S1 is best heard where?
A. 2nd intercostal space left of the sternal border
B. 2nd right sternal border
C. Apex of the heart
D. Base of the heart
Answer is C.
S1 is heard best at the apex of the heart
•Closure of atrioventricular valves
•Heart louder at the apex of the heart
•Occurs during systole
S2 is best heard where?
A. Base of the heart
B. 5th intercostal space right of the sternal border
C. Apex of the heart
D. Right lower sternal border
Answer is A.
S2 is heart best at the base of the heart
•Closure of semilunar valves
•Heart louder at the base of the heart
•Occurs at the onset of diastole
Your patient has arthritis that affects the weight-bearing joints such as the hands, knees, hips, and spine. This type of arthritis is most likely:
A. Rheumatoid arthritis
B. Osteoarthritis
The answer is B.
Osteoarthritis is a form of arthritis that causes deterioration of the articular hyaline cartilage of the bones. It affects the weight-bearing joints. This can include the hands, knees, hips, and spine because these joints experience a lot of stress.
An elderly female patient asks why she has to go for a bone density test. She says she feels fine, walks every day, takes her calcium supplements, and there is no family history of osteoporosis in her family. Her past medical history is hypertension, hyperlipidemia, smoking 30 years x 1ppd (pack per day) and obesity. What is the nurse’s best response?
A. Screening is important for all postmenopausal patients
B. Your BMI (body mass index) is >34
C. Some of the medications may cause lethargy, so you might exercise as often
D. There is a long history of nicotine exposure
The answer is A
The gold standard is the bone density test. Known as the dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scan, an analysis is made of the hip and spine. The DEXA scan measures bone mass density. Serial height measurements can also be part of the diagnostic process. Serum levels of calcium, albumin, electrolytes, complete blood count, and thyroid levels are also important for diagnostic purposes.
Risk factors for osteoporosis: advancing age, genetics, lifestyle (smoking, alcohol use), nutritional factors, small frame, being female, disease process (diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis), anemia, Cushing syndrome, malabsorption syndromes, post-menopause.
What is the function of the peripheral vascular system?
A. Transport oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the circulatory system.
B. Transport deoxygenated blood only throughout the circulatory system.
C. Allow arteries to carry deoxygenated blood throughout the circulatory system.
D. Allow veins to carry oxygenated blood throughout the circulatory system.
The answer is A
The peripheral vascular system contains an intricate system of arteries and veins that transports oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the circulatory system
True or False: Peripheral arterial disease leads to a decrease in rich oxygenated blood being delivered to the lower extremities, which leads to ischemia and necrosis of skin tissue.
The answer is True
Peripheral arterial disease leads to a decrease in rich oxygenated blood being delivered to the lower extremities, which leads to ischemia and necrosis of skin tissue.
A patient who suffered a stroke one month ago is experiencing hearing problems along with issues learning and showing emotion. On the MRI what lobe in the brain do you expect to be affected?
A. Frontal lobe
B. Occipital lobe
C. Parietal lobe
D. Temporal
The answer is D.
Frontal lobe- responsible for reasoning, abstract thoughts, and concentration, it contains the Broca’s area that is responsible for expressive aspects of spoken and written language
Parietal lobe- ability to interpret sensations from anywhere on or within the body, it takes information and interpret it to a form that can be understood, and location awareness (so you understand things around you)
Temporal lobe- part of the brain that help you use your senses to understand and respond to the world around you; plays a key role in how you communicate with other people, your ability to access memories, use language, and process emotions, it contains the Wernicke’s area which is responsible for speech comprehension
Occipital lobe- smallest lobe, processes visual signals sent from your eyes and turn that into information the rest of the brain can use
The order of heart valve auscultation is the following (starting at the angle of Louis):
A. Pulmonic, aortic, tricuspid, mitral
B. Aortic, pulmonic, tricuspid, mitral
C. Tricuspid, pulmonic, aortic, mitral
D. Mitral, tricuspid, pulmonic, aortic
Answer is B
Remember: All Patients Effectively Take Medication
APT-M 2245
Aortic- 2nd intercostal space
Pulmonic -2nd intercostal space
Tricuspid- 4th intercostal space
Mitral- 5th intercostal space
Erb’s Point- 3rd intercostal space
You are listening to the apical pulse at the ______________ which is known as the ______________ for a full ________________.
