From superficial to deep, what are the three structures contained in the parotid gland?
Facial nerve
Retromandibular vein
External carotid artery
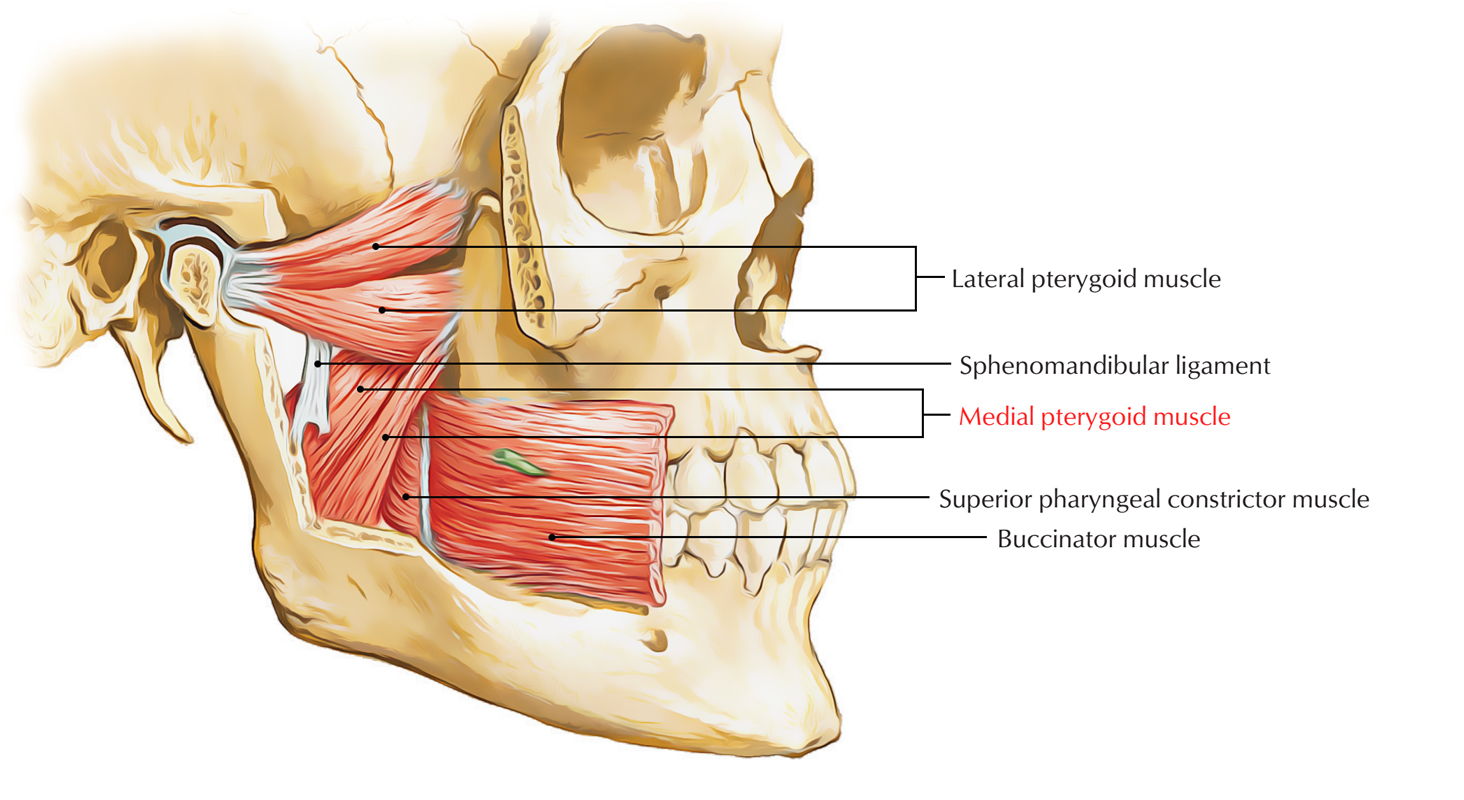
What muscle is a quadrangular shaped, two headed muscle arising from the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate and the tuberosity of the maxilla, inserting on the medial surface of the angle and ramus of the mandible?
Medial pterygoid muscle
What is the somatic gateway to and from the cortex? What is the visceral gateway to and from the cortex?
