This type of mole is 69XXX or 69XXY
What is a Partial Mole?
This is a description of Palmer's Point
What is the area in the left upper quadrant 3 cm below the costal margin and in the midclavicular line?
This is the length of the average ureter.
What is 25-30 cm?
These are the most pathogenic HPV variants.
What are 16,18, 31, 33
16 accounts for most causes of cervical cancer
MLH 1, MSH 2, MSH 6, PMS 2
[Two Parter!]
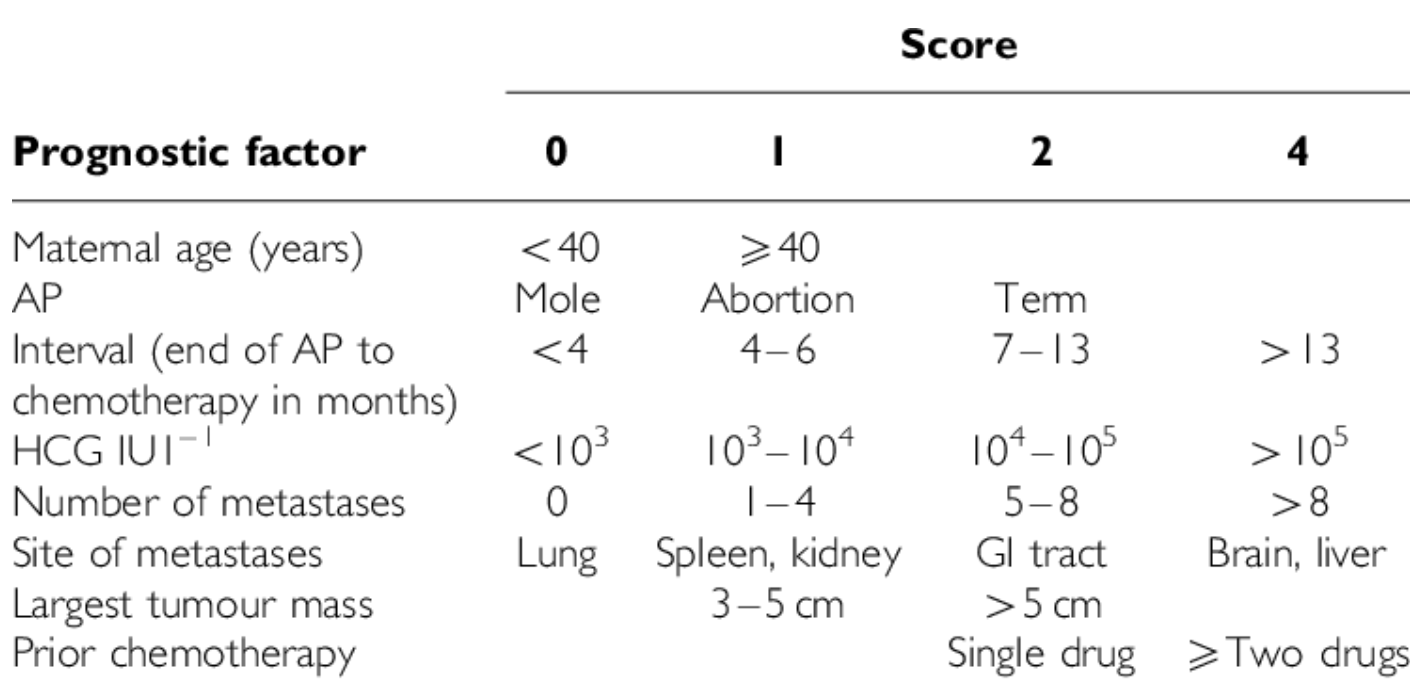
This is the standard treatment for a high risk WHO Score (name of the drugs!)
And, What is that WHO score?
- What is EMA-CO?
Etoposide, Methotrexate, Actinomycin D - Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine
- 7
This is a description of the Maylard incision.
