What are the benefits of seeds?
1. Dispersal
Seeds are able to be dispersed much father distances without much negative impact to them. It also always them to limit competition with parent plant.
2. Dormancy
Seeds allow the embryo to post pone further growth and development until conditions are more favorable.
3. Nourishment
Seeds allow a type of nutrition that the young plant needs to survive after germination.
4. Endosperm
The endosperm serves as nourishment for the developing embryo.

Identify the Phylum, Genus, and Common Name of this plant. Identify 3 traits of it.

Phylum: Cycadophyta
Genus: not specified
Common Name: Sago Palm
1. Contain large cones
2. Palm like appearance and leaves.
3. Slow growing
False: This is true for Angiosperms
What is the purpose of plant roots?
The general purpose of plant roots is that they function to anchor themselves in the soil, absorb and transport nutrients throughout the plant, and store food resources.
What is the difference between Monocots and Eudicots?
Monocots: An angiosperm plant that is organized and emerges as a one seed leaf, parallel leaf veins, scattered vascular bundles, multiple of three flower parts and fibrous roots.
Eudicots: Eudicots emerges as a two seed leaves, branched leaf veins, vascular bundles arranged in a ring manner, flower parts of multiples of 4 or 5, and a taproot.
What is unique about pollen?
Pollen lightweight substance that is strictly a male function which allows sperm to be transported to egg producing structures. Unlike with seedless vascular plants, water is not required in the transport and is able to travel further distances.
Identify the Phylum, Genus, and Common Name of this plant. Identify 3 traits of it.

Phylum: Coniferophyta
Common Name: Giant Sequioa
1. Evergreen
2. Largest gymnosperm in the phyla
3. Male and female cones
4. Needle like leaves with a waxy coating.
True or false: Gymnosperms have pollinators while Angiosperms rely on the wind to disperse pollen.
False: Angiosperms have pollinators and Gymnosperms rely on the wind.
Define these roots:
Root Hairs
Fibrous Roots
Tap Roots
Buttress Roots
Root hairs: Tiny hair like roots that increase the plants absorption.
Fibrous Roots: Thin roots that go off in various directions and explant over large distances. Great at capturing water.
Tap roots: A thick central roots that grows vertically downward into deeper depths to gain more water resources.
Buttress Roots: Roots that grow above ground for more stability.
Identify and label the Vascular Bundles, Xylem and Phloem. Identify it's a monocot or eudicot.

Monocot Stem
Define a seed. What does it entail?
Seeds are packaged embryos that are encased in a protective layer with a food supply called an endosperm.
Identify the Phylum, Genus, and Common Name of this plant.
Phylum: Coniferophyta
Common Name: Coast Douglas Fir
Fill in the blank.

What are the traits of stems?
Stems have a shoot system that is made up of the following:
Stems, Leaves, Reproduction structures (Flowers)
Stems grow above ground to support the leaves and flowers of the plant.
Apical Meristems
Aerial Stems

Identify and label the Vascular Bundles, Xylem and Phloem. Identify it's a monocot or eudicot.

Eudicot Stem
Identify the the structure that the arrow is pointing too.
Pollen tube :)
Identify the image below. Label the air sacs.
AMAZING!
How does a fruit form?
It forms after the fertilization of an angiosperm egg and sperm. Develops from the ripened ovaries of flowers.
Name 2 types of modified leaves.
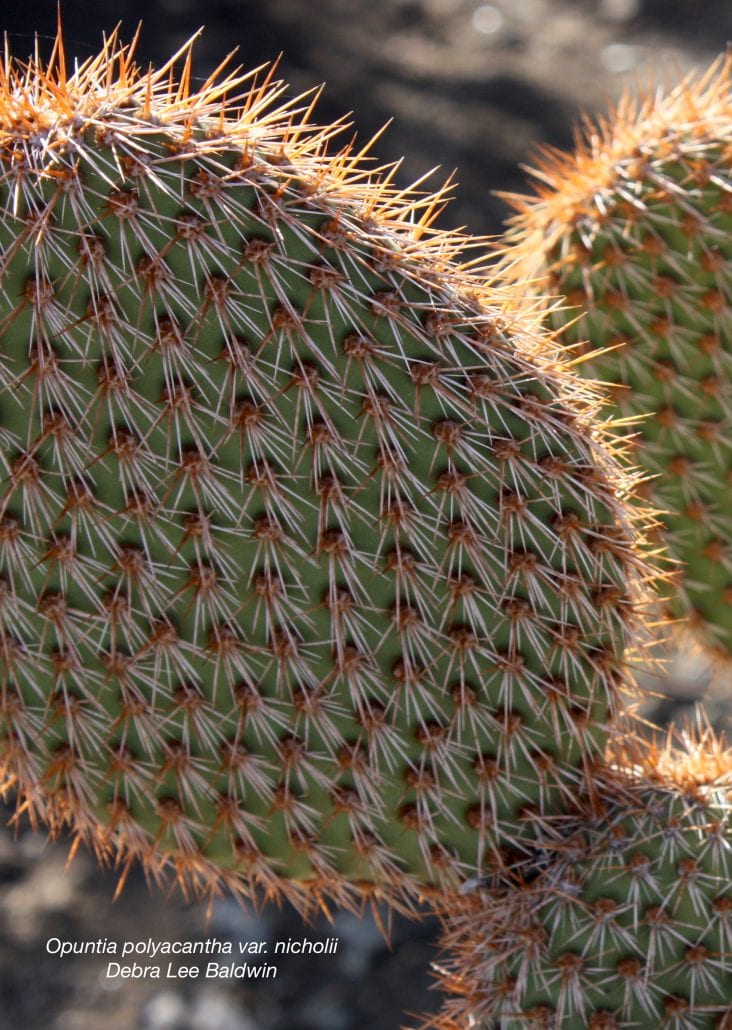