Somatic: Thalamus
Visceral: Hypothalamus
What branch of the cerebral part of the internal carotid artery is an anastomois with the vertebrobasilar system?
Posterior communicating artery
Which cerebellar nuclei is positioned most medially and is functionally associated with the vermis?
Fastigial nucleus

What is the efferent part of the cerebral cortex? What is the afferent part?
Efferent: layer V
Afferent: layer IV
The pterygoid venous plexus is connected to the cavernous sinus via what?
Emissary veins
Aqueous humor is secreted by epithelial cells of the ciliary body. What chamber does it flow to first? Next?
Posterior, then through the iris to anterior. (Then it drains to the scleral venous sinus via canal of Schlemm)
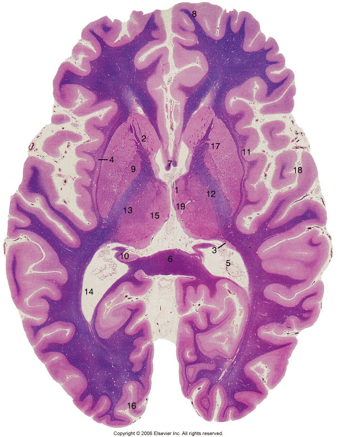
What is 17?
17: Putamen of the basal nuclei
What are the caudolateral area and the rostromedial area of the hypothalamus associated with?
Caudolateral: sympathetic
Rostromedial: parasympathetic
What is the medial border of the parotid bed?
Styloid process and the three muscles that attach to it

What are the three powerful elevators of the mandible?
Temporalis, medial pterygoid, masseter

The thalamus is partitioned in anterior, medial, lateral, and intralaminar cell groups by what structure?
The internal medullary lamina
What artery supplies the caudolateral cerebellum and the inner ear?
Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
What are the three types of neurons in the granule layer of the cerebellar cortex?
Granular cell forming parallel fibers - excitatory
Golgi cells - inhibitory interneurons
Unipolar brush cells: excitatory
What fissure separates the left and right hemisphere?
Longitudinal fissure
Where is the pterygopalatine gangion located in relation to the maxillary nerve?
It is just inferior to it in the pterygopalatine fossa
What is the small elevation in the lacrimal lake called?
Lacrimal caruncle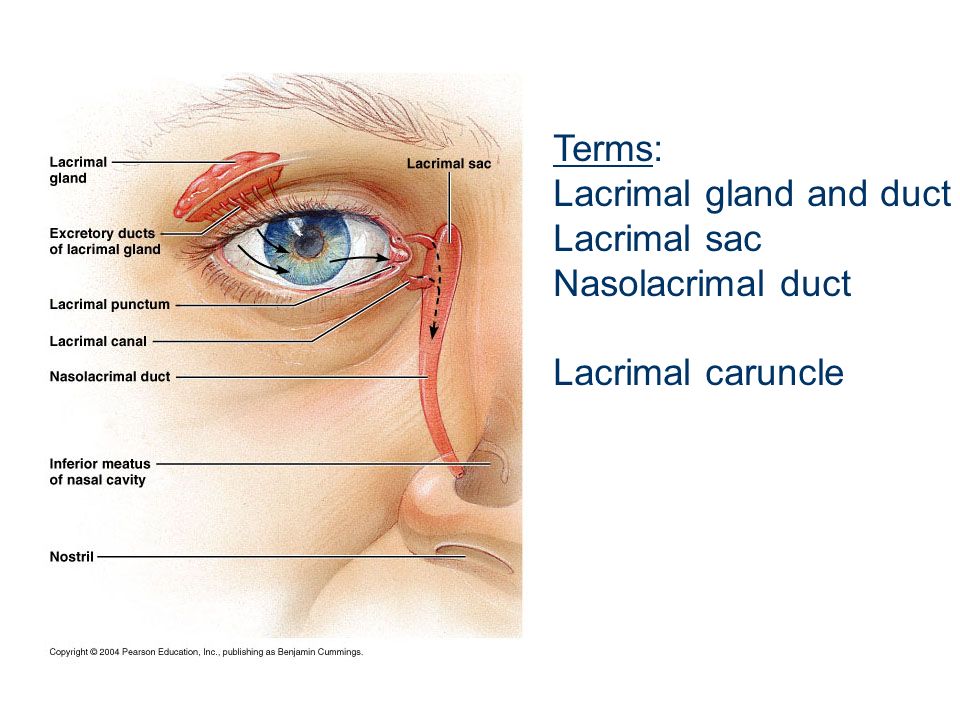
 What is 15?
