This feature of the skull is found at the connection between the parietal and occipital bones.
What is Lambda?
The spinal accessory nerve traverses this space in the posterior cranial fossa to exit and innervate the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
What is the Jugular Foramen?
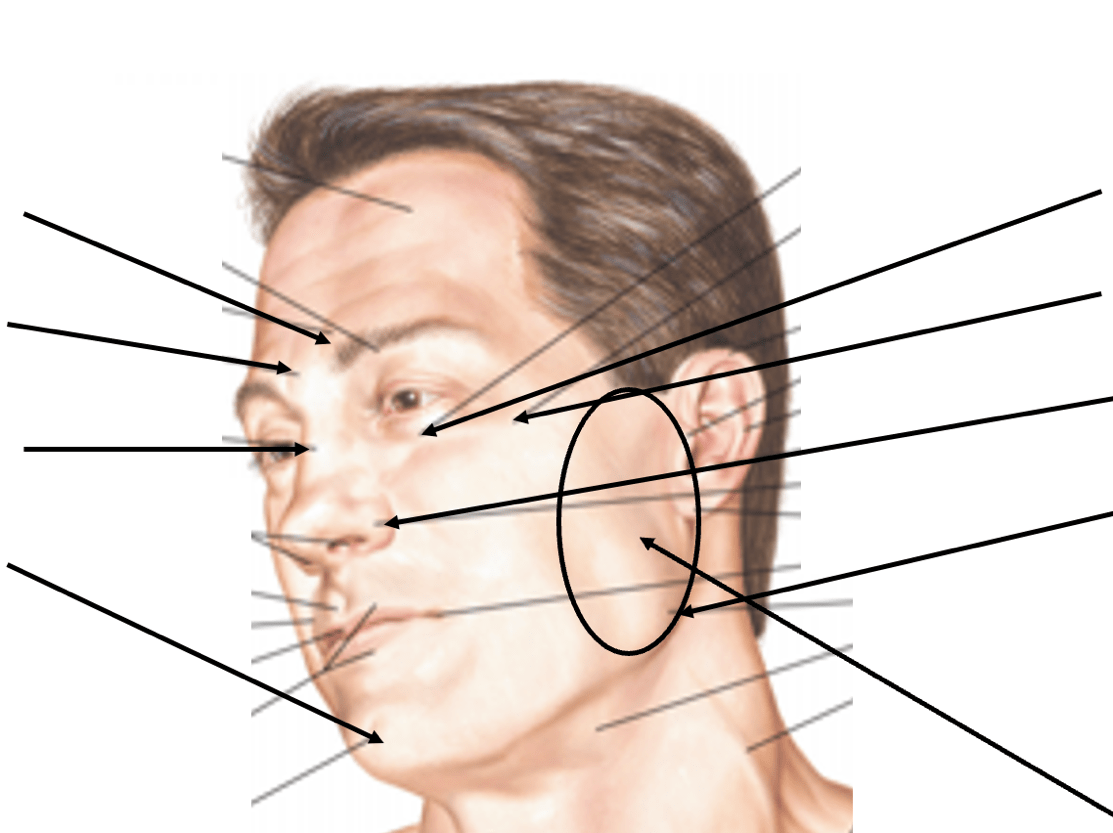
Identify the surface anatomy structure indicated by the black circle.
What is the parotid gland?
