Contains fluid and hair cells and is shaped similar to a snail
Cochlea
Which structures could be damaged to result in SENSORINEURAL hearing loss?
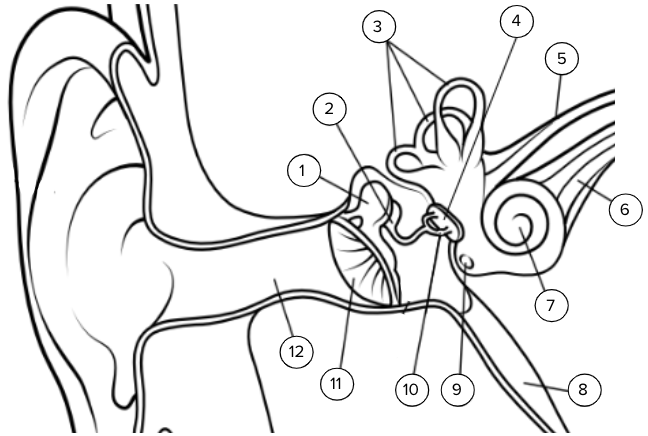
cochlea, cochlear nerve (7, 6)
How is the Rinne test done?
Place tuning fork on bone to test bone conduction until noise can't be heard anymore, then flip fork to test air conduction
What is used to differentiate left ear vs right ear on an audiogram?
Left ear = blue x
Right ear = red circle
Which of these is a more accurate picture of a sound wave?

B
Thin piece of skin that is at the end of the ear canal
Tympanic membrane (ear drum)
Which structures could be damaged to result in CONDUCTIVE hearing loss?

ear canal, tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, stapes, oval window (12, 11, 1, 2, 10, 4)
What is the Rinne test used for?
It is used to diagnose CONDUCTIVE hearing loss
Describe this patient's hearing loss:
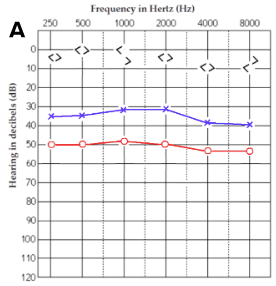
mild conductive hearing loss in left ear, moderate conductive hearing loss in right ear
Which sound wave has the highest frequency?
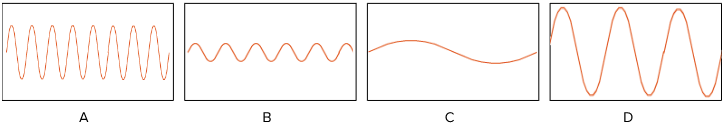
A
Which structures are part of the middle ear?

malleus, incus, stapes, oval window (1, 2, 4, 10)
What is the name and function of structure 3?

Semicircular canals, help to maintain balance
What are two tests that can be used to detect sensorineural hearing loss?
Speech-in-noise test and pure tone test
Describe this patient's hearing loss:
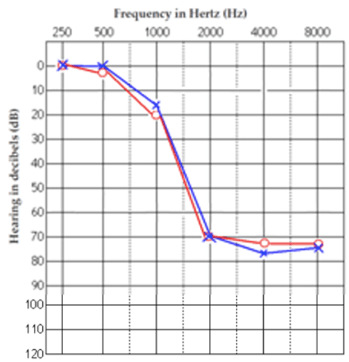
Severe high frequency hearing loss in both ears
Which sound wave is the loudest?

D
What is structure 2?

Incus
Which structures are NOT involved in hearing and what are their names?

3, 5, 8 (semicircular canals, vestibular nerve, eustachian tube)
What can you conclude about the patient's LEFT ear?

They have conductive hearing loss in the left ear
Describe this patient's hearing loss:
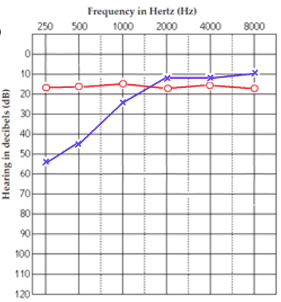
Moderate low frequency hearing loss in left ear
Which sound wave has the lowest pitch?

C
What is structure 9 and what is its function?

Round window, allows the fluid in the cochlea to move
Place the steps of hearing in the correct order:
The bones in the middle ear vibrate
The eardrum vibrates
Signals are sent to the brain
The fluid in the cochlea moves
- Signals are sent to the cochlear nerve
The oval window vibrates
Sound waves travel down the ear canal
The hair cells in the cochlea move
7, 2, 1, 6, 4, 8, 5, 3
Does this patient have sensorineural hearing loss in the right ear?

We cannot tell with these results
Describe this patient's hearing loss:
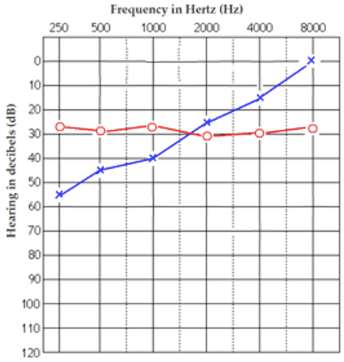
Mild hearing loss in right ear, moderate low frequency hearing loss in left ear, mild mid frequency hearing loss in left ear
Describe 3 pros and 3 cons of giving your child a cochlear implant
Pros: allows people to hear who would otherwise have no way of hearing, provides more opportunities in life, makes it easier to communicate with more people, able to be turned off whenever the user chooses
Cons: only works if you get it young, unpredictable results, sound quality is greatly reduced, does not function well with a lot of background noise, invasive surgery, shrinks the deaf community and deaf culture