What is 15?
15:Medial thalamic nuclei
What does the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus control?
Circadian rhythms
The lateral ligament of the TMJ prevents what type of dislocation?
Posterior
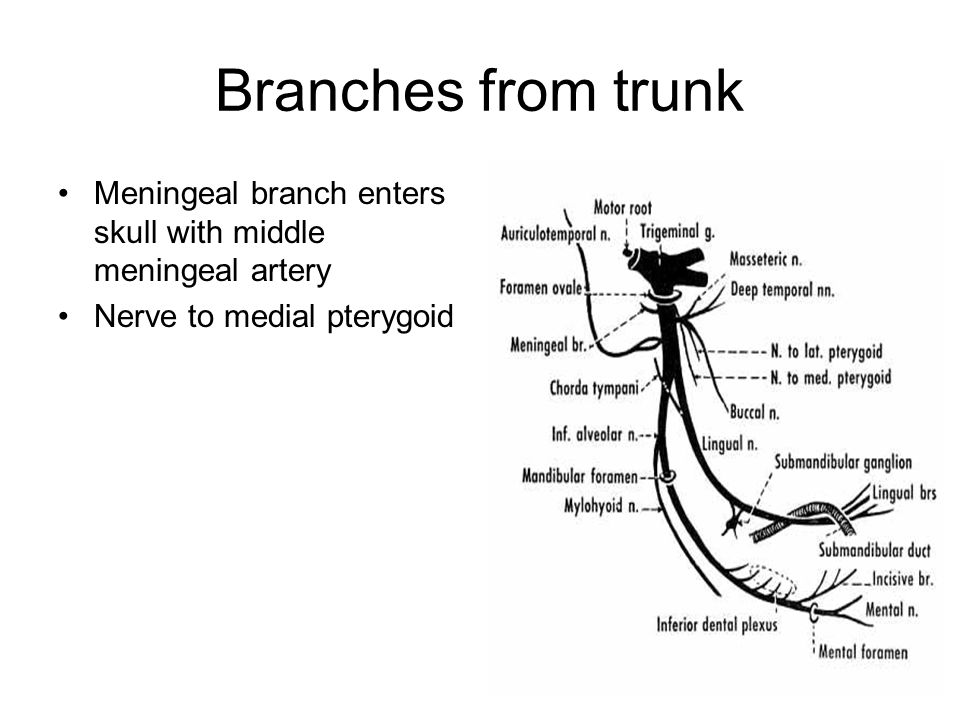
What branch of the mandibular nerve (V3) leaves the trunk, and then re-enters the cranial cavity via foramen spinosum in company with the middle meningeal artery?
Meningeal branch
Which nuclei in the thalamus modulate other nuclei but do not project to the cortex themselves?
Reticular nuclei
What supplies the rostral (superior) cerebellum?
Superior cerebellar artery
What are the types of neurons found within the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex?
Basket cells - inhibitory
Stellate cells - inhibitory
What structure would you find deep to the Sylvian fissure/lateral sulcus?
Insular lobe
Where are the postganglionic, parasympathetic neuron cell bodies located for the lacrimal gland?
In the pterygopalatine ganglion
What cells modify the signals from photoreceptors onto bipolar cells?
Horizontal cells
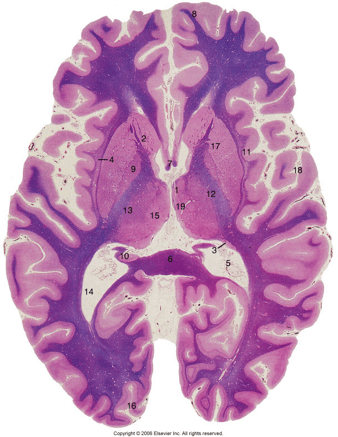 What is 13?
What is 13?
13: Lateral Thalamic Nuclei
The largest single input to the hypothalmus is form what?
The fornix
The TMJ is innervated by what nerve?
V3 - auriculotemporal and masseteric branches
What carries the taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue? What carries the sensation?
Taste for anterior 2/3 of tongue is via chorda tympani, a branch of VII. It joins the lingual nerve, which carries sensation from anterior 2/3 of tongue.
