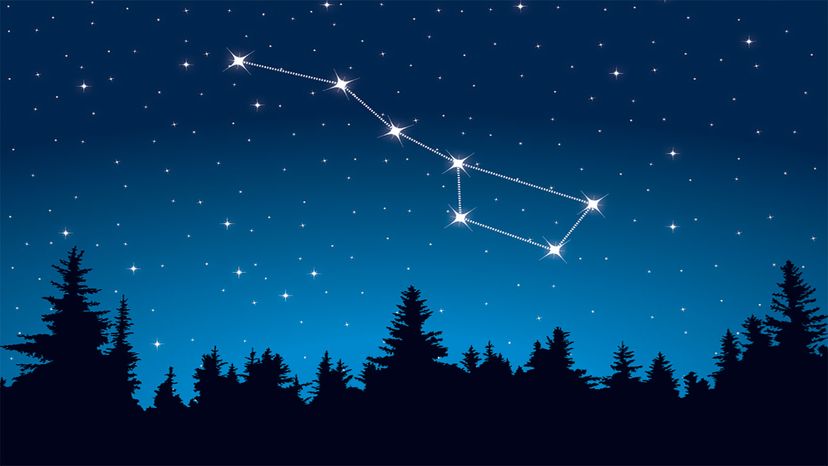
What do we call a group of stars that forms a pattern in the sky that looks like a familiar object, animal, or character? (p.370)
A constellation looks like spots of light arranged in a particular shape when viewed from Earth.
What property of stars indicates its temperature? (p.374)
The color of a star
What is the lowest layer of the Sun's atmosphere, and the layer from which light is given off? (p.375)
The photosphere is often called the "surface of the Sun"
The H-R diagram shows the relationship between which two properties of a star? (p.380)
Its temperature and its absolute magnitude.

Stars begin as a large cloud of gas and dust called what? (p.382)
A nebula
What do we call a large group of stars, gas and dust held together by gravity? (p.386)
A galaxy
Why do the positions of constellations appear to change throughout the year? (p.371)
Because as the Earth orbits the Sun, different constellations come into view while others disappear.
What color do hot stars appear? (p.374)
The hottest stars appear to be a blue-white color.
What is the layer that extends about 2,000 km above the photosphere? (p.375)
The chromosphere
Most stars seem to fit into a diagonal band along the H-R diagram. What is this band called? (p.380)
The main sequence
About 90% of stars are main sequence stars.
When the particles of a nebula move closer together, the temperatures increase to a point where fusion can begin, and a star is born. At what temperature does fusion begin? (p.383)
10 million Kelvin
What is the shape of the Milky Way Galaxy? (p.386)
Spiral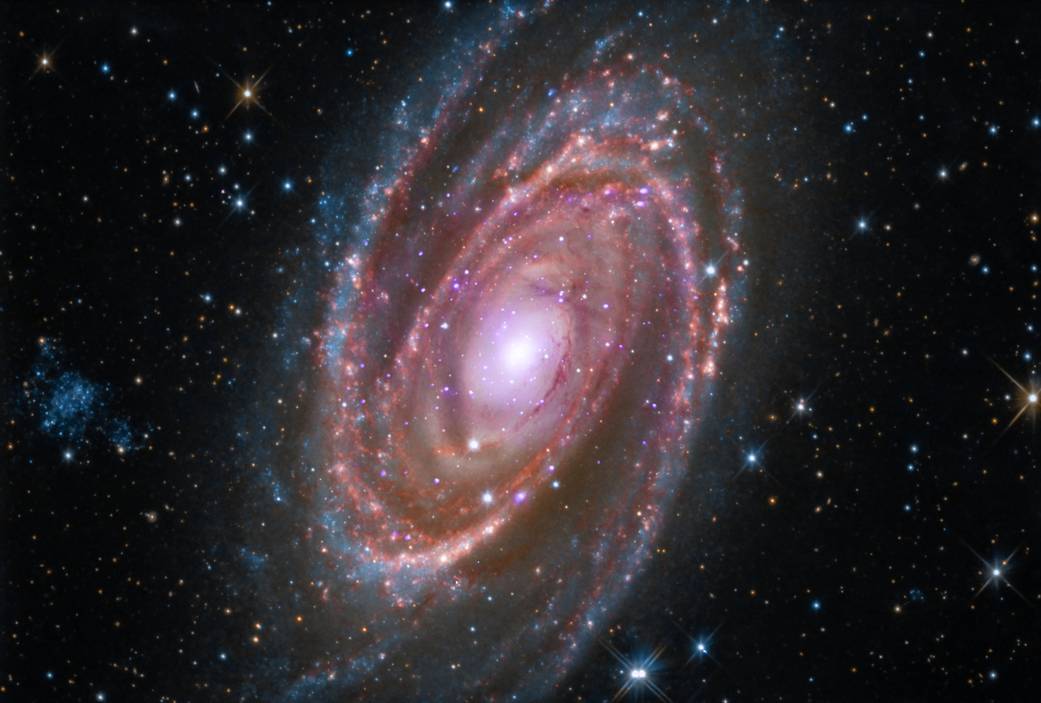
It has the greatest apparent magnitude, because it is closer than other stars that might give off more light.
