Most common myopathic process leading to HF
Dilated Cardiomyopathy.
Explain the Classification of HF by stages
Stage A: at risk
Stage B: Abnormal structure/Function but never symptomatic
Stage C: Symptomatic
Stage D: Refractory/De-compensated
Laboratory markers of HF
BNP and N-terminal proBNP
Common signs of fluid overload
Hepatomegaly and Gallop rhythm
What is the treatment for Stage B HF?
ACE-I
Patient less than one year of age diagnosed with HF, what needs to be done?
Echocardiogram to rule out ALCAPA
What is the first line agent for Stage A HF?
NONE!
Most common cause of acquired CMP
Myocarditis
Most common electrolyte abnormality
Hyponatremia
What is the main desired effect of Spironolactone
Antifibrotic
Most common cause of tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy
Atrial Ectopic Tachycardia
True or False
Furosemide is a common diuretic to be used in Stage B HF
Used in Stage C not B
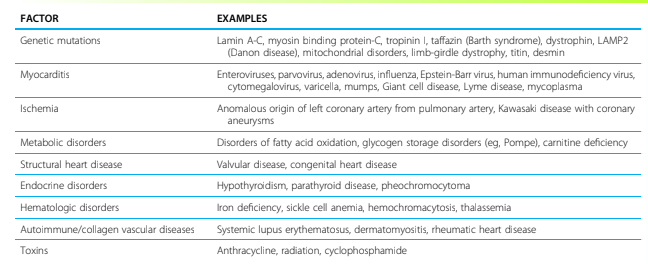
Mention 5 different risk factors known to causes DCM
Genetic, Myocarditis, Ischemia, Metabolic, Structural, Endocrine, Hematologic, Autoimmune, Toxins
Name 3 possible EKG findings
Ventricular Hypertrophy by Voltage Criteria
SVT
A Fib, A Flatter
AV Block
Ventricular Tachycardia
True or False
Dobutamine improves survival by activating Beta receptors; increasing contractility of myocardium and decreasing vascular tone
It does not improve survival.
Higher Mortality
True or False
Most cardiologists agree that pulmonary overcirculation from left-to-right shunt is NOT HF.
TRUE
What are the two conditions mentioned that place a patient into Stage A of HF
1. Cardio-toxic chemotherapy
2. Chronic Kidney Disaese
Most common inheritance pattern of DCM
Autosomal Dominant
Bi-atrial enlargement is a sign of:
Restrictive CM
True or False
Adult studies showed better survival with Milrinone, but it has not been shown in Pediatric studies
False.
Adult studies showed greater risk of arrhythmia and death.
Definition of Heart Failure
Clinical syndrome in which heart disease reduces cardiac output, increases venous pressure, and is accompanied by molecular abnormalities that cause progressive deterioration of failing heart and premature myocardial cell death.
Classified by age, mention the age ranges with at least one age group-specific etiology of HF
Newborns and Infants: ALCAPA, Inborn Error of Metabolism, Coarctation of Aorta, Critical Aortic Stenosis
Age 2-5: Kawasaki
Age >5: Rheumatic Heart Disease, Hypothyroidsim, SLE
Mention 3 Risk factors causing DCM, with 2 examples on each
Mention 3 methods to overcome diuretic resistance in patients receiving chronic diuretic therapy:
Higher doses, add Chlorothiazide, Continuous infusion
Summarize the stages and their treatments
Stage A: None
Stage B: ACE-I, B-Blocker
Stage C: ACE-I, B-Blocker, Spironolactone, Lasix, Digoxin
Stage D: Main therapy, IV Diuretics, Pressors