How could you increase the gravitational potential energy of an object without changing its mass?
Raise the object farther off the ground
What type of heat transfer is when hot fluids rise and cool fluids sink?
What is Convection
Heat moves from the _____ object to the ______ object.
hotter ; cooler
Feeling the warmth from a campfire.
Radiation
Which best explains how roasting marshmallows happens?
a. Heat from the fire is conducted into the marshmallow.
b. The coolness of the marshmallow is conducted into the fire.
c. Heat from the fire is radiated into the marshmallow.
d. The coolness of the marshmallow is radiated into the fire.
The least amount of potential energy is at
C
The transfer of heat energy from the sun to Earth.
Radiation
Beneath the Earth's crust hot magma is rising and cool magma sinking.
Convection
Accidently burning your hand on a hot metal pan.
Conduction.
A pot is heated on a stove. Which process causes the metal handle of the pot to also become hot?
a. combustion
b. convection
c. radiation
d. conduction
D
Any form of energy is always measured in...
Joules (J)
What type of heat transfer occurs through direct contact when objects are touching?
What is Conduction
What method of heat transfer is this?

Conduction (energy transfer via contact)
Radiation is when _____________ waves travel through space, without direct contact.
electromagnetic
People sitting around a campfire are able to feel the heat from the fire. How are the people able to feel the heat from the fire without touching the fire?
a. The heat from the fire travels through the ground and heats the ground around the people.
b. The heat from the fire is conducted through air molecules to the people.
c. The heat from the fire rises in the air and then settles around the people.
d. The heat from the fire radiates from the fire to the people.
D
What is the equation to work out Kinetic Energy
1/2 mass x velocity2
What method of energy transfer is this?
(Description: Heat flows from the hotter cup into the cooler hands. )

Conduction (energy transfer via contact)
What method of heat transfer is shown in the photo?
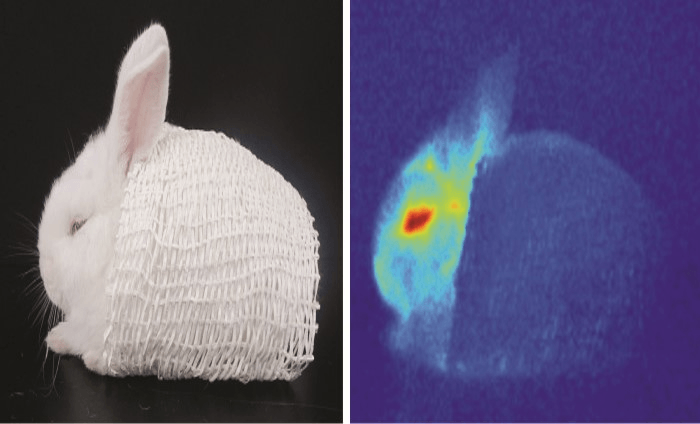
It is showing heat radiation
Name all modes of heat transfer.
conduction, convection and radiation
Bill stands in a swimming pool and notices that the water around his feet is a lot cooler than the water near the surface. Which process causes this difference in temperature?
a. convection
b. evaporation
c. radiation
d. conduction
A
What is the equation to work out gravitational potential energy?
mass x gravitational field strength x height
What method of heat transfer is shown here?
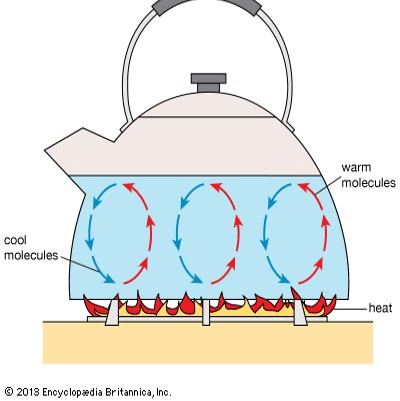
Convection heating (hot fluid rises, cool fluid sinks)
Describe an example of radiation.
Answers will vary. The warmth we feel from a fire.
Explain why it’s much colder at the bottom of a pool than at the top.
Convection makes the cool water sink and the hot water rise.
Stirring a cup of hot tea causes a metal spoon to get warm. Which statement best explains why the spoon gets warm?
a. Heat energy transfers from the metal spoon to the hot liquid.
b. Heat energy transfers from the hot tea to the spoon.
c. Heat energy transfers from the air to the hot liquid, and then to the spoon.
d. Heat energy transfers from the hot liquid to the cup, and then to the spoon.
B
Sarah's book has a mass of 1.2kg. It is on a shelf that is 4.5m above the ground. The gravitational potential energy is...
52.92J
Which type of heat transfer is responsible for winds and precipitation, playing an important role in Earth's weather patterns.
Convection
Give one specific example of convection.
Answers will vary. The convection currents in the ocean and atmosphere.
Describe an example of conduction.
Answers will vary and must involve direct contact.
A spoon is placed into a mug of hot coffee. As the spoon sits in the coffee it begins to get warm. Which direction did the heat move?
a. From the spoon to the coffee
b. From the coffee to the spoon
c. From the surroundings to the coffee
B