What is when the incision is made 5-8 cm above the pubic symphysis. The site of skin incision is above and parallel to traditional Pfannenstiel incision. The rectus fascia and muscle are cut transversely and the incision is extended as far laterally as needed. The anterior rectus sheath is NOT separated from the muscle to facilitate easy closure at the end of the surgical procedure. The inferior epigastric vessels which span across more than half of the rectus muscle's width are identified and ligated
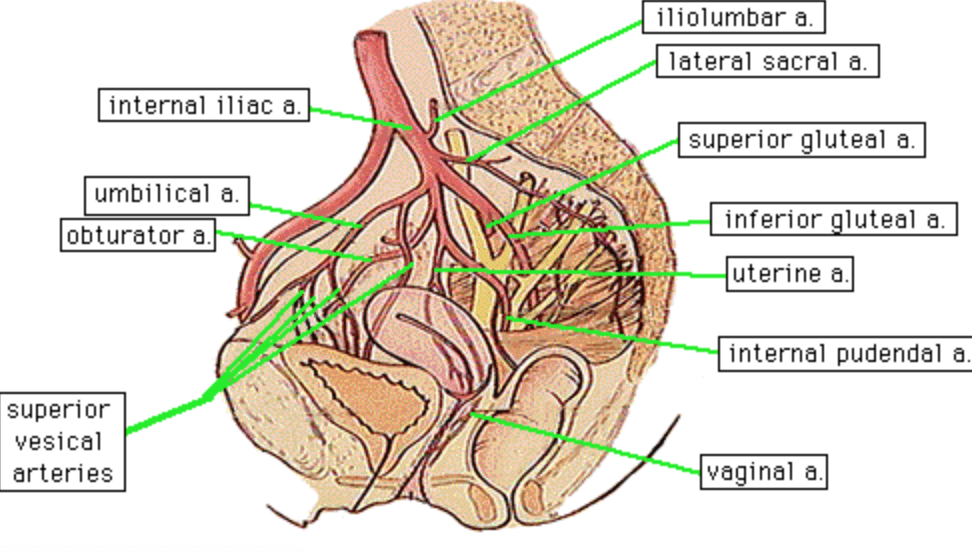
These are the 3 arteries that branch off of the posterior internal iliac artery
Iliolumbar
Lateral Sacral
Superior Gluteal
This is the age range indicated for the HPV vaccine
Bonus 100 pts: A recent study showed the most efficacy when the vaccine is given by this age.
9-46
What is 17

This is the lifetime risk of breast cancer in BRCA positive patients and the risk of ovarian cancer in BRCA 1 and BRCA 2 patients, respectively
The lifetime risk of breast cancer for a woman who carries a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation is approximately 65–74%.
The lifetime risk of ovarian cancer is 39 – 46% for a woman with a BRCA1 mutation and 12–20% for a woman with a BRCA2 mutation. BRCA mutations occur in 3–5% of all cases of breast cancer
These are the cells in the placenta/GTN that secrete hCG
What are trophoblasts (specifically syncytiotrophoblasts)?
[Two Parter!]