A. 3rd ICS; PMI; 30 seconds
B. 2nd ICS; PMI; 60 seconds
C. 5th ICS MCL; PMI; minute
D. 4th ICS MCL; PMI; minute
The answer is C
During a head-to-toe assessment of a patient with arthritis, you note bony outgrowths on the proximal interphalangeal joint. These outgrowths are known as __________ and occur in ______________.
A. Heberden’s Node, osteoarthritis
B. Bouchard’s Node, spinal stenosis
C. Heberden’s Node, rheumatoid arthritis
D. Bouchard’s Node, osteoarthritis
The answer is D.
Bouchard’s Node are bony outgrowths on the proximal interphalangeal joint (middle joint of the finger and occur in osteoarthritis). Heberden’s Node occur on the distal interphalangeal joint (finger joint closet to the fingernail).
The healthcare provider is preparing to assess abduction of the legs. What should the healthcare provider instruct the patient to perform?
A.Ask the patient to lie supine and raise the right leg while it is extended
B.Ask the patient to straighten the leg and bring it away from the body
C.Ask the patient to bend the knee to the chest
D.Ask the patient to straighten the leg and bring it to the midline of the body
The answer is B
Abduction moves an extremity away from the median of the body. A is testing hip flexion, C is testing hip flexion, and D is testing adduction
A patient is diagnosed with Raynaud’s Disease. Which explanations below most accurately describe this condition? Select all that apply:
A.Raynaud’s disease is triggered by cold temperature or stress.
B.Raynaud’s disease occurs due to vasospasm of the peripheral veins
C.Raynaud’s disease affects the toes, fingers, and sometimes the ears and nose.
D.Raynaud’s disease is prevented by glucose control
The answers are A and C.
Raynaud’s Disease occurs when vasospasm of peripheral arteries occurs. It mainly affects the fingers and toes (it can also affect the ears/nose). It is triggered by exposure to cold or during stress. It can be prevented by keeping the toes, fingers, ears, and nose warm and avoid stress. Medications can also be used as well that help prevent vasospasm.
You’re assessing a patient’s health history for peripheral vascular disease. What signs and symptoms reported by the patient would indicate the patient may be experiencing peripheral arterial disease? Select all that apply:
A. “I often wake up at night with leg pain and have to dangle my leg out of the bed to ease the pain.”
B. “If I stand or sit too long my legs start to feel heavy and achy.”
C. “It hurts to elevate my legs.”
D. “Sometimes when I’m walking my legs start to cramp and tingle to the point where I can’t walk until the pain goes away.”
The answers are A, C, and D.
Peripheral arterial disease occurs when there is impediment of blood flow to the lower extremities (hence the lower extremities are being deprived of blood flow and this causes pain). The pain most commonly occurs at night and can wake up the patient. It is known as “rest pain”. This occurs because when the legs are horizontal the blood flow is compromised, and it causes pain…therefore the patient will report they dangle the leg off the bed to help ease the pain (the dependent position (dangling) will help blood flow down to the extremity). In addition, it hurts to elevate the legs (again because this further compromises blood flow). Option B occurs in peripheral venous disease. Option D is known as intermittent claudication and is a HALLMARK sign and symptom in PAD.
A patient’s MRI imaging shows damage to the cerebellum a week after the patient suffered a stroke. What assessment findings would correlate with this MRI finding?
A. Vision problems
B. Balance impairment
C. Language difficulty
D. Impaired short-term memory
The answer is B.
The cerebellum is important for coordination and balance.
You are palpating the precordium with the ____________ of your hand and note a pulsations and thrills. How do you document the findings?
A. dorsal surface; normal
B. dorsal surface; abnormal
D. palmar; normal
E. palmar; abnormal
The answer is E.
Normal finding: No pulsations are felt at the five landmarks
Abnormal finding: Pulsations, lifts, heaves
The palmar surface is used to palpate the 5 landmarks
You are palpating the carotid pulse and auscultating the apical pulse to determine the difference in the rate. What is this called?
