This scale is used to evaluate children after a head injury.
PECARN


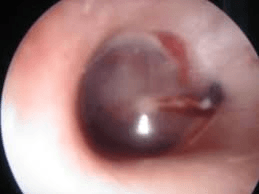
22 yo female presents to the clinic after falling down stairs at home. What is this finding concerning for?
Hemotympanum, when trauma is suspected, may indicate basilar skull fracture.

A 22-year-old female accompanied by her friends presents to the clinic after reporting that she was watching a parade when she tripped on a curb causing her to hit her head on the concrete. Denies any loss of consciousness. Denies visual changes. No nausea or vomiting. States "I feel fine." Additionally states "I only had a few beers" Her friends are concerned and want her to be evaluated in the clinic. Denies any additional injury. What is the next step?
Due to intoxication, patient will need to be transported to the emergency department for further evaluation.
True or False. According to our textbook when evaluating a patient with altered mental status a complete physical exam should include particular focus on Patient's general appearance, VS, hydration status, signs of physical trauma, LOC, and neurological symptoms.
True
Advise to get adequate sleep on a nightly basis. brain rest may be restrictive as any of these, not going to work/school, not reading, using a computer, or doing homework; and not watching tv or playing video games.
All decision instruments have been formulated and validated for effectiveness during the acute phase, typically when patients present within what time frame from the initial injury?
24 hours of injury. There is no evidence basis for guidance when patients present beyond the initial 24-hour period. Prompt imaging for patients with worsening symptoms of any sort is prudent.
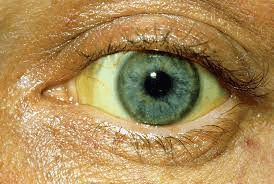 58 yo male presents with AMS to the clinic accompanied by his wife. You see this on exam. What would you be concerned about in this patient? What history would you want to know?
58 yo male presents with AMS to the clinic accompanied by his wife. You see this on exam. What would you be concerned about in this patient? What history would you want to know?
Icterus
Name at least 5 concussive symptoms.
Concussive symptoms would include headache, nausea, dizziness, visual disturbance, loss of consciousness, mood or behavior changes, concentration or other cognitive difficulties, drowsiness/fatigue, vomiting, vertigo, sleep disturbances, coordination difficulty
87-year-old female presents to the clinic accompanied by her granddaughter with concerns " my grandma is not acting right". Vital signs reveal temperature 99.2, heart rate 92, respiratory rate 16, blood pressure 164/92, pulse ox 97% on room air. Urine analysis performed with positive nitrates. You treat this patient for urinary infection, with plan to discharge home and follow up 1-2 days with primary care. Based on the information provided above what needs to be documented in your MDM.
Any abnormal vital signs need to be addressed. Specifically patient's blood pressure., And if patient is having any additional symptoms associated with abnormal blood pressure such as chest pain, headache, visual changes etc. Inquire if patient has history of blood pressure and if taking any medications. Did patient take medication today. Additional differentials, and red flags with return precautions
A patient with ongoing symptoms after a head injury should be told to follow up with their primary care provider or urgent care clinician within what time frame?
1 or 2 days
What is the "normal" score according to the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)
15

According to the textbook, When evaluating a patient presenting with a heat urgency, {blank} can be used to evaluate volume status and may be helpful in differentiating between minor illness and major illness.
Orthostatic findings