What does the lateral geniculate nucleus project to? What does the medial geniculate nucleus project to?
Lateral geniculate nucleus projects to the visual cortex. Medial geniculate nucleus projects to the auditory nucleus.
What supplies the ventral/midline medulla?
Anterior spinal artery
What are the two main types of afferent fibers in the cerebellum?
Mossy fibers - excitatory - synapse with golgi cells and granular cells in the cerebellar glomerulus
Climbing fibers - excitatory - course from the olive to the cerebellar cortex, ascend Purkinje dendrites and synapse. The inferior olivary nuclei receive input from the cerebral cortex and sends it to all parts of the cerebellum
What gyrus, rostral to the parahippocampal gyrus, is very sensitive to hemorrhage in the brain?
Uncal gyrus - this is called uncal herniation
Which of the following is NOT a branch off of the third part of the maxillary artery?
Pharyngeal branch, artery of the pterygoid canal, descending palatine, supraorbital, infraorbital, sphenopalatine
Supraorbital - it is a branch off of the superficial temporal artery
The fovea is comprised of what type of photoreceptor?
Cones
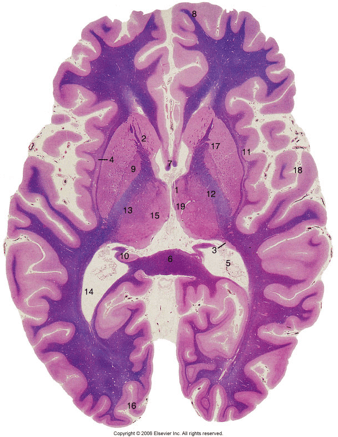 What is 10?
What is 10?
Hippocampus
Pituitary tumors that press on the optic chiasm do what?
Cause tunnel vision
The maxillary artery and inferior alveolar nerves can be found between the maxilla and what ligament?
The sphenomandibular ligament, which will limit inferior movement
What ganglion can be found immediately inferior to the foramen ovale?
Otic ganglion - it will contain the cell bodies for postganglionic parasympathetics to the parotid gland via the auriculotemporal nerve
What part of the thalamus collects information form the contralateral body and projects it to the primary sensory cortex?
The VPL (Ventral posterolateral) nucleus
What supplies the lateral medulla?
Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
Damage to the vestibulocerebellum would produce what symptoms?
Difficulty with posture, balance, and gait on SAME SIDE as lesion
Parts of cerebral cortex within a hemisphere
