The smallest unit of light is called a __________
Photon
Define reflection and refraction.
Reflection - light bounces off an object
Refraction - Light bending as it passes through another medium
Is the image upright or inverted?
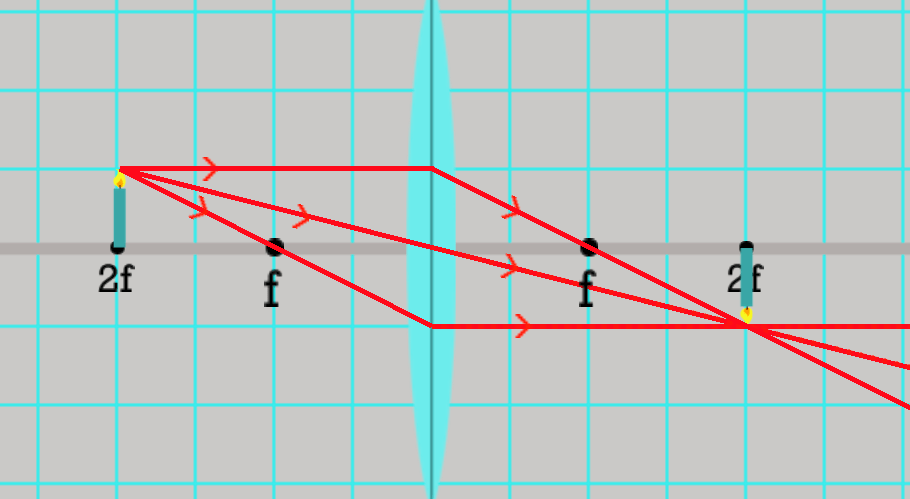
Inverted.
The colour _______ has the longest wavelength of light, will _________ has the shortest wavelength.
Red, Purple (violet)
What is wavelength?
The distance between the crests of 2 waves. The greater the distance, the longer the wavelength.
What are the 2 categories of light? Give an example of each?
Natural (sunlight, stars, lightning, forest fire, volcanoes, some plants and animals)
Artificial (Candles, lasers, lightbulbs, electronics, torches)
What is the difference between specular and diffuse reflection?
Specular - smooth mirror like surface that makes a clear reflection.
Diffuse - When light hits a rough surface, creating a blurry reflection.
What is the difference between concave and convex?
Concave makes a cave shape, while convex bulges outwards.
Explain why a red shirt looks red.
It is red because the shirt absorbs all wavelengths of light except red. The red light is reflected, so our eyes only see the reflecting red wavelength of light, making the shirt look red.
What is frequency?
The number of waves that pass a point in a given amount of time. The greater the number of waves, the higher the frequency.
What is myopia?
Near-sightedness. Things close by appear clear, but distant objects are blurry.
____________ - A solid object that light cannot pass through.
Opaque
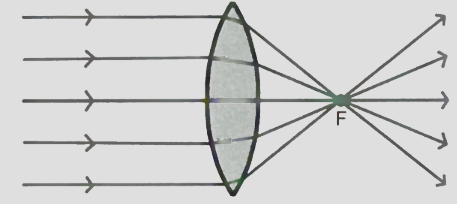
Do convex lenses cause light to spread out or focus?
Focus.
Why would you warm up faster on a summer day if you are wore a black shirt than if your wore a white shirt?
A shirt is black because it absorbs all wavelengths of light, while a white shirt reflects all wavelengths.
This is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum we can see.
Visible light.
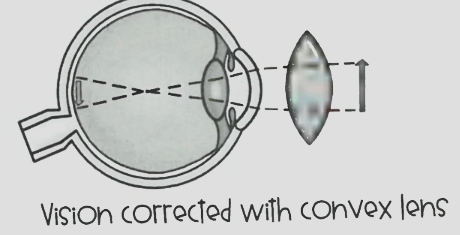
How can you correct Hyperopia?
A convex lens.
When light travels from air to water, light will bend _________ the __________.
Towards, Normal
Is the image: Real or simulated? Inverted? Bigger or smaller? Is the lens concave or convex?