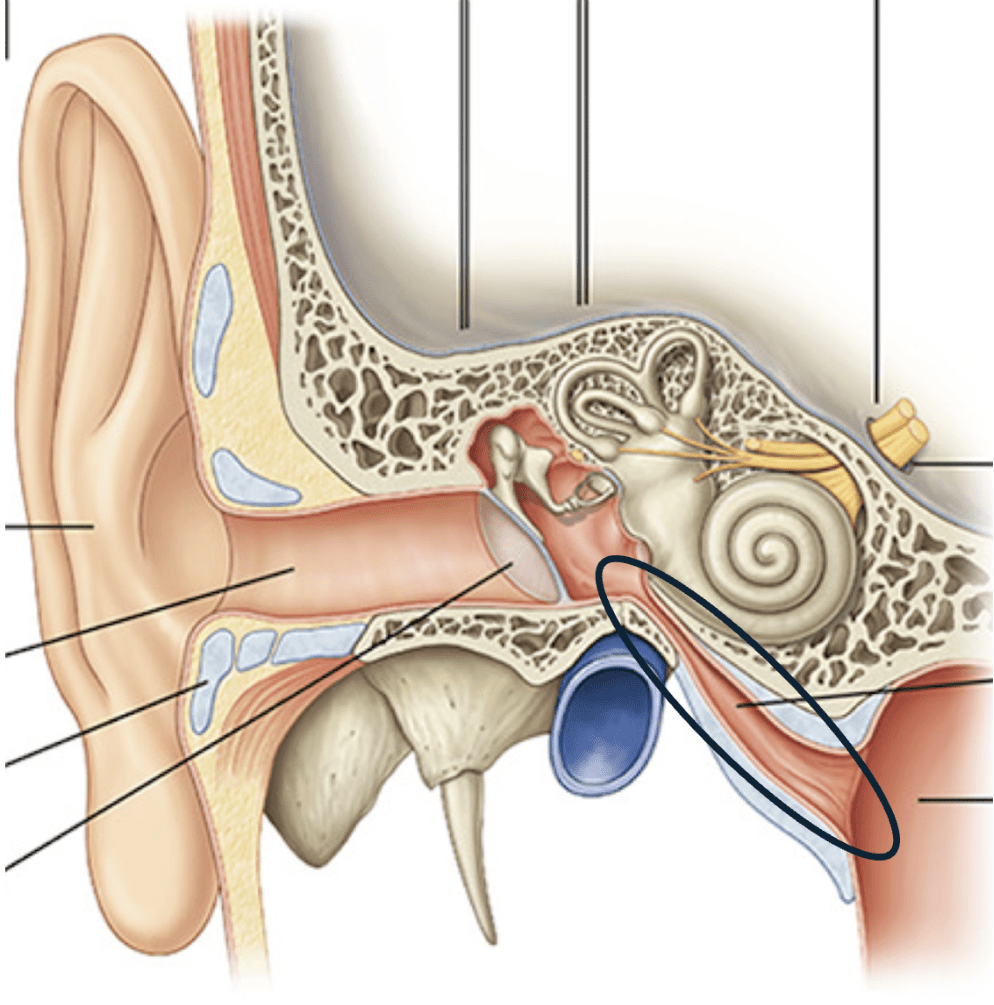
Identify the structure indicated by the black circle.
What is the pharyngotympanic tube?
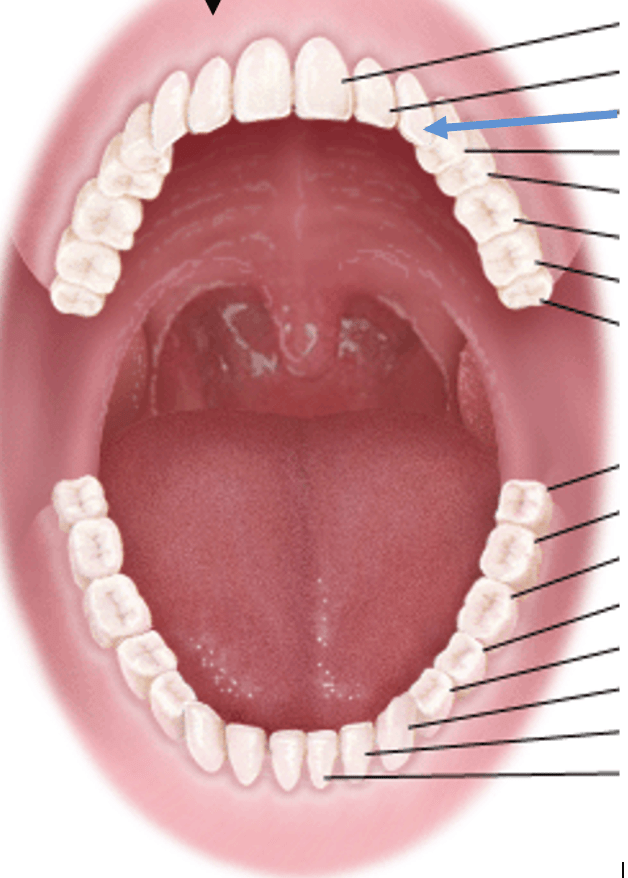
Identify the tooth indicated by the blue arrow.
What is the maxillary canine tooth, cuspid #11?
This key foramen of the cranial vault is a passageway that does not transmit a cranial nerve.
Identify the foramen and the structure it conveys.
What is foramen spinosum and the middle meningeal artery?
Identify the pharyngeal arch origin and the muscle/muscles that are supplied by CN IX, the glossopharyngeal nerve.
What is pharyngeal arch 3 and the stylopharyngeus muscle?
The muscles of facial expression are almost all paired. Many of them arise subcutaneously from fascia or bone and are innervated by the facial nerve.
Identify the function of the procerus muscle of the nasal group.
What is wrinkling the top of the nose?