A. Pulse pressure
B. Pulse amplitude
C. Pulse deficit
D. Pulse oximetry
The answer is C.
Pulse Deficit (PD) is a physiological phenomenon defined as the difference between the simultaneously counted number of apical pulsations and the pulse rate at the periphery. The pulse rate may be the carotid. or radial pulse.
You are inspecting the patients gait during their musculoskeletal assessment. Upon inspection, you notice the patient right leg is stiff and when he goes to walk forward, it drags or swings around in a semicircular motion. The patient has a history of cerebral palsy noted on his chart. How would you document the patient’s gait?
A. Propulsive
B. Scissor
C .Waddling
D. Steppage
E. Spastic
A spastic gait causes you to walk with one stiff leg. When you lift that leg to walk, it either drags or swings around in a semicircular motion (circumduction). This type of gait is common among people diagnosed with cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis or hemiplegia.
A waddling gait happens because of weakness in your hip girdle and upper thigh muscles. To make up for the weakness, you sway from side to side and your hip drops with each step. It's also called myopathic gait and can be caused by several conditions.
A propulsive gait is a stooped, stiff posture with the head and neck bent forward.
The answer is E
Scissor gait is flexion in the legs, hips and pelvis accompanied by extreme adduction leading to the knees and thighs hitting, or sometimes even crossing
Steppage is the inability to lift the foot while walking due to the weakness of muscles that cause dorsiflexion of the ankle joint.
You are assessing the patient’s bilateral arm muscle strength. Upon assessment, the patient can move her joints in a gravity eliminated position. What grade level would you document?
A.Grade 0
B.Grade 1
C.Grade 2
D.Grade 3
E.Grade 4
Grade 5
The answer is C
0: Unable to contract muscle in a gravity eliminated position
1: Able to contract muscle slightly
2: Able to move joint in a gravity eliminated position
3: Able to move joint against gravity
4: Able to move joint with some resistance through range of motion.
5: Able to move joint with full resistance through range of motion
What is the function of the lymphatic system?
A. Carry lymph nodes throughout the circulatory system.
B. Remove waste from the body’s tissue by flowing it upward throughout the circulatory system
C. Produce white blood cells to help fight infection, maintain fluid and protein balance, and move lymph fluids in an upward flow through the circulatory system.
D. Help maintain the body’s pulse and temperature.
The answer is C
Lymphatic system that carries lymph fluid throughout our circulation. The functions of the lymphatic system are as follows:
Production of white blood cells (i.e., lymphocytes) in the lymph nodes to help fight off invading pathogens.
Fluid and protein balance: as blood moves through the arteries and veins, 10 percent of the fluid is filtered by the capillaries, along with vital proteins, becomes trapped in the tissues of the body; the lymphatic system collects this fluid and returns it to the circulatory system.
Immunity and spread of infection: the lymphatic system plays an essential role in the immune functions of the body: it is the first line of defense against disease.
Your patient has severe peripheral arterial disease. When the lower extremities are elevated you would expect them to appear _______________ and, when they are in the dependent position you would expect them to appear _________________. Fill in the blanks:
A. cyanotic; rubor
B. rubor; pallor
C. cyanotic, pallor
D. pallor; rubor
The answer is D.
In severe PAD, if the lower extremities are elevated they will turn pale (pallor). However, if they are in the dependent position (dangling) they will appear rubor (red and warm…this occurs due to inflammation of the vessels).
You’re educating a group of nursing students about left side brain damage. Select all the signs and symptoms noted with this type of stroke:
A. Aphasia
B. Denial about limitations
C. Impaired math skills
D. Issues with seeing on the right side
E. Disoriented
F. Depression and anger
G. Impulsive
H. Agraphia
The answers are A, C, D, F, and H.
Patients who have left side brain damage will have aphasia, be AWARE of their limitations, impaired math skills, issues with seeing on the right side, no deficit in memory, depression/anger, cautious, and agraphia. All the other options are found in right side brain injury.
