This muscle contracts to start breathing in.
What is the diaphragm?
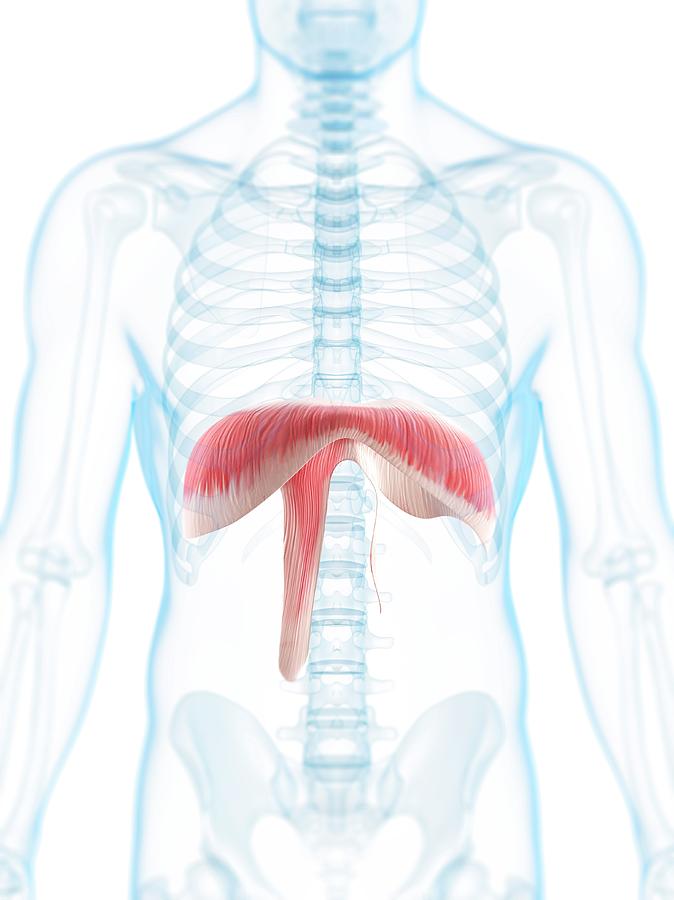
This is the general term for the group of muscles that are not primary but help the body with deep inspiration.
What are accessory muscles?
This type of automatic breathing helps maintain the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body.
What is life breathing?
This is the volume of air moving in and out during quiet, resting breathing.
What is tidal volume (TV)?
This simple clinical task measures how long a person can sustain a vowel sound on one breath.
What is maximum phonation time (MPT)?
When air moves into the lungs because the chest cavity gets bigger, this event is happening.
What is inhalation (inspiration)?

These muscles are positioned laterally between the ribs and run downward and forward to elevate the rib cage during inhalation.
What are the external intercostals?
During quiet tidal breathing, the respiratory cycle is divided into 40% inhalation and this percentage of exhalation.
What is 60%?
This is the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled after a normal tidal inspiration.
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)?
This assessment uses bands around the rib cage and abdomen to measure how the chest wall moves during breathing.
What is respiratory inductance plethysmography (RIP)?
This is the tiny air sac where oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves it.
What is the alveolus?

These deeper muscles run perpendicular to the external intercostals and are primarily active during forced exhalation.
What are the internal intercostals?
Life breathing and speech breathing differ in their inhalation-to-exhalation ratio, with speech requiring a much longer exhalation phase.
What is life breathing at about 40% inhalation and 60% exhalation, and speech breathing at about 10% inhalation and 90% exhalation?
This is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a maximal exhalation.
What is residual volume (RV)
This medical specialty performs Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) tests to measure oxygen, carbon dioxide, and pH levels in the blood.
Respiratory Therapist
This step of respiration moves oxygen through the bloodstream to the body’s tissues.
What is gas transport?

This specific nerve, arising from the spinal roots C3 through C5, provides the necessary innervation for the diaphragm to function.
What is the phrenic nerve?
This physical law explains that as lung volume increases, air pressure decreases, causing air to flow into the lungs.
What is Boyle’s Law?
This formula calculates Vital Capacity (VC).
What is VC = IC + ERV?
This respiratory test measures lung volumes and airflow to assess overall pulmonary function.
What is spirometry?
This process happens inside the body’s cells when they use oxygen to make energy and release carbon dioxide.
What is internal (cellular) respiration?

This is the set of thoracic spinal nerves (T1-T11) responsible for innervating both the internal and external intercostal muscles.
What are the intercostal nerves?
Speech breathing provides the controlled airflow and pressure needed to sustain phonation and connected speech.
What is subglottic pressure?
This is the equation for Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
What is TLC = TV + IRV + ERV + RV?
This device is used in clinical practice to measure a patient’s oxygen saturation levels (O2 Sat)
What is a pulse Oximeter?