What are the three types of rocks?
Sedimentary, Igneous, Metamorphic
What are the three types of plate boundaries?
convergent, divergent, transform
What is a volcano?
opening in Earth's crust that allows molten rock from beneath the crust to reach the surface
What is an earthquake?
shaking and vibration of the Earth's crust due to movement of the Earth's plates
What are the Earth's layers starting from the inside?
Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, Crust
What forms of energy drive the rock cycle?
Heat and Mechanical
What drives the plate movement and where does this movement happen?
convection currents in the mantle (asthenosphere)
Do all volcanoes occur at plate boundaries? Explain.
No, Hawaii is formed from a hot spot underneath the Pacific Plate.
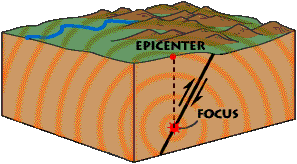
Where is the epicenter located in relation to the focus?
Explain precautions that can be made to protect life from various geohazards and include meteorological hazards. Some examples include landslides, earthquakes, tsunamis, sinkholes, groundwater pollution and flooding.
The best methods would be to avoid living in areas prone to landslides, earthquakes, tsunamis, sinkholes or flooding. If you choose to live in an area at risk for these hazards, then you should be aware of times when the risk is the greatest. Avoid living in regions where groundwater contamination is more likely – such as near a chemical waste site, areas with old septic systems, or areas prone to saltwater intrusion.
What is happening at #3 and 4?
heat and pressure
What is the difference of continental drift and plate tectonics? What evidences did they have?
Continental Drift-continents drifted apart, once formed Pangea. evidence: similar fossils on different continents, continents fit together like a puzzle, similar rock types on different continents
Plate Tectonics-interaction between lithospheric plates, gave the mechanism for the continents drifting...convection currents in the mantle; Evidence: paleomagnetism of the ocean floor
Where on the Earth do you find the most volcanoes? What is this place called? Why do volcanoes occur here?
The Ring of Fire on the Pacific Plate; convergent-subduction zone between two plates
What does magnitude measure? What is the difference between P and S waves?
Magnitude measures size or intensity of the earthquake. P waves are primary waves, arrive to seismic station first, and vibrate along the same direction as the direction of travel. S waves are secondary waves, arrive to the seismic station second, and vibrate at right angle to the direction of travel
How is soil created from rock? Include all of the layers.
A solid block of rock is slowly weathered over time (both physical & chemical weathering) until eventually small bits of weathered rock appear above the solid mass. This is considered the C horizon (partially weathered rock). Over time this partially weathered rock continues to break down into smaller pieces of rock and it is combined with decayed plant matter as the very early plants die and decompose to form the beginning of nutrient-rich matter. This creates the subsoil or B horizon. As this material continues to break down and more & more decaying plant matter accumulates, the final layer in the soil profile (the A horizon or topsoil) is formed. This completes the soil profile. Dead organic material accumulates on top (O horizon).
Explain how this could be both chemical and physical weathering.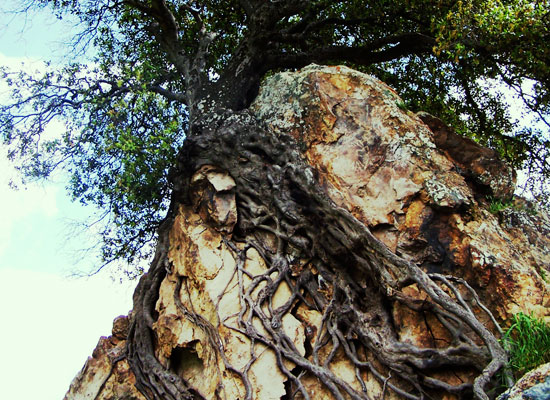
Chemical-plant secretes chemicals that alter rock
physical- roots grow and break rock apart
Explain ridge-push and gravity pull and how they move the plates.
As plates move, they will eventually subduct beneath another plate. The weight of the plate pulls the rest of the plate down with it, which is called gravity pull. The opposite, ridge push, happens when the upwelling of new lithosphere pushes the plate along at a mid-ocean ridge.
Define lahar and tell which type of volcano create lahar.
A lahar is a mudflow caused by volcanic activity. Lava is often mixed in with the mud, causing very hazardous conditions. They are generally formed at composite or cinder cone volcanoes
What types of plate boundaries are earthquakes likely to occur near? Describe what happens.
Transform. When the force of the moving blocks finally overcomes the friction of the jagged edges of the fault and it unsticks, all that stored up energy is released.
Explain how current geologic landforms developed such as Appalachian Mountains, fall zone, shorelines, barrier islands, valleys, river basins, etc. using the geologic time scale.
When the North American Plate smashed together it created the Appalachian mountains. They have eroded since then. Barrier islands have formed because of deposition on sediment. The tributaries make up our river basins, all connected to the Mississippi. The fall line is an area of eroded rocks between the piedmont and costal plains.
Explain the process from magma to a sedimentary rock.
Magma-->cooling and solidification-->igneous rock-->weathering and deposition-->sediment-->compaction and cementation-->sedimentary rock
For each boundary (transform, divergent, convergent-subduction, and convergent -collision):
a. Define the action at each plate
b. Give the features formed
c. Name a specific location on Earth where this can be seen
Transform- motion is horizontal, they move opposite of each other, earthquake, EX: san Andreas fault
Divergent- the plates move away from each other, mid oceanic ridge, EX: Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Iceland Rift Valley
Convergent-Subduction: oceanic plate is pushed under the continental plate and causes magma to form and volcanoes, ocean trench EX: Mariana Trench, Andes Mountains
Convergent-Collision- creates mountain ranges, EX: Himalayas
What are the three types of volcanoes, what type of lava, slope, and an example.
Cinder Cone: Felsic(Ash, cinders, bombs); overall steep slope (30-40 degrees); Paricutin, MEXICO
Composite: Felsic and Mafic lava (layers of cinder and lava); increasing slope (5-30 degrees); Mt. St. Helens, Washington, U.S.A.
Shield: Mafic (slow, runny lava flows); least steep slope (5-10 degrees); Mauna Loa, Hawaii
An earthquake occurred and the difference between the P and S waves arriving at the seismic stations is 9 minutes. How far away is the earthquake?
8000 km
Explain how processes change sea-level over time – long & short term. Infer the effects on landforms such as shorelines and barrier islands.
Global warming processes can cause sea-level to rise over time. Ice caps and ice sheets can melt, causing large amounts of fresh water to be added to the oceans. This has an impact on shorelines and barrier islands because these areas will become flooded at more water is added to the oceans. In a short-term sense, sea level can rise during storms as the storm surge approaches the shoreline.