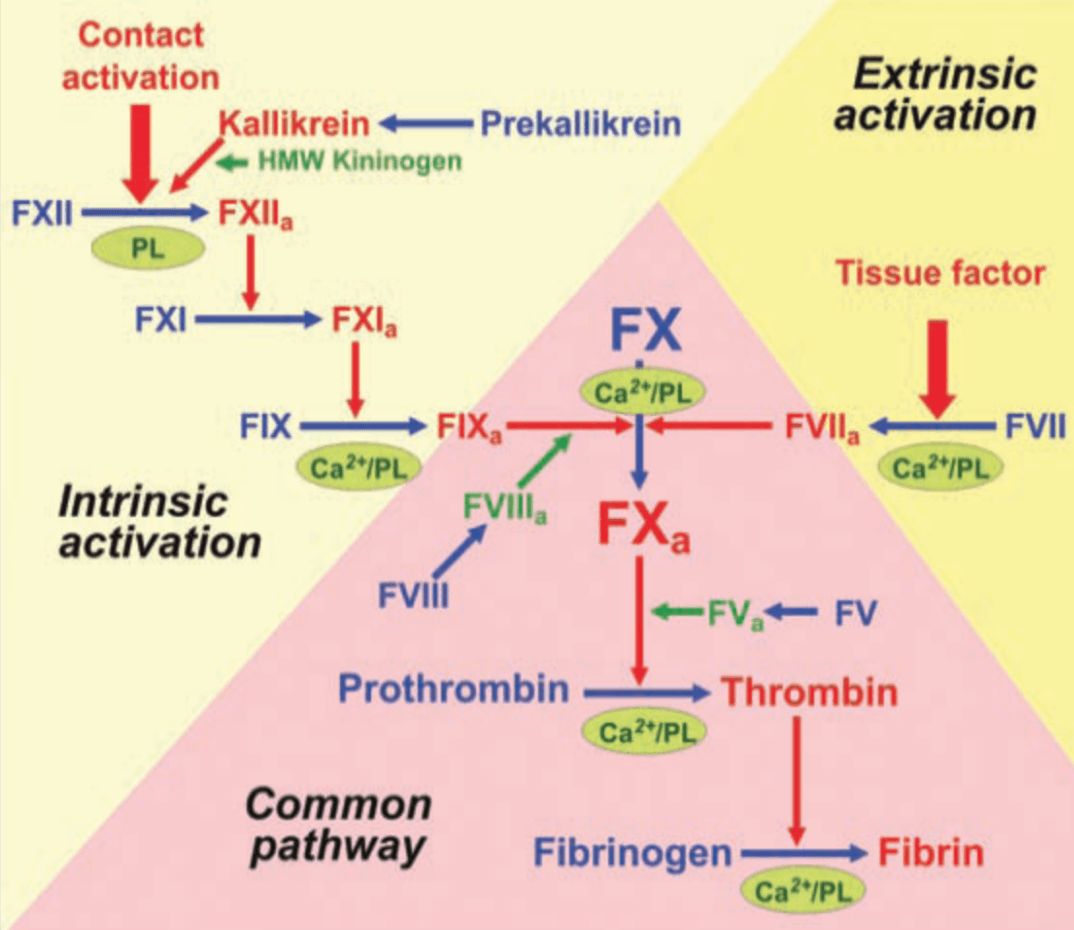
This coagulation test measures the intrinsic pathway
AND
Describe the intrinsic pathway
- aPTT (what we follow when titrating heparin)
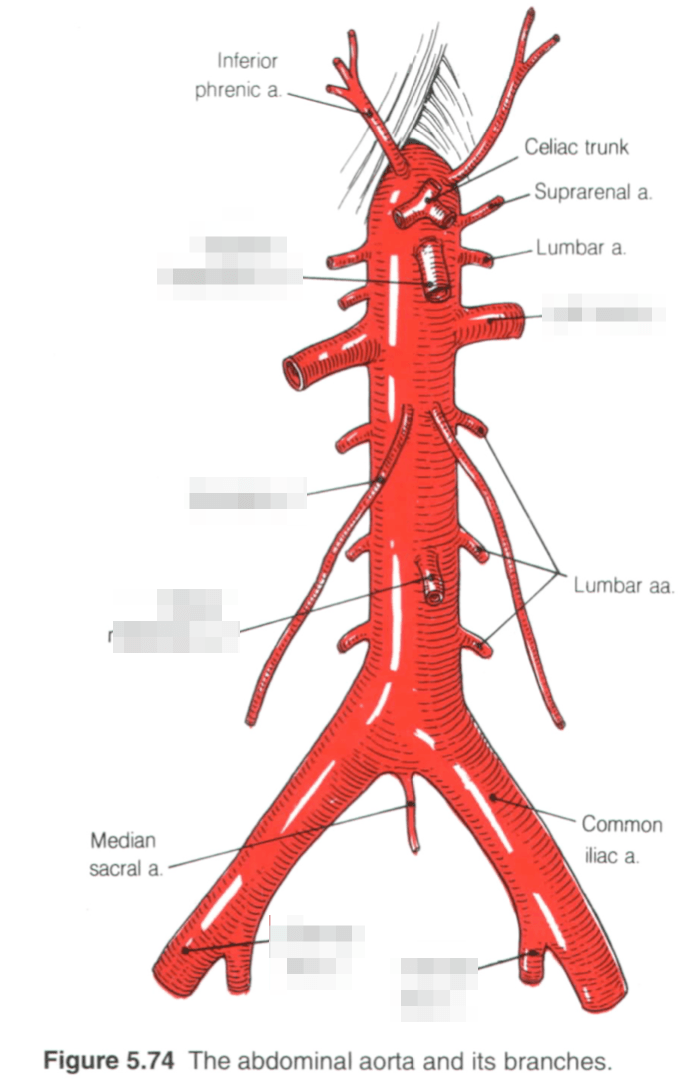
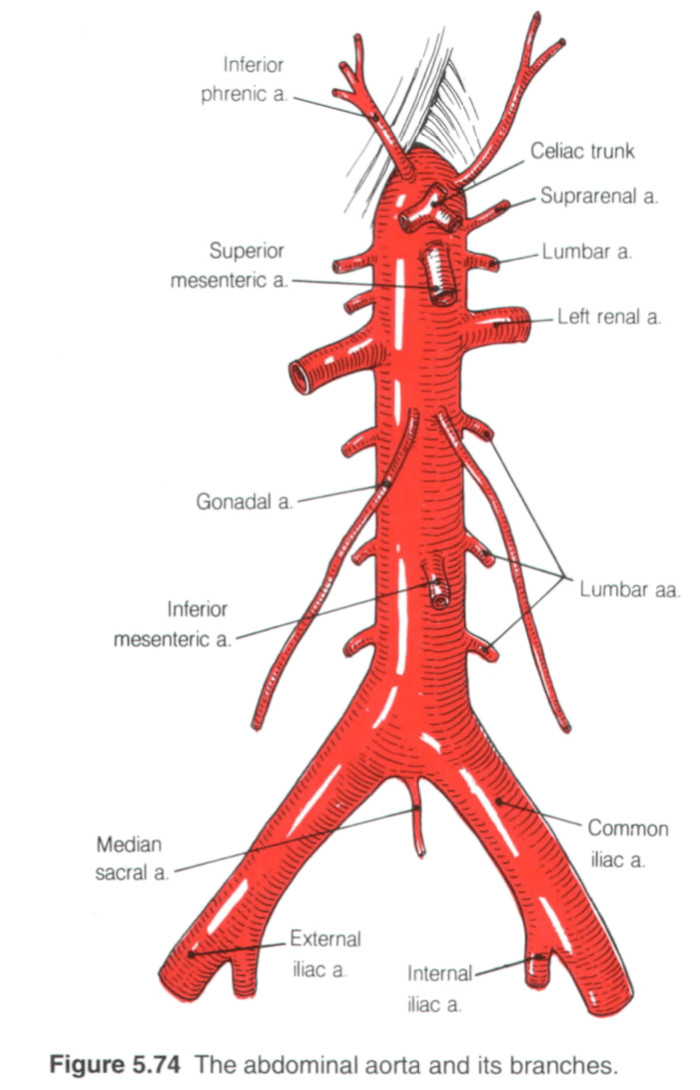
Name all the blurred arteries
This is the appropriate treatment for a 26 yo G0 with cervical cancer limited to the cervix 1 cm in size who desires to preserve fertility
Radical trachelectomy with pelvic LND
A recent meta analysis: Median 5-year recurrence-free and overall survival were 94.6% (range 88-97.3%) and 97.4% (range 95-99%), respectively. The posttrachelectomy pregnancy rate was 23.9%, with a live-birth rate of 75.1%.
This is the chromosome that BRCA 2 is located on; AND this is the inheritance pattern of the BRCA mutations.
What is chromosome 13 and Dominant?