Tendrils: Leaves that occur in a twirling formation that can be seen on grapes and other fruit trees.
Spines
What are 3 ways that fruits/seeds are dispersed.
Wind/Air - Ex: Dandelion
Animal Attachment - Ex: Seeds that have hooks latch themselves to animals wandering around
Eaten by animals - Ex: Seeds are consumed by bird, bird poops out seeds, seeds are then dispersed.
Identify and label the Xylem and Phloem. Identify it's a monocot or eudicot root.

Monocot root:
Identify and label the Xylem and Phloem. Identify it's a monocot or eudicot root.
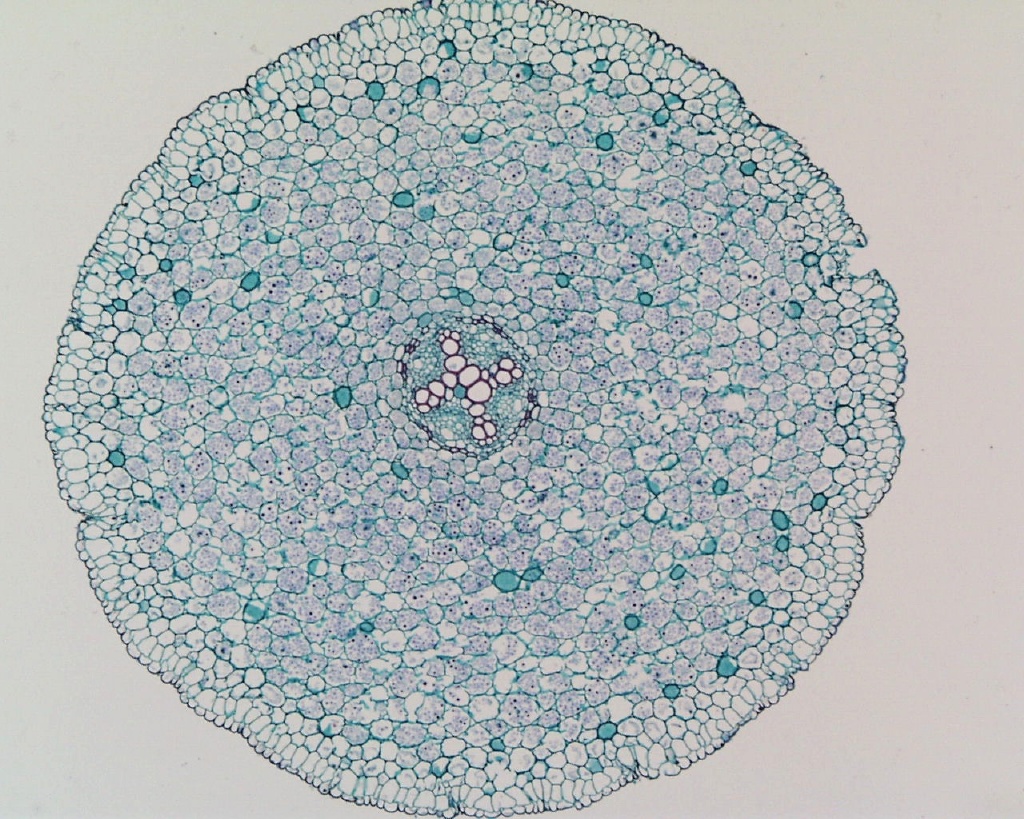
Eudicot root:
Identify and label the Xylem and Phloem. Identify it's a monocot or eudicot leaf.

Eudicot Leaf:
Identify and label the Xylem and Phloem. Identify it's a monocot or eudicot leaf.

Monocot Leaf:
Identify the Eudicot & Monocot leaf venation.
A = Monocot leaf
B = Eudicot leaf

