Why do ridge-and-furrow greenhouses often have higher humidity issues compared to single-span structures?
Shared walls reduce air movement and trap moisture.
What does glazing mean in a greenhouse?
The covering material that lets light in.
What greenhouse is best for large commercial operations?
Ridge and Furrow Greenhouses
The material used to cover a greenhouse and allow light to enter.
Glazing
Why do greenhouses overheat even in winter sunlight?
Solar radiation is trapped inside.
One disadvantage of using wood as a frame?
It can rot or be damaged by moisture.
Why does plastic film need frequent replacement?
UV degradation and physical wear.
Which greenhouse is built into a hillside and works best on slopes?
Uneven-Span
Define: Dead Load
The permanent weight of the greenhouse structure itself (frame, glazing, gutters).
Why is light transmission important?
Plants need light for photosynthesis.
Which greenhouse does not always have permanent heating?
Hoop-house/High Tunnel/Quonset
Which covering is the cheapest option?
Polyethylene (plastic film)
Why use a retractable-roof greenhouse?
Allows control of temperature and exposure.
Define: Live Load
Temporary or moving weight placed on a greenhouse (snow, wind, workers, equipment).
What type of greenhouse is used most in coastal regions where climate is mild and there are prevailing winds?
Sawtooth Greenhouse
Why are lean-to greenhouses rarely used for commercial production?
Limited space and uneven light distribution.
Rank these coverings from most forgiving to least forgiving if frame spacing is imperfect:
polycarbonate, plastic film, glass
Plastic film → Polycarbonate → Glass
What type of greenhouse is pictured below? 
Gothic Arch
Define: Truss
A rigid, triangular framework used to support the roof.
Rank these by risk of crop damage due to light quality, highest to lowest: clear glass, diffused polycarbonate, shade cloth
Clear glass → Diffused polycarbonate → Shade cloth
Which covering would you immediately rule out for a hail-prone area: glass, polycarbonate, or double-layer plastic?
Glass!
Which glazing material is strong but expensive?
Glass
What type of greenhouse is pictured below?
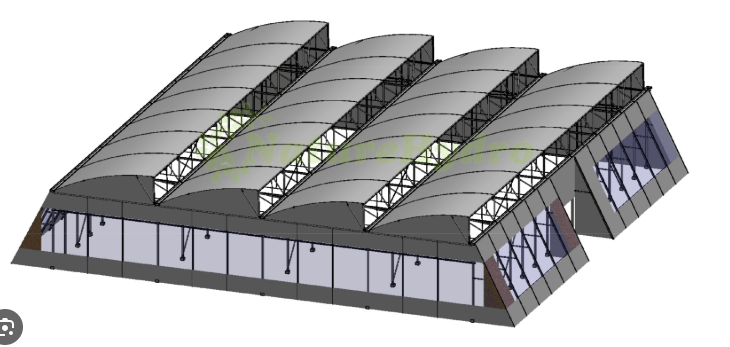
Sawtooth
Define: Roof Pitch
The steepness or slope of the greenhouse roof.
A Dutch Venlo greenhouse has taller gutter heights than a barrel vault greenhouse. What climate advantage does this structural difference create?
Greater air volume, which buffers temperature and humidity swings,
Why are hoophouses more likely to fail during heavy snow events?
Lightweight frames and low roof pitch increase snow load risk.
A greenhouse switches from clear plastic to diffused plastic and sees less leaf scorch but no change in air temperature. What property of the covering caused this change?
Light Diffusion
What type of greenhouse is pictured below?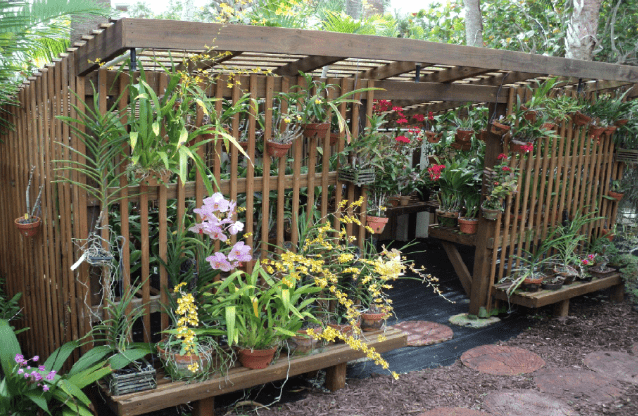
Lath House
Define: Purlins
A horizontal beam that supports the roof covering and connects trusses.
Define: Hardening Off
Hardening off is the gradual process of acclimating greenhouse-grown plants to outdoor environmental conditions by slowly reducing protection and exposing them to lower temperatures, increased light intensity, wind, and lower humidity before transplanting.
Why do ridge-and-furrow greenhouses require stronger foundations than single-span houses?
Greater total weight and wind load.
Why is aluminum a good greenhouse frame option?
It is lightweight and rust-resistant.
This greenhouse roof style is designed to naturally vent hot air using prevailing winds.
Sawtooth greenhouse
This structure uses the insulating properties of soil and minimal or no artificial heat to protect plants or stored crops from freezing by maintaining a stable, cool temperature.
Cold frame or bulb cellar
What is a major climate-related disadvantage of connected greenhouse structures?
Humidity and disease can spread more easily between bays
Which greenhouse type becomes less efficient as size increases, and why?
Lean-to — limited expansion and uneven light
Two greenhouses use the same plastic film and heating system, but one loses heat much faster at night.
What covering-system difference best explains this?
One uses single-layer plastic while the other uses double-layer plastic with air inflation
A grower is deciding between a gothic arch and a barrel vault greenhouse for a snowy climate.
Which design performs better under snow load and why?
Gothic arch — steeper peak allows snow to slide off
Define: Load Rating
Maximum weight a structure can safely support.
Why do disconnected greenhouses allow for more precise crop-specific climate control than connected greenhouses?
Each structure can be heated, ventilated, and managed independently