The salpingopharyngeus muscle functions to elevate the pharynx, originating from the pharyngotympanic tube and inserting onto the pharyngeal wall.
Identify the muscle's innervation.
What is the vagus nerve?
The styloglossus muscle originates from the styloid process of the temporal bone and inserts on the root of the tongue.
Identify its function.
What is elevation and retraction of the tongue?
Three cranial nerves are seen emerging from the anterior side of the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction.
Identify the primary function of the nerve emerging most medially at this location.
What is abduction of the eyes?
The Facial nerve (CN VII) features both sensory and motor axons. Identify its special sensory functional component and primary function relayed by the chorda tympani nerve.
What is SVA and taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
The muscles of mastication, innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, all function in causing movement at the temporomandibular joint.
The temporalis muscle, one of the four, originates from the temporal fossa and inserts onto which structure?
What is the coronoid process of the mandible?
The posterior cricoarytenoid muscle shares common innervation with all but one of the intrinsic laryngeal muscles, yet it has a unique function.
Identify the function of this muscle.
What is abduction and external rotation of the arytenoid cartilages?
The facial nerve (CNVII) provides the secretomotor parasympathetic innervation to all of the salivary glands except for one.
Identify the one exception: the gland and the nerve that supplies it.
What is the parotid gland and the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)?
The dural septa are reflections of the meninges that divide the cranial cavity into spaces that communicate with each other.
This septal structure functions in providing protection for the gland that sits in the depression of the sella turcica. Identify the gland and the group of sinuses that surrounds it.
What is the pituitary gland and the cavernous sinuses?
The functional fiber type of the associated cranial nerve synapses on the otic ganglion.
Identify the fiber type and nerve, be specific.
What are preganglionic parasympathetic fibers and CN IX, glossopharyngeal nerve?
The triangles of the neck are quite complex. The anterior triangle of the neck is bordered anteriorly by the midline of the neck and superiorly by the mandible.
Identify its posterior border and a visceral structure found in this area.
What is the SCM and the thyroid gland, esophagus, trachea, or thyroid cartilage?
The frontal sinus and anterior ethmoid air cells have a unique drainage pathway.
Identify their drainage termination point and the structure/route they travel through to reach this destination.
What is the Semilunar Hiatus in the middle nasal meatus and the frontonasal duct?
The maxillary artery, a branch of the external carotid artery, supplies the pterygoid muscles of the infratemporal fossa.
Identify the specific function and innervation of the Lateral Pterygoid muscle.
What is depression, protrusion, and lateral displacement (side-to-side movement) of the mandible and mandibular division of the Trigeminal nerve?
A 68-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset weakness in his right leg and foot. He also reports difficulty initiating movement and some behavioral changes over the past few hours. Neurological examination reveals decreased strength in the right lower extremity, intact sensation, and preserved upper extremity strength. MRI reveals an ischemic infarct in the medial aspect of the left frontal and parietal lobes.
Which of the following arteries is most likely occluded in this patient?
What is the Anterior Cerebral Artery (ACA)?
A 45-year-old female presents with a constricted pupil (miosis), drooping eyelid (ptosis), lack of sweating (anhidrosis) on the right side of her face, and a flushed complexion (vasodilation). She has a history of chest pain, and imaging shows a mass in the apex of her lung.
What is the most likely diagnosis, and what is one possible peripheral injury that could cause this syndrome?
What is Horner syndrome caused by a Pancoast tumor?
A 65-year-old male presents with a swollen, painful jaw and difficulty chewing on the left side. He has a history of smoking and hypertension. On physical examination, the physician detects a murmur over the left carotid artery, and Doppler ultrasound confirms reduced blood flow in the left external carotid artery.
Identify the branch of the external carotid artery that is most likely receiving reduced blood flow, contributing to his symptoms.
What is the maxillary artery?
A 45-year-old female presents with difficulty moving her right eye. Upon examination, the patient is asked to follow a target in different directions. She is able to move the right eye upward, but when asked to look downward and medially, the right eye does not perform the movements normally.
Identify the muscle likely affected, and which two movements are typical of this muscle.
What is the superior oblique muscle and downwards and outwards?
A 45-year-old male presents with persistent facial pain and difficulty chewing. Upon physical examination, a tender mass is noted near the upper jaw, and imaging reveals a tumor located near the infratemporal fossa. The tumor is compressing a major artery that supplies both the infratemporal fossa and the pterygopalatine fossa.
Identify the artery and one of its terminal branches.
What is the maxillary artery and sphenopalatine a., post. sup. alveolar a., greater palatine a., infraorbital a., pharyngeal a., or the artery of pterygoid canal?