The age of rocks and geologic features compared with other rocks and features nearby
What is relative age?
Represent species that existed on Earth for a short length of time, were abundant, and inhabited many locations.
What is index fossils?
The three types of unconformities covered in class.
What is unconformity, angular unconformity, and nonconformity?
The principal that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are on the bottom.
What is superposition?
The principle of relative age dating pictured in the image below.
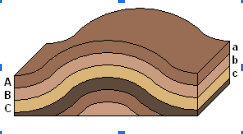
What is original horizontality?
Pictured below, younger sedimentary layers are deposited on top of older, horizontal sedimentary layers that have been eroded.
What is disconformity?
A piece of an older rock that becomes part of a new rock.
What is inclusion?
As pictured in the image below, sediments are deposited in large, continuous sheets in all lateral directions.
What is lateral continuity?
Pictured below, sedimentary layers are deposited on top of tilted or folded sedimentary layers that have been eroded
What is angular unconformity?
A surface where rock has eroded away, producing a break or gap, in the rock record.
What is unconformity?
This picture shows which principle of relative aging.
What is inclusions?
Pictured below, younger sedimentary layers are deposited on older igneous or metamorphic rock layers that have been eroded
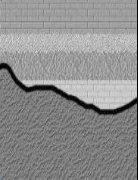
What is nonconformity?
Matching rocks and fossils from separate locations.
What is correlation?
In the picture below, principle of relative age dating one geologic feature (fault or dike) cuts across another feature, the feature that IT cuts across is older.
What is cross-cutting relationships?
These are used to help geologist to make correlations in relative rock aging.
What are index fossils?