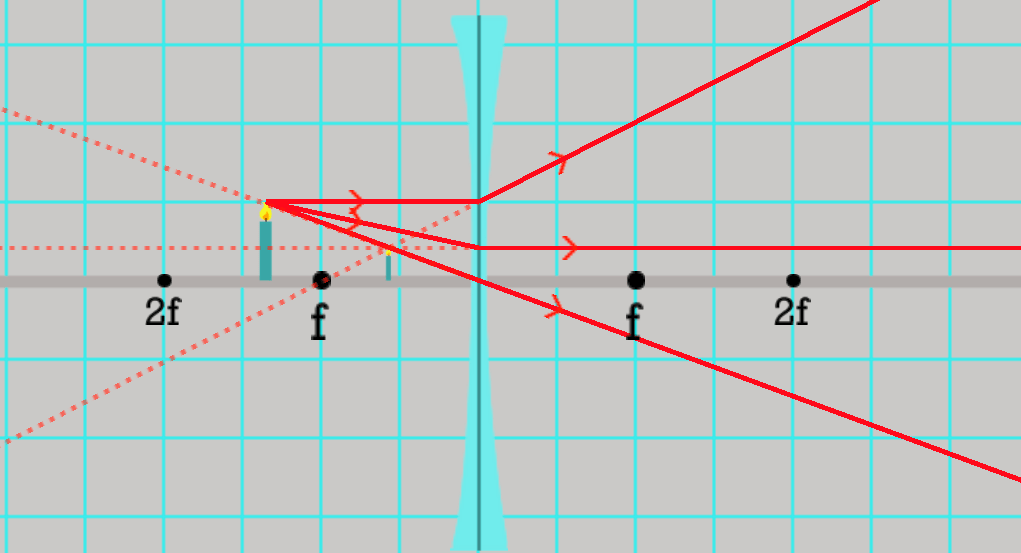
Simulated (same side of lens as the object)
Not inverted
Smaller
Concave lens (thin in middle, sticks out at top and bottom, makes a cave)
What are the 2 parts to a shadow? Describe each.
Umbra - darker part
Penumbra - lighter part
This is the shortest wavelength on the electromagnetic spectrum. Used to treat cancer, is highly radioactive, and is produced by nuclear energy and in supernovas.
Gamma Radiation
What are the 4 types of luminescence? Explain how each works.
Fluorescence - glows when a light is shining on it. (detergent)
Bioluminescence - When animals/ plants create light (fireflies)
Phosphorescence - Stores radiation and will continue to glow even after a light is turned off. (glow in the dark sticker)
Chemiluminescence - Chemical reaction produces light. (glowsticks)
In reflection, the angle of __________ is equal to the angle of ___________.
Incidence, Reflection
What type of mirror is being used? Is the image bigger or smaller? Real or simulated? Inverted?
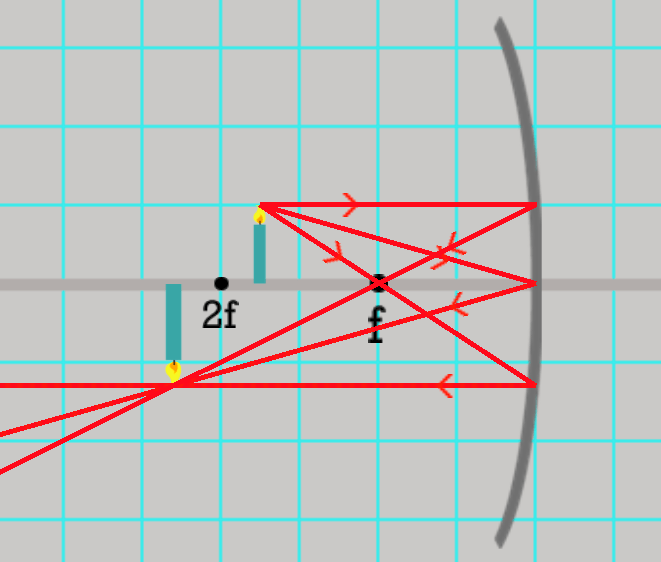
Concave, Bigger, Real, Inverted.
Explain additive and subtractive colour theory. Give an example of when each is used.
Additive - used red, green, blue as a base. Starts with a black background, and mixing all 3 colours makes white. Used for screens.
Subtractive - Uses cyan (blue), magenta (purple), and yellow as a base. Starts with a white background, and mixing all 3 colours makes black. Used in printers, magazines, photos.
List all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, from longest wavelength to shortest.
Radio waves, Microwaves, Infrared waves, Visible light, Ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and Gamma waves.