The SA node is considered the __________ of the heart. What sequence does the electrical impulse follow?
A. Conductor; Bundle branch to Purkinje fibers to AV node
B. Pacemaker; SA node to AV node to Bundle of His to Bundle branches to Purkinje fibers
C. Conductor; SA node to AV node to Bundle of His to Bundle branches to Purkinje fibers
D. Pacemaker; AV node to SA node to Bundle of His to Bundle branches to Purkinje fibers
The answer is B.
The SA node is considered the natural pacemaker of the heart; The flow of the electrical conduction is SA node to AV node to Bundle of His to Bundle branches to Purkinje fibers
The semilunar valves are the tricuspid and mitral valves.
A. True
B. False
The answer is false
Atrioventricular valves separate the atria from the ventricles and include the following:
• Tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle.
• Mitral valve separates the left atrium from the left ventricle.
Semilunar valves separate the ventricles from the pulmonary artery and aorta and include the following:
• Pulmonic valve separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary artery.
• Aortic valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta.
You are caring for a patient whose nervous system has progressive gotten worse over the last 5 years. He has become slower in movement and has noticeable tremors in his right hand. His has also begun dragging his feet along the ground without lifting them when he ambulates. This gait is known as____________. Upon assessment the physician suspects that the patient has _______________ disease.
Shuffling: characterized by dragging one's feet along or without lifting the feet fully from the ground
Parkinson's disease is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves. Symptoms start slowly. The first symptom may be a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder may also cause stiffness or slowing of movement. A patient who has Parkinson’s disease may have the presence of a shuffling gait; this is a key characteristic symptom of the disease.
You are conducting a Romberg test on your patient. Which findings indicate a positive result?
A. Swaying to right side
B. Swaying to left side
C. No swaying
D. Falling
E. Maintains position
The answer is A, B, D
Positive Romberg Test
•Swaying or falling to one side
•May indicate cerebellar dysfunction or lesions in the cerebellum or spinal cord.
Using the finger pads of your index and middle fingers, you gently palpate using circular motions the ten facial and neck lymph nodes region. What are considered normal findings? Select all that apply
A. Node greater than 1 cm
B. Node less than 1 cm
C. Node that is discrete, movable, and nontender
D. Node that is matted, hard, tender
E. No lymph nodes are palpable
The answer is B, C, E
Normal findings
No lymph nodes are palpated.
If palpated, the lymph node should be less than 1 cm, discrete, soft, moveable, and nontender.
You are assessing a patient with pitting edema to their bilateral lower extremities. The edema is 6mm and last up to one minute. How would you document your finding?
A. Grade 1
B. Grade 2
C. Grade 3
D. Grade 4
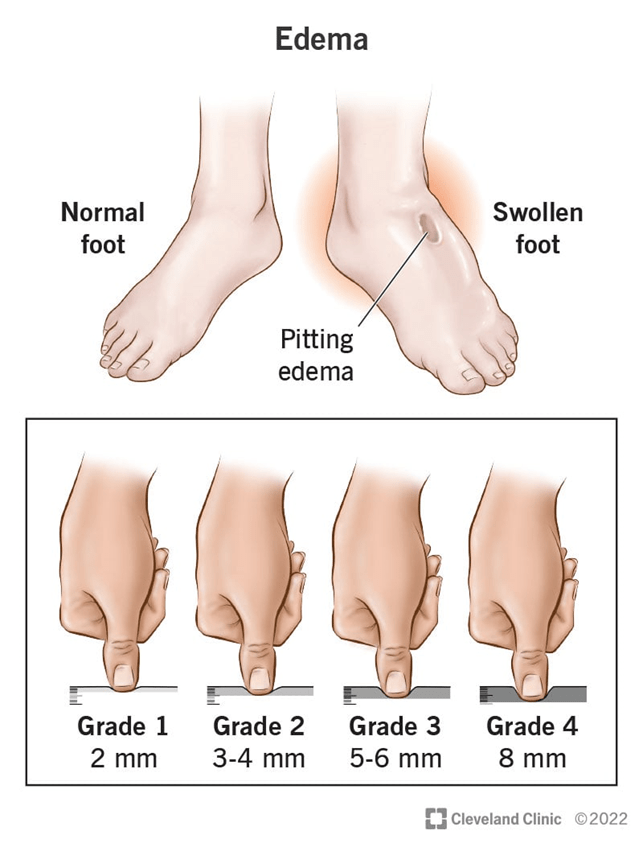
The answer is C.
