- protects eye from foreign objects and excess light
- skin covering folds that spread lubricating secretions over eye
What are eyelids
- contains circular and radial smooth muscle
- adjusts pupil size to regulate amount of light entering the eye
What is the iris
Filled with vitreous humour, maintains intraocular pressure and holds retina in place
What is the posterior cavity of eye
Irregular curvature of lens/cornea
What is astigmatism
- absorbs excess light to prevent scattering (cause visual confusion)
- contains many blood vessels
- supplies nutrients to posterior 1/3 surface of retina
Filled with watery, aqueous humour that provides oxygen and nutrients to lens and cornea
What is the anterior cavity of eye
Changes shape to focus images
What is the function of the lens of eyes
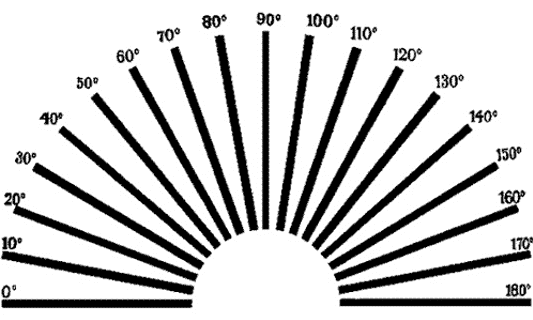
What is used to test for astigmatism
- transparent vascular mucous membrane
- lines inner surfaces of eyelids and covers anterior surface of sclera
What is conjunctiva
- ciliary muscles regulates shape of lens
- ciliary processes produces aqueous humour
What is the ciliary body
- results when eyeball is too long or lens is too curved
- corrected by decreasing refraction
What is myopia (near-sighted)
- ~120 million dim light receptors
- excited by low light intensity
- produces images in shades of grey
What are extrinsic eye muscles
Directs light rays into eye and helps focus them on the light-sensitive retina at the back of the eye, providing clear vision
What is the cornea
- ~6 million bright light receptors
- excited by high light intensity
- provide colour vision
What are cones
1. Retinal image formation
2. Conversion of image to nerve impulse
What are two main processes for vision
Lacrimal gland--> lacrimal ducts--> lacrimal fluids flows over eye--> lacrimal punctum--> lacrimal canaliculus--> lacrimal sac--> nasolacrimal duct--> nasal cavity
What are the pathway for tears
- correct by increasing refraction
What is hyperopia (far-sighted)
Condition occurs when drainage of aqueous humour is blocking causing the humour not to be reabsorbed so the fluid build up increases intraocular pressure
What is glaucoma
Light-->photoreceptor cells-->bipolar neurons-->ganglion neurons (axons exit eye as Optic Nerve)-->optic charisma (axons from medial half of each retina cross to the optic side)-->optic tract-->thalamus-->visual sensory area in occipital lobe of cerebrum
What is the visual nervous pathway