What color do relatively cool stars appear? (p.374)
They look orange or red.
What is the largest layer of the Sun's atmosphere, and extends millions of km into space? (p.375)
The corona
Among the main sequence stars, do the hottest or the coolest stars generate the most light? (p.381)
The hottest
A main sequence star
What galaxy shape can look like a football? (p.387)
Elliptical
Rigel does not look as bright as Sirius in the night sky, although it does give off more light. What do we call the measurement of the actual amount of light given off by a star? (p.372)
Absolute magnitude
What color do stars that have the same temperature as our Sun appear? (p.374)
Yellow
What are areas of the Sun's surface that appear dark because they are cooler than the surrounding areas? (p.376)
Sunspots
What do we call a star that is hot but not bright? They are located on the lower left of the H-R diagram. (p.381)
White dwarfs
When hydrogen in the core of the star is depleted, a balance no longer exists between pressure and gravity. The core contracts, and temperatures inside the star increase. This causes the outer layers of the star to expand and cool. In this late stage of its life cycle, what is the star called? (p.383)
A giant or supergiant
What do we call the shape of a galaxy that isn't spiral or elliptical, and can be many different shapes? (p.387)
Irregular galaxies are smaller than the other types of galaxies.
There are two irregular galaxies (called the Clouds of Magellan) that orbit the Milky Way
What is the distance that light can travel in one year? (p.373)
A light-year.
Light travels at 300,000 km/s, or about 9.5 trillion km in one year.
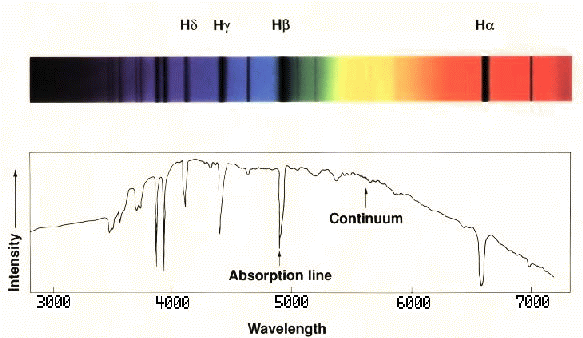
What do scientists observe to study the composition of stars? (p.374)
The stars' spectra (or rainbow band of colors)
The intense magnetic fields associated with sunspots may cause huge arching columns of gas. What do we call these? (p.376)
Prominences
What do we call large stars that are extremely bright but not hot? They are located on the upper right of the H-R diagram. (p.381)
Giants
The largest giants are called supergiants.
If the star had a relatively low mass, after the star's core uses up much of its helium, it contracts even more and its outer layers escape into space, leaving behind a hot, dense core. What does the star become? (p.383)
A white dwarf
What is at the center of many galaxies, including the Milky Way? (p.387)
A supermassive black hole.
Evidence for the existence of the black hole comes from observing the orbit of a star near the galaxy’s center. Additional evidence includes X-ray emissions detected by the Chandra X-ray Observatory. X rays are produced when matter spirals into a black hole.
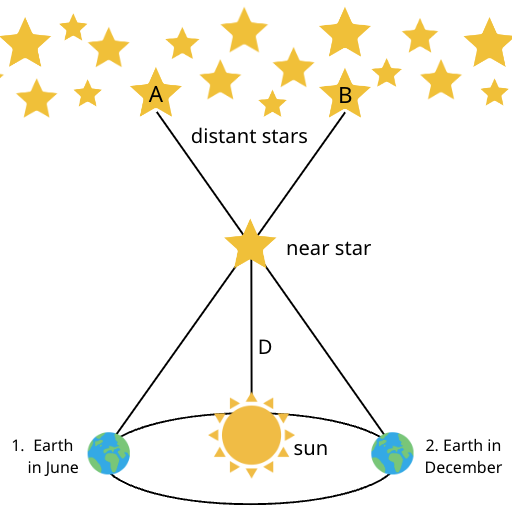
How do scientists determine the distance from Earth to nearby stars? (p.373)
One way is to measure parallax.
Parallax is the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions.
What tool to scientists affix to a telescope to break the light of a star into its component colors? (p.374)
A spectroscope
What occur when large amounts of electrically-charged gas are ejected suddenly from the Sun’s corona, and can cause auroras? (p.377)
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs)
The Sun and other stars create energy by fusing hydrogen to make what other element? (p.381)
Helium
If a high-mass star's outer portion explodes in a supernova, it could become either a neutron star, or what? (p.384)
A black hole
What is the leading theory about the formation of the universe? (p.391)
The big bang theory states that approximately 13.7 billion years ago, the universe began with an enormous explosion.