These are the 8 categories factored into the WHO prognostic score for GTN
What are:
This is the pathology of Heparin induced thrombocytopenia (specifically: this is the complex formed that causes clotting)
What is caused by antibodies that bind to complexes of heparin and platelet factor 4 (PF4), activating the platelets and promoting a prothrombotic state.
FYI: HIT is more frequently encountered with unfractionated heparin (UFH) than with low molecular weight heparin (LMWH).
This generally describes the course of the ureter in the pelvis AND the 3 main areas of narrowing.
What goes over the pelvic brim, crosses over the external and internal iliac, runs in the medial leaf of the broad ligament, crosses under the uterine artery, inserts into the bladder?
- Ureteropelvic junction (renal pelvis)
- Over the pelvic brim
- Ureterovesical junction
A. Time from treatment to relapse
B. Histology of tumor
C. Grade of tumor
D. Size of tumor
E. B and C
F. C and D
What is time since treatment to relapse?
Patients who completed chemoradiotherapy 2 years or less from the date of recurrence have a significantly shorter survival (8 months versus 33 months).
This is the appropriate screening for a 28 yo patient with positive BRCA2 mutation
The combination of alternating MRI and digital mammography starting at age 25–30 years achieves the greatest reduction in breast cancer mortality in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers.
This is the WHO score for a 41 yo patient with an 11 month year old diagnosed with GTD and found to have:
HCG 110,000, one 4 cm brain met
What is 13?
These are the 8 avascular spaces in the pelvis.
(Name 7/8 for points)
Space of retzius
Vesicovaginal space
Paravesical space (x2)
Pararectal space (x2)
Rectovaginal space
Presacral space
The identification of these pelvic floor muscles (name 3/4):
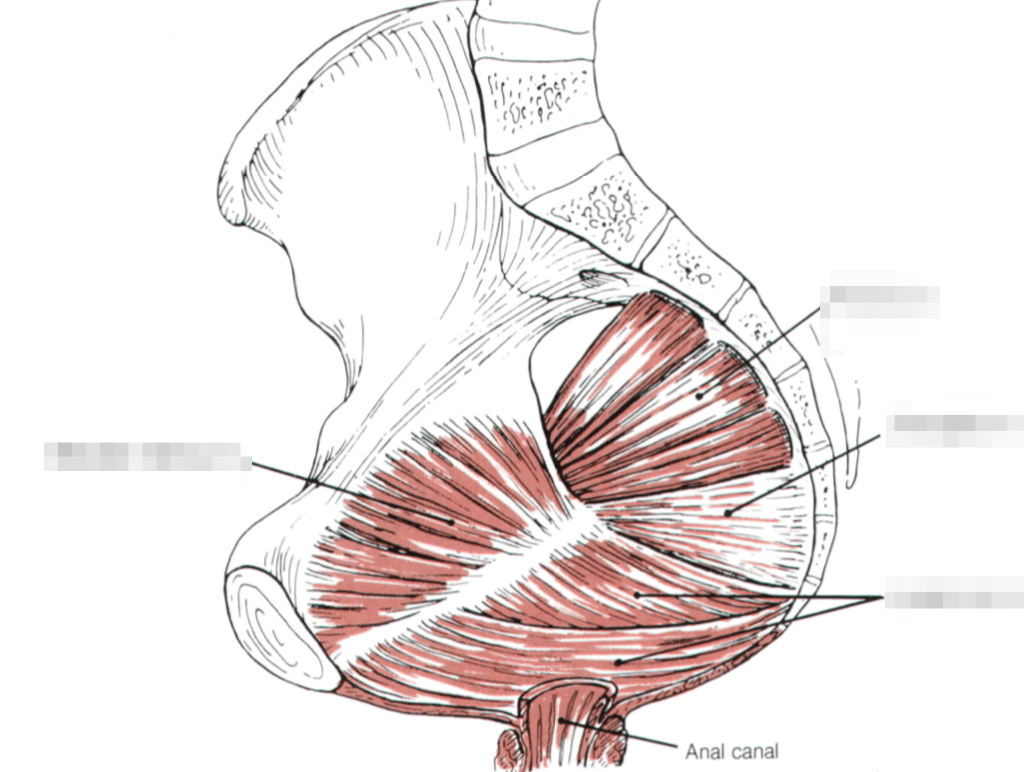
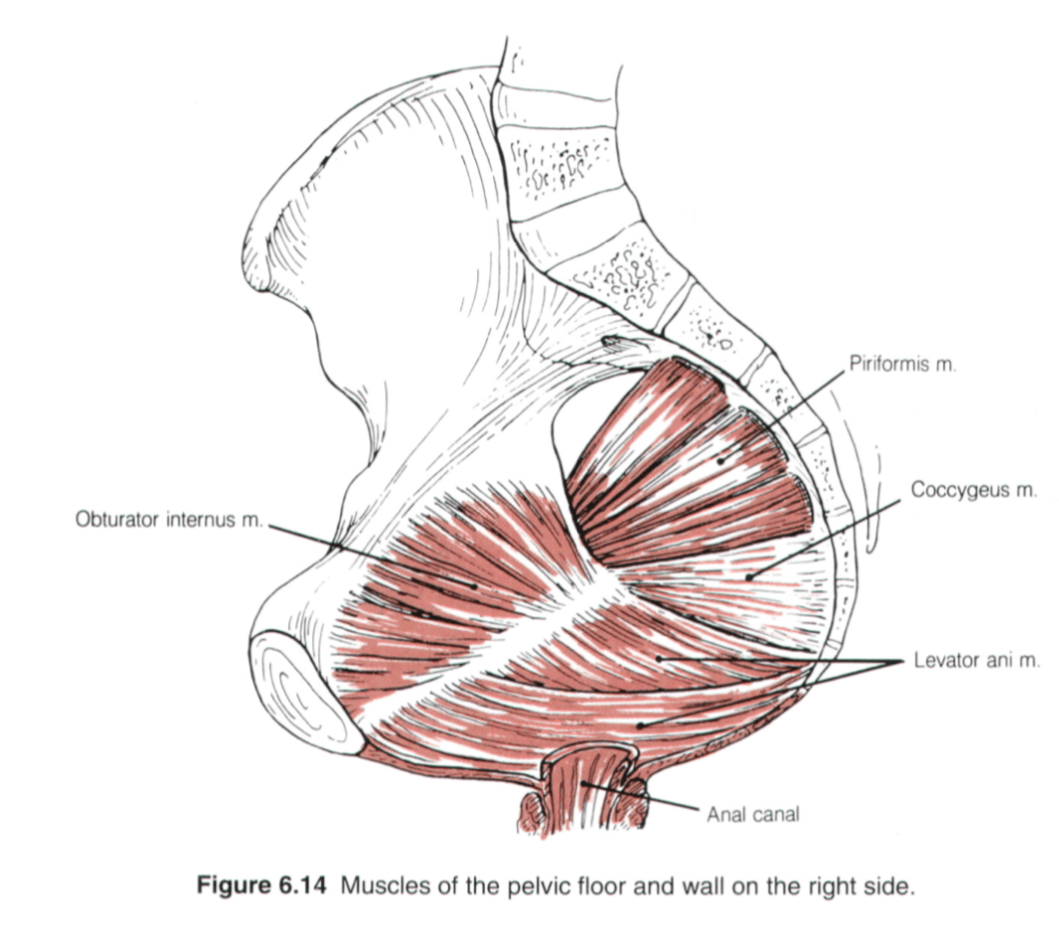
These are the indications for beginning pap smears before age 21
What is HIV/AIDS, hx of organ transplant, immunosuppressed
This is the name given to the idea that individuals with hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome inherit one defective allele in BRCA1 or BRCA2 from their father or mother, but they have a second, functional allele. If the second allele becomes nonfunctional as a result of a somatic mutation, cancer can develop.
What is “two-hit hypothesis”?