Grade 1 is up to 2mm and rebounds immediately
Grade 2 is 3-4 mm and rebounds with 15 seconds
Grade 3 is 5-6 mm and rebounds in 60 seconds
Grade 4 is 8mm and rebounds in 2-3 minutes
You are assessing a patient who suffered a traumatic brain injury during a motor vehicle accident. Upon assessment you notice the patient opens her eyes to sound, is alert but confused, and moves her upper extremities with normal flexion. What is her level of traumatic brain injury according to the Glasgow coma scale?
A. Mild
B. Moderate
C. Severe
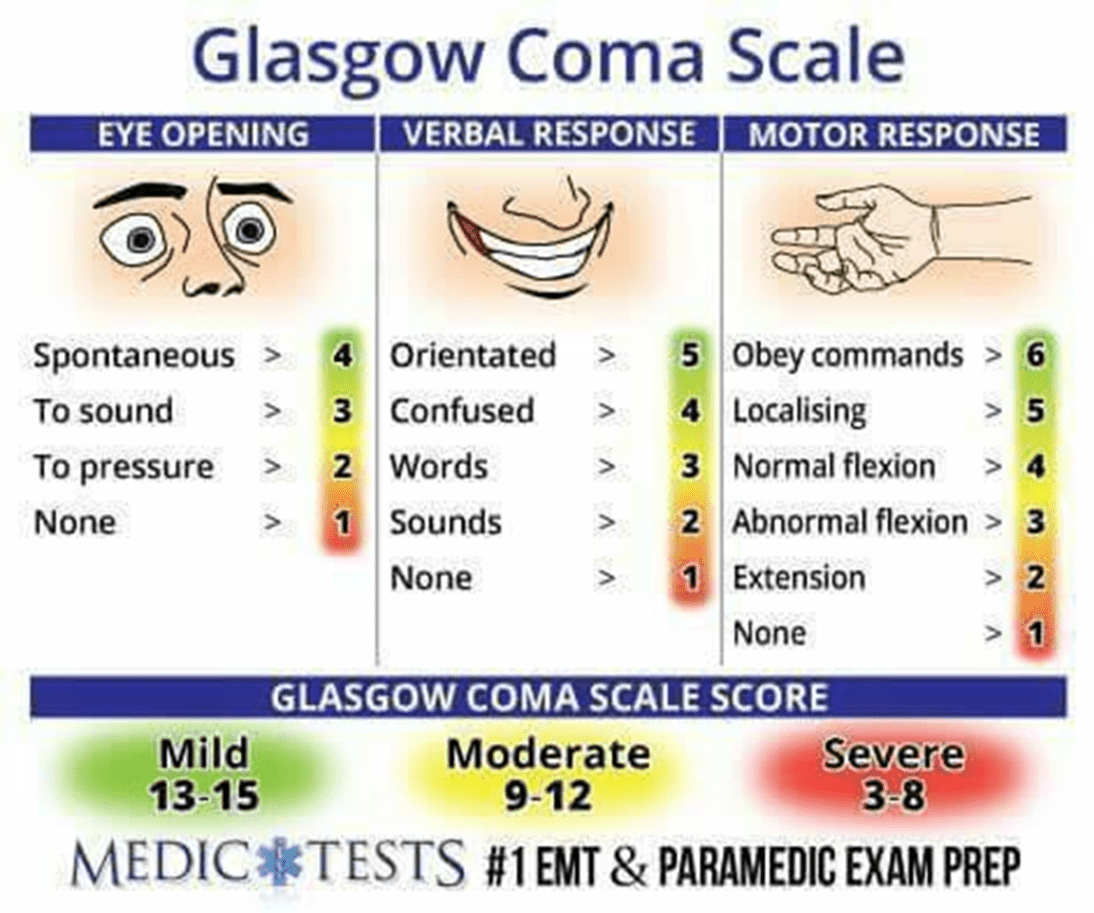
The answer is B
Eye=3, Verbal =4, Motor=4 total 11
S2 represents the closure of?
