the ability of a substance to hold heat
heat capacity
a substance that lets heat energy (and electrical energy) move through it easily
conductor
a change of state from a solid directly to a gas
sublimation
____________ has the highest heat capacity of anything on earth, except ammonia
water
the fastest way to melt a cube of ____________ is to break it into tiny pieces, because this increases the ____________
ice
surface area
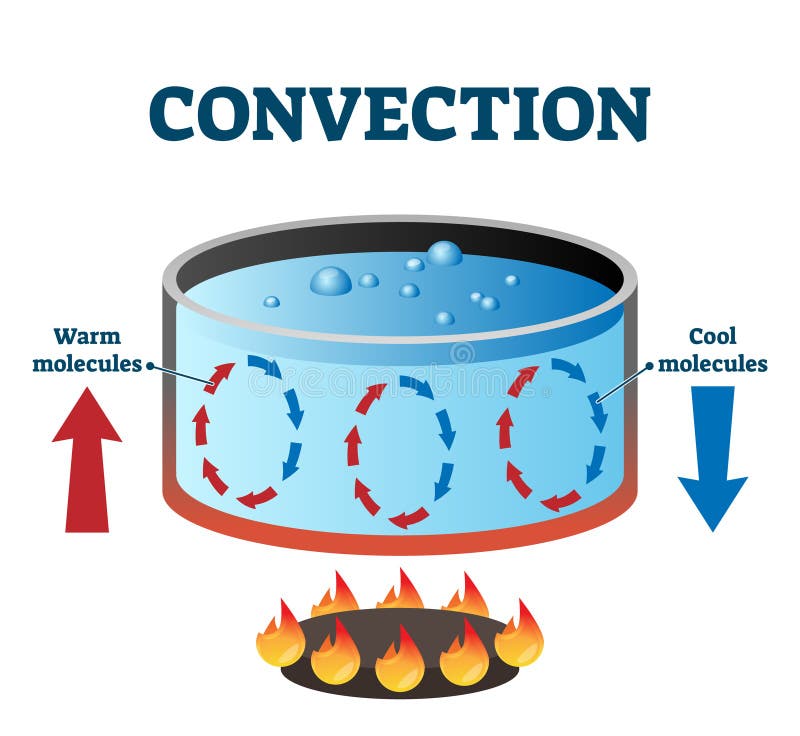
- water in center hottest
- particles move quickly, turn to gas & rise
- that water is replaced by water from the sides (bottom), which is replaced by water from the sides (top), creating a circular motion
the energy that is transferred from matter at a higher temperature to matter at a lower temperature
heat energy
any substance that does not allow heat energy (or electrical energy) to move through it easily
insulator
the process of changing state from a liquid to a gas
evaporation
train tracks are left with gaps between the rails so that when the weather changes there is room for the rails to ____________ and ____________
expand and contract
or
contract and expand
we measure ____________ kinetic energy because not all of the ____________ in one substance will move at exactly the same speed.
average
particles
Describe different traditional First Nations and Metis shelters, in particular discussing what materials were used and why.
wigwam - mud insulation, made of bark/hides/saplings
igloo - made of ice - available
teepee - made of hides
- all shaped so snow and water will run off
- all have heat source and insulation
a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance
temperature
a device that controls temperature by switching a heating system on or off
thermostat
a probe that uses a thermistor at its tip that is connected to a computer
computer sensor
the First Nations peoples used the materials that were ____________ to them.
available
in Plains Cree tradition, no part of the buffalo was ____________.
Explain what happens to the sun's energy when it comes to earth.
- only small amount comes to Earth
- some is absorbed in atmosphere and some is reflected back in atmosphere
- some is absorbed by land and water and some reflected back from water and land
- radiation
the point at which a solid changes state to a liquid
melting point
the point at which a liquid changes state to a gas
boiling point
substances that indicate the temperature of an object by changing colour
liquid crystals
all hot substances transfer heat by ____________
radiation
radiation does not require ____________
contact
describe the three states of matter, and explain how heat affects them using your knowledge of the particle theory
solid - particles tight, when heated the particles move faster, have more energy and eventually spread and become liquid
liquid - particles looser, when heated the particles move faster, have more energy and eventually spread and become gas
gas - particles fill a space, when heated the particles move faster, have more energy and eventually move faster and volume increases (expansion)
- particles move faster and spread apart when heat is added
increase the volume of a substance
expand
decrease the volume of a substance
contract
a device that measures temperature by having wires connected to a voltmeter
thermocouple thermometer
matter can ____________, ____________, or let heat energy pass through it with little absorption or reflection.
absorb/reflect
or
reflect/absorb
The roads in Saskatchewan are usually filled with potholes after ____________ rather than ____________.
winter
summer