What makes the equation of a line parallel? Perpendicular?
Parallel: Same slope
Perpendicular: Opposite Sign Reciprocal Slope
A square is ______________ a rectangle.
ALWAYS
How do we prove a parallelogram is a square?
A square is a parallelogram that has:
1. 4 right angles
2. Congruent diagonals that are perpendicular
3. Have 4 equal sides
4. Have 2 sets of opposite sides that are parallel.
What is the value of x + y?
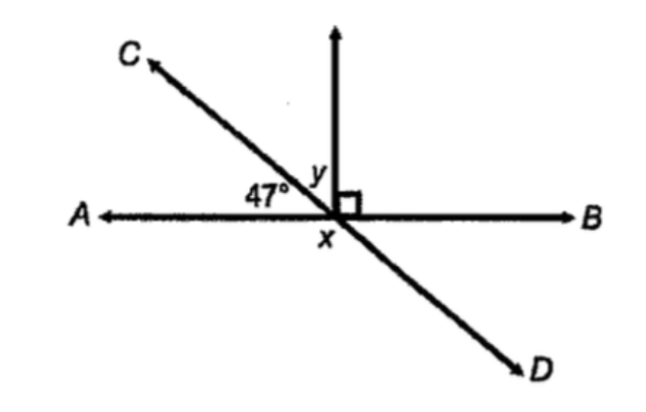
x = 133 degrees
y = 43 degrees
133 + 43 = 176 degrees.
What are angles A, B, C and B + D?
A = 120 degrees
B = 60 degrees
C = 120 degrees
B + D = 120 degrees
What is the slope of the line f' which is parallel to line f?
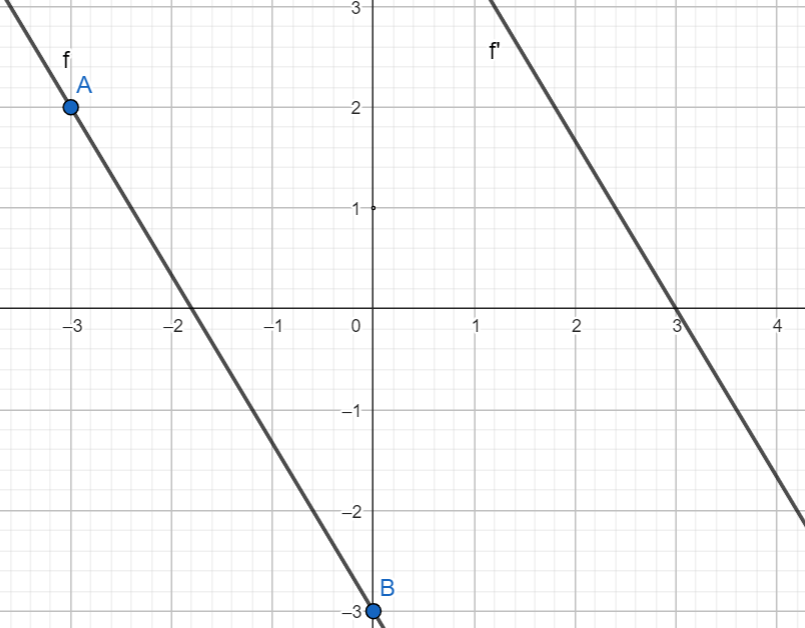
-5/3
Each side of a square is 10 cm. How long are the diagonals? (Round to the nearest hundredth)
Diagonals = 14.14 cm
The vertices of quadrilateral ABCD are A(-6, 2), B(0, 4), C(-4, 0), D(2, 2). What kind of quadrilateral is ABCD?
A. Trapezoid
B. Square
C. Parallelogram that is not a rhombus
D. Rhombus that is not a square
C. Parallelogram that is not a rhombus
The parallel lines are cut by a transversal creating the angles shown. Determine which angles must be congruent to angle x.
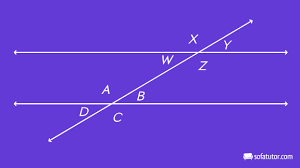
X = Z = A = C
What is the value of angle C?
