Because a fingernail is very soft. If a fingernail can scratch talc, talc must be even softer than a fingernail. )
Made from heat and pressure
Metamorphic Rock
The process of breaking down rock into sediments
Weathering
The process of transporting sediments
Erosion
If you were to travel from the surface to the center of Earth, the temperature would...
A. Stay the same
B. Decrease
C. Increase
Increase
What causes the convection currents in the mantle?
A. Pressure from the crust
B. Heat from the core
C. Heat from the sun
D. The tilt of the Earth
B. Heat from the core
Joy saw small crystals shining in the sunlight on the surface of a mountain slope. These were most likely...
A. Minerals
B. Sand
C. Rocks
D. Soil
Minerals
Broken down pieces of rock
Sediments
If erosion is the transportation of rocks, weathering is the ________________ of rocks
A. Dropping off
B. Transportation (movement)
C. Breaking apart
D. Condensation
C. Breaking apart
If weathering is the breaking down of rocks, erosion is the ______________ of rocks
A. Dropping off
B. Transportation (movement)
C. Evaporation
D. Condensation
B. Transportation (movement)
Which layer of the Earth is a solid, iron-rich zone?
A. Outer Core
B. Crust
C. Inner Core
D. Mantle
Inner Core
What kind of plate boundary creates rifts like this?
A. Transform
B. Divergent
C. Convergent
D. All
B. Divergent
Which of the following is NOT a property of minerals?
A. Naturally made
B. Same arrangement of atoms
C. Organic
D. Solid
Organic
(Minerals are inorganic, which means they are not living and were never part of anything living)
Under what conditions can igneous rock be transformed into metamorphic rock?
A. if layers of sand accumulate over it and harden over a period of time
B. if it is heated and put under pressure for long periods of time
C. if it is exposed at the surface and is weathered over a period of time
D. if it is forced deep into Earth, where it melts into magma
B. if it is heated and put under pressure for long periods of time
Which of the following is Not an example of mechanical weathering?
A. Frost wedging
B. Rusting
C. Wind breaking rock overtime
D. Tree Roots breaking rock over time
B. Rusting
Which of the following is NOT an example of erosion?
A. A large garage-sized boulder fell to the base of the hill, crushing two vehicles and crashing into a house.
B. There is a long meter-deep scar in the soil where a section of the riverbank has moved downward into the river.
C. It is fun to wade in the shallow areas of the river; the smooth rocks are rounded and sometimes slippery from the water flowing over them
D. When it rains, the water flows across our pasture and washes away soil into a sunken area.
C. It is fun to wade in the shallow areas of the river; the smooth rocks are rounded and sometimes slippery from the water flowing over them
Which BEST describes the physical properties of the Earth’s core?
A. a solid lower part and a liquid upper part
B. contains volcanic, sedimentary and granitic rocks
C. semi-molten
D. water and organic substances
A. A solid lower part and a liquid upper part
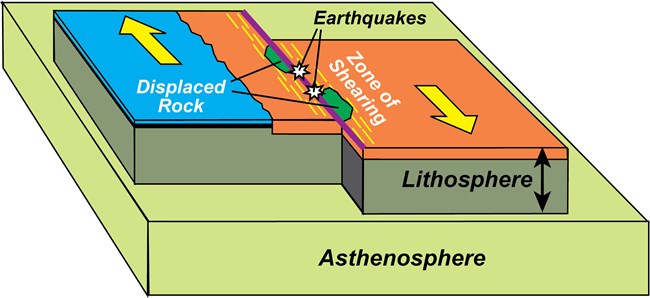
What kind of plate boundary creates Earthquakes?
A. Convergent
B. Transform
C. Divergent
D. All
B. Transform
Which of the following is true:
A. All minerals are made of rocks.
B. All rocks are made of fossils.
C. All minerals are made of dirt.
D. All rocks are made of minerals.
D. All rocks are made of minerals
Sedimentary rock is formed when rock fragments, minerals, and the remains of plants and animals are deposited as sediments and are then...
A. chemically weathered by water.
B. compacted and cemented together.
C. melted due to increased temperature and pressure.
D. recrystallized under the weight of the layers.
B. compacted and cemented together.
Which of the following is NOT an example of chemical weathering?
A. Acid rain breaking down rock
B. Rusting
C. Tree roots breaking apart rocks
D. Fire turning rock to ash
C. Tree roots breaking apart rocks
Which of the following is an example of erosion
A. The pavement near a tree’s roots bulges upward and has many more cracks than the other sections of the driveway.
B. A large piece of a boulder breaks off after being blasted by wind for years.
C. Water soaks into rocks and expands when it freezes causing the cracks in the rocks.
D. Water freezes into a glacier, trapping dirt inside. When the glacier moves, the dirt inside is also transported.
D. Water freezes into a glacier, trapping dirt inside. When the glacier moves, the dirt inside is also transported.
 The convection shown in the diagram is powered by heat from which part of the Earth? (Where does the heat come from?)
The convection shown in the diagram is powered by heat from which part of the Earth? (Where does the heat come from?)
A. Ocean
B. Crust
C. Core
D. Sun
Core
1. What type of plate boundary has a subduction zone as shown?
2. What kind of landform is created when there is a subduction zone?
1. Convergent Plate Boundaries
2. Volcanoes
Robby went on a field trip where he mined for minerals. He was so excited that he found real gold because it was yellow and shiny!
His teacher asked him to do a test to prove that he had found real gold. He used a ceramic plate and scratched the mineral on the plate. He noticed a greenish black streak on the plate. Robby was disappointed, because gold has a golden yellow streak.
He had really found pyrite.
Which test did Robby use to determine if he had found gold?
A. Plate Test
B. Streak Test
C. Scratch Test
D. Color Test
B. Streak Test
Which of these BEST describes the concept of the rock cycle?
A. rocks are continually changing, and any type of rock may be
transformed into another type by appropriate processes
B. sedimentary rocks may be remelted several times
C. rocks move in circles on the earth as the earth rotates
D. rocks can be moved from place to place on the earth without changing
A. rocks are continually changing, and any type of rock may be
transformed into another type by appropriate processes
Explain how water can weather rocks
Weathering - Water physically breaks down the rock through abrasion (rubbing against the rock) and turns the rock into sediments
Explain how water can erode rocks
Erosion - Water carries the sediments to another place