A. Aortic and Pulmonic valves
B. Aortic and Mitral valves
C. Mitral and Pulmonic valves
D. Tricuspid and Aortic valves
Answer is: A
Second heart sound (S2) is known as the “dub” sound. This is the sound of both semilunar valves closing
Explain the flow of the blood through the heart
Deoxygenated blood enters the heart from the body system via the superior and inferior vena cava. Blood enters the right atrium through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The ventricle contracts in response to pressure changes caused by increased volume and heart stretch pushing blood through the pulmonic valve into the pulmonic trunk that bifurcates into the right and left pulmonary artery. Once in the lungs, gas exchange occurs at the alveolar level. Oxygen transport occurs and the blood is then pushed back through the right and left pulmonary veins into the left atrium, through the mitral valve into the left ventricle (the largest, most powerful portion of the heart) and then up and out through the aortic valve into systemic circulation.
During the musculoskeletal assessment of the patient, you ask them to bend over at the waist to assess their spine. Upon assessment your note an exaggerated inward curve of the lumbar vertebrae. How would you document this finding?
A. Osteoarthritis
B. Kyphosis
C. Lordosis
D. Scoliosis
The answer is C
Lordosis: an exaggerated inward curve of the spine that typically affects the lower back
•Scoliosis: sideways curve of the spine
•Kyphosis: an exaggerated, forward rounding of the upper back
* Osteoarthritis is a form of arthritis that causes deterioration of the articular hyaline cartilage of the bones. It affects the weight-bearing joints.
A nursing student is explaining Friedreich's ataxia. You know the student has an understanding when they state:
A. The patient has a rare degenerative disease that they develop in their younger teens
B. The patient has an inherited degenerative disease that is developed as an older adult
C. The patient has a common disorder that develops due to damage to the spinal cord
D. The patient has a disorder that is common in older adults and causes difficulty with ambulating
The answer is A
Friedreich's ataxia is a rare, inherited, degenerative disease. It damages the spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and the cerebellum portion of the brain. This conditions tends to develop in children and teens and gradually worsens over time.
What are signs of arterial insufficiency? Select all that apply
A. Pain described as “sharp, burning, or throbbing” and is worse with activity and at night
B. Loss of hair around the area
C. Excoriation of the skin
D. Coarse, shiny, tight skin
E. Base of ulcer is brown, black, yellow
F. May cause affected area to be darker than none affected area
G. Pain is cramping
The answer is A, B, E, F
Excoriation of skin, coarse, shiny, tight skin, and pain is cramping are signs of venous insufficiency
You are conducting an assessment on your patient when she states she has been experiencing a cramp-like pain in her legs when she runs 2 miles for her morning exercise. How would you document this symptom?
A. Intermittent claudication
B. Chronic claudication
C. Arterial insufficiency
D. Embolism
The answer is A.
Intermittent claudication is a symptom of PAD; cramp-like pain felt in the buttock, thighs, or calves during exercise or walking; due to decreased blood flow and lack of oxygen (tissue ischemia) to the legs. The pain intensifies gradually as the patient continues to walk until he or she must stop completely. The patient with intermittent claudication does not feel any discomfort at rest because the blood flow and oxygen supply in the limb are then replenished
A patient has right side brain damage from a stroke. Select all the signs and symptoms that occurs with this type of stroke:
A. Right side hemiplegia
B. Confusion on date, time, and place
C. Aphasia
D. Unilateral neglect
E. Aware of limitations
F. Impulsive
G. Short attention span
H. Agraphia
The answers are B, D, F, and G.
Patients who have right side brain damage will have LEFT side hemiplegia (opposite side), confused on date, time, and place, unilateral neglect (left side neglect), DENIAL about limitations, be impulsive, and have a short attention span. Agraphia, right side hemiplegia, aware of limitations, and aphasia occur in a LEFT SIDE brain injury.