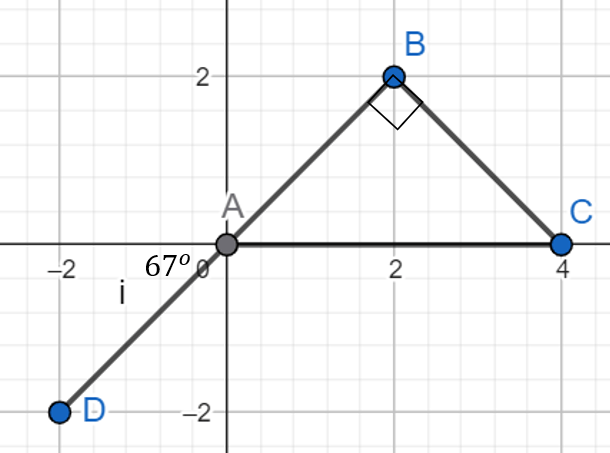
C = 23 degrees
What is the slope of the line perpendicular to line AB?
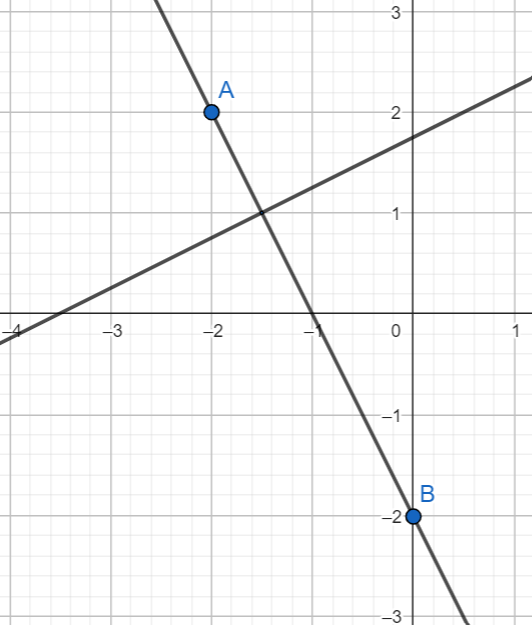
1/2
ABCD is a trapezoid. Base AB is 4 cm and base DC is 20 cm. What is the midsegment FE?
FE = 12 cm
The ordered pairs that describe the locations of three vertices of a parallelogram on a coordinate plane are given.
(0, 3), (2, 2), (4, 3)
Which ordered pair describes a possible location of the fourth vertex of the parallelogram?
A. (-1, 2) B. (3, -2) C. (1, 5) D. (2, 4)
D. (2, 4)
In the figure below, the lines are parallel. What is the value of x?
A. 113 B. 51 C. 141 D. 39
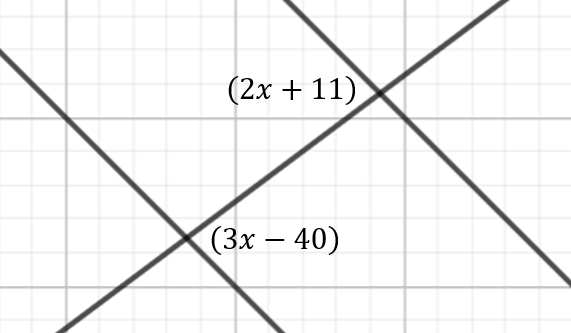
B. 51
Find the missing interior angles. (Not to scale)
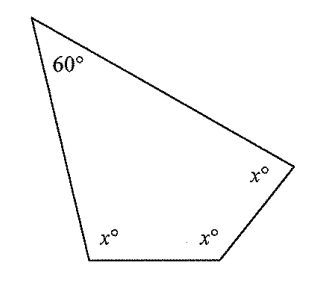
x = 100 degrees
What is the equation in standard form of the line that passes through the point (5,2) and is parallel to the line represented by 2x + 5y = 25?
A. 2x + 5y = -20
B. 2x - 5y = 15
C. 2x + 5y = 20
D. 2x + 5y = -15
C. 2x + 5y = 20
ABCD is a rhombus. If its diagonals measure 12 cm and 16 cm, what is the perimeter of the rhombus?
Perimeter = 40 cm
A quadrilateral has vertices A = (0, 0), B= (1, 3), C = (0, 4) and D = (-1, 1). Prove that ABCD is a parallelogram.
Slope AB = 3 = Slope DC
Slope CB = -1 = Slope DA
Therefore, ABCD is a parallelogram.
