This is the pacemaker of the heart
SA node
Explain the difference between the left and right lung.
right lung has 3 lobes: super, middle, inferior
What is a virus? Explain 2 characteristics.
Non-living microscopic agents made up of an outer protein shell, called a capsid, and either DNA or RNA.
What condition of the eye has symptoms of inflammation of the clear area of the eye, increased blood flow that causes redness?
pink eye/conjunctivitis
What is reabsorption and why is it important?
returning useful substances (water, glucose, salts) back into the blood stream because these substances need to be used in the body. Allowing the urinary system to only get rid of excess substances and also toxic substances
What is the difference between arteries and veins. List 3 things.
Arteries:
away from heart
thicker and muscular
higher pressure
Veins:
toward the heart
thinner less muscular
lower pressure
During inhalation what is the diaphragm doing?
contracted (down) to pull in air
Explain 2 ways skin can help protect from and infection.
-skin is part of the 1st line of defense as a physical barrier
-commensal bacteria, fungi, and viruses living on the skin help protect aid in protection
What kind of parasite causes Loiasis?
worm
What are the 3 parts of a urinalysis test?
Microanalysis
Chemical Analysis
Macroanalysis
Where is the cephalic vein located?
upper arm
Trace oxygen that enters the oral/nasal cavity until it enters the capillaries.
Nasal/oral cavity > pharynx > Larynx > Trachea > left or right Bronchus > bronchiole > alveoli > diffusion into capillary where oxygen can then be transported through the body.
Explain 2 characteristics of acquired immunity.
Specific immune defense mechanisms.
This type of immunity is acquired over a lifetime.
Trace the path of urine through the urinary system
kidneys > Ureters > bladder > urethra
Trace filtrate through the nephron
glomerulus > Bowman's Capsule > PCT > Descending loop of Henle > Ascending loop of Henle > DCT > Collecting Duct
Trace electrical currents through the heart
SA node > AV node > bundle of His > Bundle branches > Purkinje Fibers
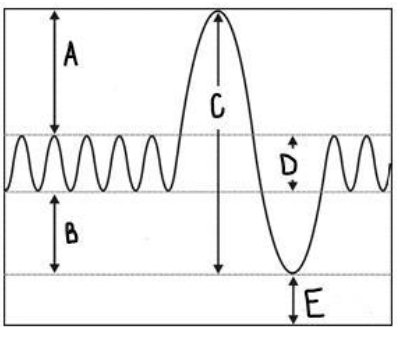
Explain what D is on the above graph.
Tidal Volume: the volume of air breathed in and out without conscious effort
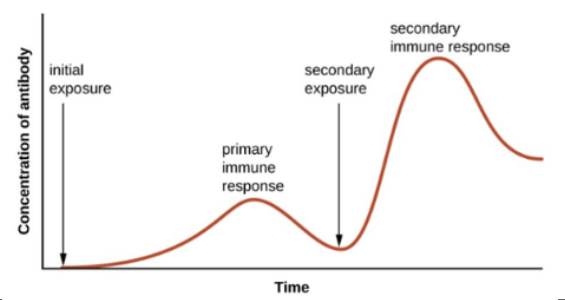
Draw a graph that shows the concentration of antibodies during initial exposure and secondary exposure.
Which part(s) of the kidney would you expect to find a nephron
medulla and cortex
What GFR indicates a need of a kidney transplant?
15 or less
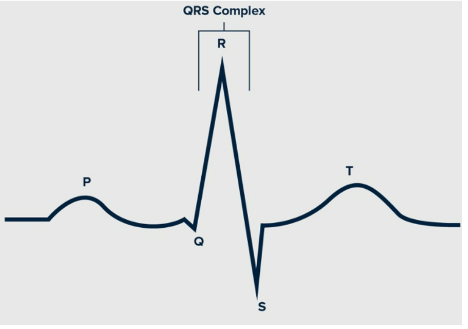
Explain what is happening in the heart at each wave.
P wave: SA node fires when atria is full of blood causing them to depolarize, leads to atrial contraction
QRS complex: firing of AV node, ventricular depolarization, leads to ventricular contraction
T wave: ventricular repolarization followed by ventricular relaxation
Explain what asthma is and how it impacts the respiratory system.
inflammation and constriction of bronchioles which makes it harder to breathe because airways are restricted.
Explain how viruses infect cells.
A summary of this:
-attach to surface of specific host cell
-virus DNA/RNA enters host cell
-removal (uncoating) of capsid, releasing viral genome
-host cell replicates viral DNA/RNA and undergoes protein synthesis
-virions (new viruses) are created
-virions mature within host cell
-virions are released from host cell
Explain where filtration happens and what is and isn't part of the filtrate created.
glomerulus into the bowman's capsule
salt, sugar, water, and urea waste is part of the filtrate
blood and protein should not be
A disease is autosomal recessive. A heterozygous woman and a homozygous dominant man have a child. What is the probability that their child will have the disease?
0