left and right hemispheres: Commissural tracts
Parts of cerebral cortex within a hemisphere: Association tracts
What is the roof of the pterygopalatine fossa?
Greater wing of the sphenoid bone

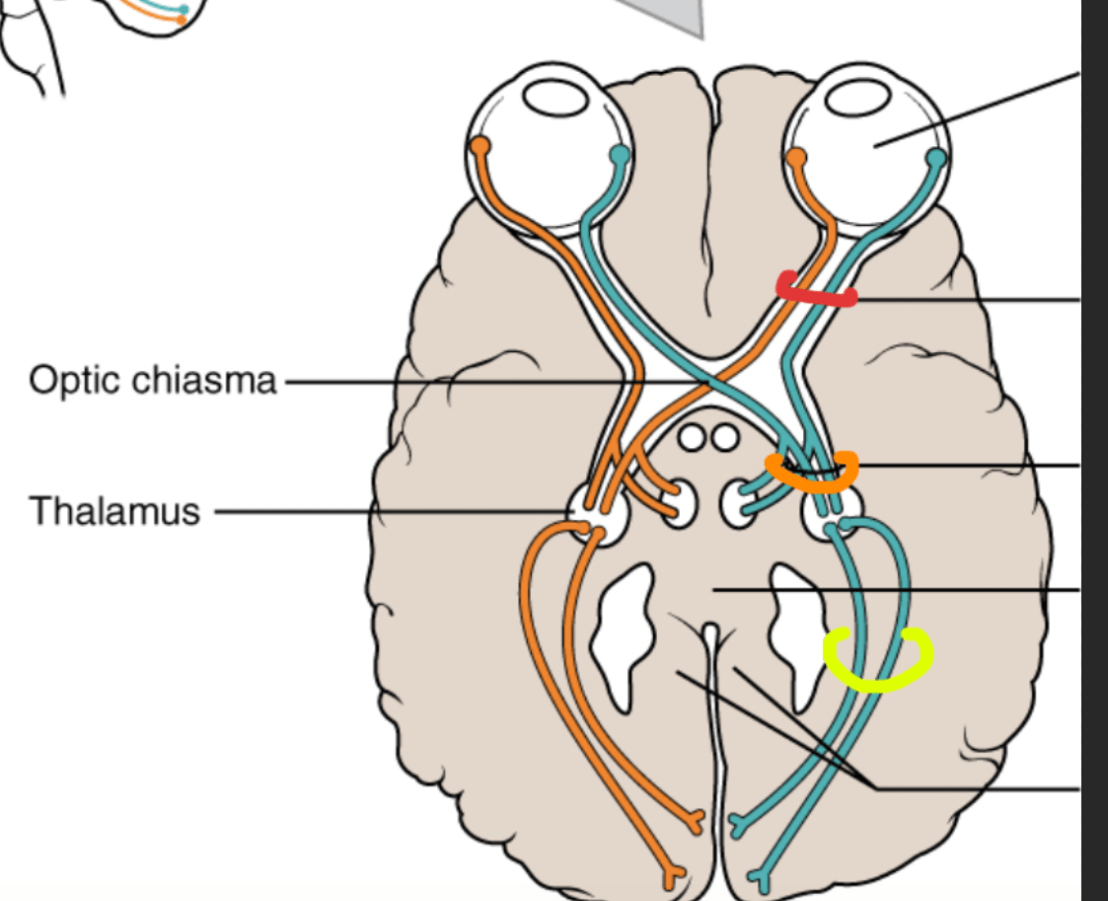 Label: Red, orange, and yellow
Label: Red, orange, and yellow
Red: Optic nerve (to chiasm)
Orange: Optic tract (chiasm to LGN)
Yellow: Optic radiations (LGN to primary visual cortex)
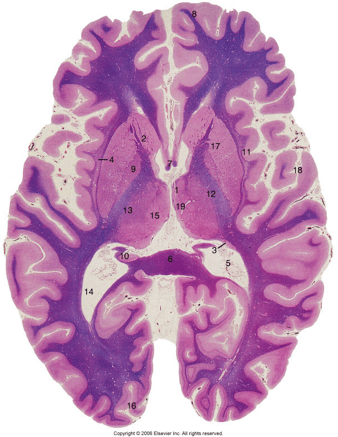 What is 7?
What is 7?
7: Fornix
Damage to the subthalamus causes what?
Hemiballismus (uncontrollable flailing of the upper limb)
The sympathetic input to the parotid gland come from preganglionic bodies located in the _________, which synapse and give rise to postganglionic bodies in the ___________ _______ ________, which follow the __________ to get to the parotid gland.
T1-T2 lateral horns
superior cervical ganglion
external carotid plexus/external carotid artery
What meshwork of veins surrounds the lateral pterygoid muscle?
Pterygoid plexus
The genu of the internal capsule contains what tract? What cranial nerves?
What is the most common site of berry aneurysm?
Anterior cerebral artery/anterior communicating artery
What cells contain the only efferent fibers from the cerebellar cortex? What is their effect?
Purkinje, they are inhibitory
Thalamic axons from the VPL/VPM project onto the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus. Where are the feet represented? What about the face?
The feet are dorsomedial, the face is ventrolateral
After the greater petrosal nerve leaves the middle cranial fossa, and the deep petrosal nerve (post ganglionic sympathetic) joins it, what does it become?
The nerve to the pterygoid canal
It then goes to the pterygopalatine ganglion
X/P type ganglion cells are concentrated where? What about Y/M?
X/P: Macula and fovea/central parts of retina
Y/M: Peripheral parts of retina
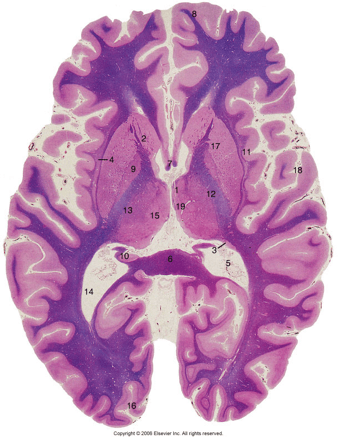 What is 1?
What is 1?
1: Anterior Thalamic Nuclei
What three reflexes are controlled by the hypothalmus?
Baroreceptor, temperature regulation, water balance