Obtaining a medical history for patients with a possible TBI traditionally includes establishment of what?
mechanism of injury, determining if any LOC or associated seizures, headache, nausea, vomiting, other injuries.
Current understanding is to have elements of the medical history that are most important for clinical decision making in adults including the following: Age 65 years or older, altered level of alertness or behavior, persistent vomiting (2 or more episodes), coagulopathy or therapeutic anticoagulation, use of antiplatelet therapy, including aspirin, neurological deficit, amnesia regarding the time period (30 minutes or more) before impact (known as retrograde amnesia), dangerous mechanism of injury(pedestrian hit by vehicle, ejection from motor vehicle, fall from elevation of 3 foot or more or 5 stairs or more)
Patients with head injury should have a detailed examination of this body part, what is it?
Cervical spine- with documentation of lack of tenderness, full range of motion, and lack of posterior pain.
What simple diagnostic tests can be performed in the clinics, Prior to transferring to the emergency department, for patients presenting with altered mental status?
Rapid glucose, chest x-ray, urine analysis, ect
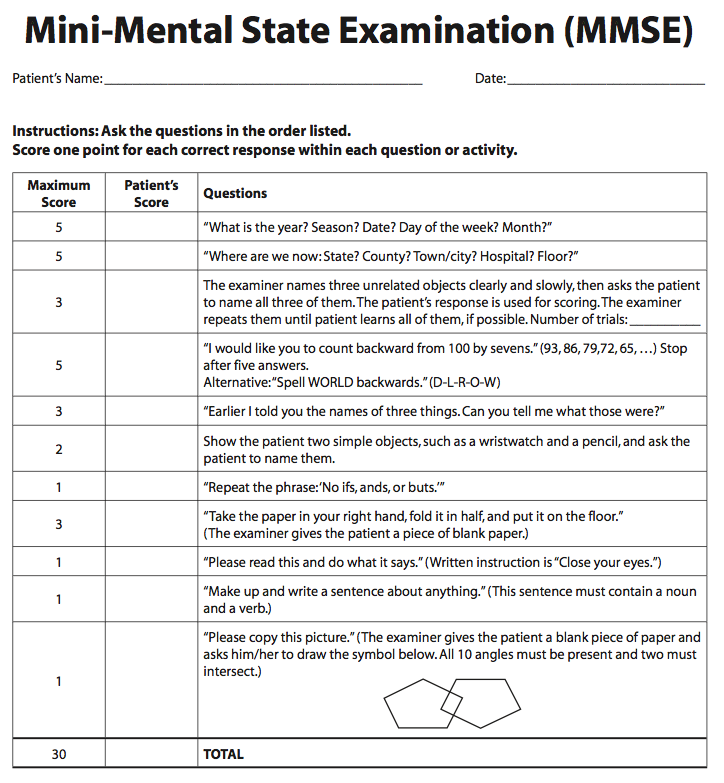
This scale may be helpful to formally document the severity and nature of mental status changes.
Mini- Mental Status Examination
A mother brings her 6 month old infant into the ED. She states the child was on a bed, rolled off,
and fell, striking an iron bedpost on the way down. Specifically, she states that the child hit the
foot of this elaborate and very ornate bedpost. There was no loss of consciousness and the child
appears to be acting normally. She did note, however, that her child’s head did not look right.
She called her pediatrician, who recommended that they come to the urgent care for a skull xray.
On exam, the child is alert and playful. Her vitals look normal for age and she has a completely
unimpressive physical examination except for an obvious abnormality to her left parietal skull: it
appears to be depressed. Now what......?
this child has some physical examination findings that are concerning for a fracture; specifically the location of the scalp hematoma. Being parietal, this
increases the risk of a fracture. Patient needs to be transfered to the ED for further evaluation.
When obtaining a patients history for suspected heat related injury key elements should include what?
Give at least 4
Exposure to high humidity, prolonged exposure, poor living conditions, comorbidities, drug/etoh, medications, hydration status, muscle pain/cramps, fainting spells, behavior changes.
When documenting on a patient treated for heat related injury what do you need to make sure is documented?
The most important aspect of treatment is the performance and documentation of rapid cooling.
Evaluate for and document the presence of drug interactions that can aggravate hyperthermia.
Document your discussion with the patient regarding the environment and risk factors.
A 26yo male patient presents to the clinic after working outside in the summer heat. You suspect heat exhaustion... what is your treatment plan.
Provide a cool environment and remove the patients extra clothing. Use of oral solution of normal saline helps to hydrate the patient. Ensure access to air conditioning prior to discharge.
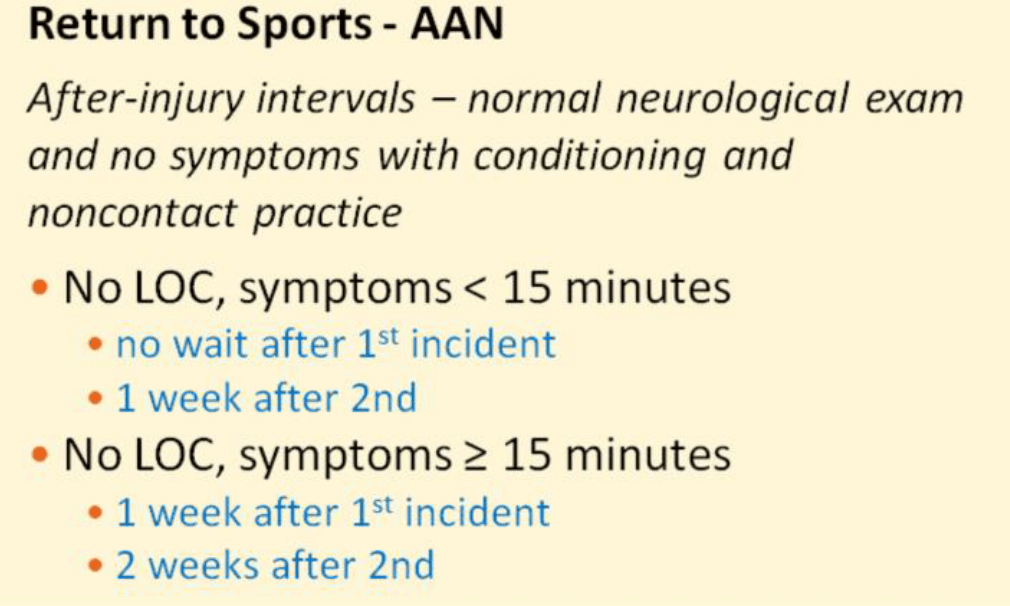
A 15-year-old male patient presents to the clinic after a head injury sustained while playing a football game. Denies LOC and estimates symptoms lasted for approx 45 minutes after the injury. States "This is the first head injury I have had." Based on PECARN criteria there is no indication for additional imaging. Plan is discharge home with follow-up in the next 1 to 2 days with primary care provider or return to clinic if unable to get an appointment. Patient asks you, "when can I play football, it's the end of the season and I dont want to miss my last game?" What is your answer.
May return in 1 week

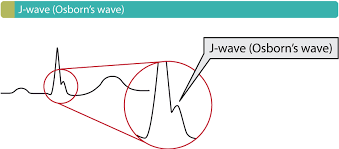
You might find this EKG finding when assessing a patient presenting with this complaint?
Patient presenting with hypothermia.
The J wave-also referred to as Osborn's wave-is defined as a wave occurring at the J-point. Conditions in which the J wave occurs may be referred to as J wave syndromes. J waves are typically most pronounced in the anterolateral (V3, V4, V5, V6) and inferior (II,aVF and III) leads. There are 4 principal causes of J waves, namely hypothermia, Brugada syndrome, early repolarization and hypercalcemia.
In a child presenting to the clinic after sustaining a head injury, what in your HPI would make you concerned for significant TBI? Name 3.

What red flags should you document in your discharge instructions as well as your MDM for patient discharged after a head injury? Name at least 5

What is the treatment for heat cramps?
Ice the involved muscle
Analgesics are useful once cramps subside
Provide potassium oral supplementation for older patients