Consider the figure shown below. If ∠E = (3/4 x + 20), then the value of x is _______? (nearest tenth)
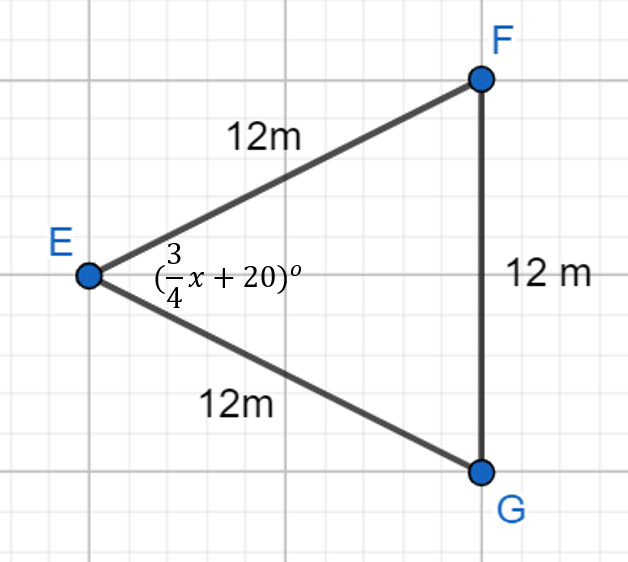
x = 53.3
Find the missing Interior Angles. (not to scale)
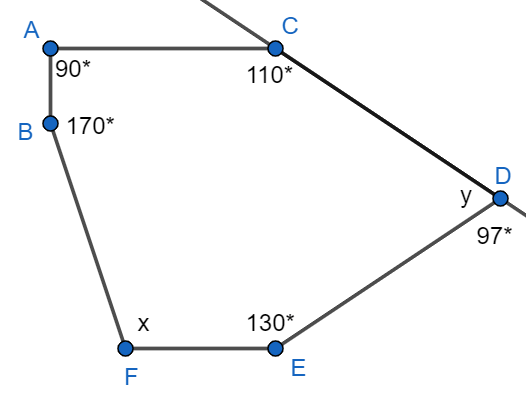
angle x = 137 degrees
angle y = 83 degrees
The longer base of a trapezoid has endpoints of (−2,−4) and (4,0). The shorter base contains the point (3,1). What is the equation of the line of the shorter base?
y = 2/3 x - 1
On a coordinate grid, Rhonda makes a quadrilateral by connecting the points A(0, 1), B(-1, -2), C(-5, -2) and D(-5, 3).
She knows ∠C is a right angle, she thinks that ∠A might be a right angle, too. Determine if her thinking is correct and provide mathematical evidence to prove if her thinking is correct or incorrect.
Slope DA = -2/5 and Slope AB = 3
Therefore, ∠A is NOT a right angle.
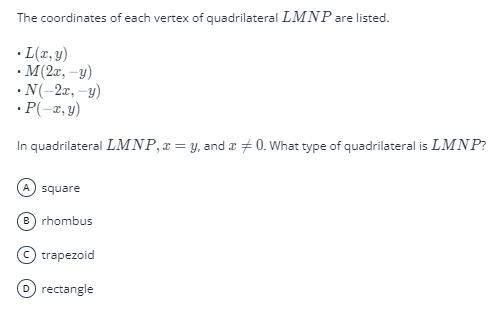
C. Trapezoid
In the figure, m∠9 = 80 and m∠5 = 68. Find the measure of each angle. Tell which vocab terms you used.
∠12 = ? ∠1 = ? ∠4 = ? ∠7 = ? ∠16 = ?
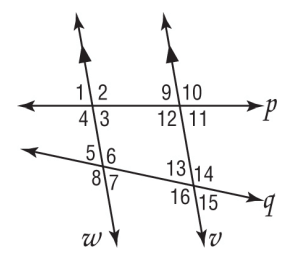
∠12 = 100*, linear pair w/ ∠9
∠1 = 80*, corresponding w/ ∠9
∠4 = 100*, linear pair w/ ∠1
∠7 = 68*, vertical angles w/ ∠5
∠16 =112*, same side interior w/ ∠7
The measures of the interior angles of a pentagon are represented by
3x, 2x – 15, 2x + 40, x + 20, and 2x - 35.
What is the measure of the largest interior angle?
x = 53 degrees
3x = 159 degrees