Name the extraocular muscles and which cranial nerve innervates them.
LR6 (SO4) all the rest are 3
Lateral rectus VI
Superior oblique IV
III - superior, inferior, medial recti, and inferior oblique
OOOTTAFVGVAH
Identify these structures
malleus, cone of light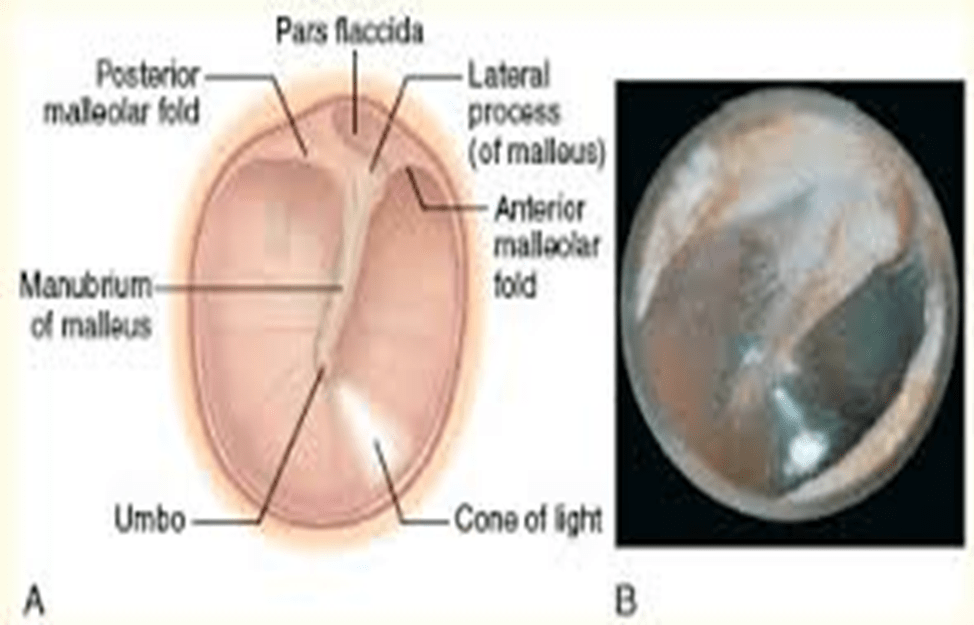
A 22 year old male returns to your office with complaints of persistent rhinorrhea. He states that his symptoms were improving with a nasal spray twice a day for the past month, but whenever he stops using it, the rhinorrhea worsens. What is the most likely culprit?
Affrin
Rhinitis Medicamentosa
A 19 year old female presents to your office with chief complaint of sore throat and fevers with T max 100.8. She denies cough. On exam you note + exudative tonsillitis and + anterior cervical chain adenopathy. What is her CENTOR score?
4
What is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
- Rapid strep
- If negative?
Culture
This painful, non-vesicular ulcerated oral lesion appeared about 2 weeks after the patient bit their cheek. They have no other sores in the oral mucosa. What is the most likely diagnosis?
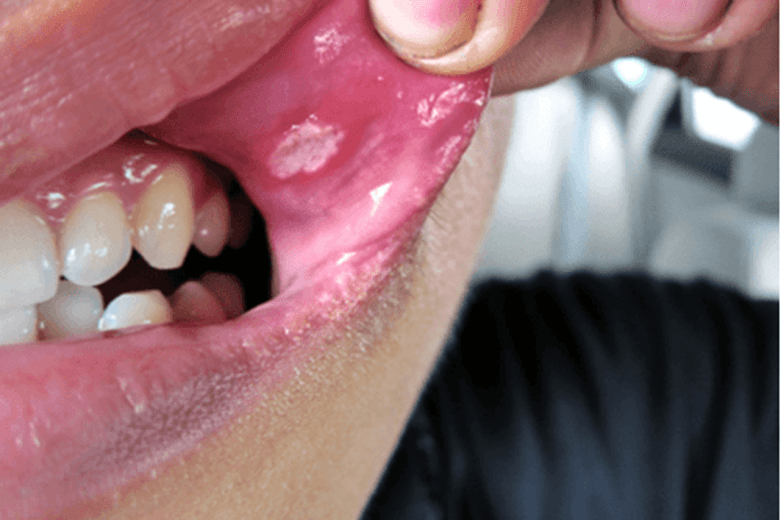
Aphthous ulcer
What systemic disorders can an aphthous ulcer be associated with?
Behçet syndrome • Celiac disease • Cyclic neutropenia • Nutritional deficiencies (iron, folate, zinc, B 1 , B 2 , B 6 , and B 12 ) • Immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency • Immunocompromised conditions, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease • Inflammatory bowel disease • MAGIC syndrome (mouth and genital ulcers with inflamed cartilage) • PFAPA syndrome (periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis, cervical adenitis) • Reactive arthritis • Sweet syndrome • Ulcus vulvae acutum
A 38 year old male presents post-op with persistent voice hoarseness. He was intubated the duration of his surgical procedure. What is the most likely cause of his voice hoarseness?
Vocal Cord Paralysis 2/2 Left recurrent laryngeal nerve damage.
What are some common causes of this injury and why?
Surgery to the neck/chest, Intubation; due to the location of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve which starts from the vagus nerve, curves inferior to the aortic arch, and ascends back up to the larynx,
A painless cyst in the eyelid caused by inflammation of a blocked meibomian gland.
What is a Chalazion?
What is a significant subjective clinical difference between chalazion and hordeolum?
Identify the following exam finding:
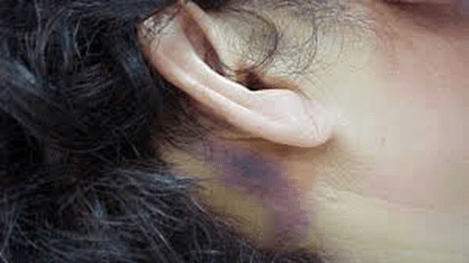
Battle sign
What is the most likely cause of unilateral purulent nasal discharge in a small child?
FB in the nares
A 20 y/o male presents to your primary care office for follow up to an urgent care visit yesterday. He went to urgent care with complaints of a sore throat, enlarged tonsils and exudates. His rapid strep was negative and throat culture is pending. He notes 2 other players on his soccer team had similar symptoms. Given the severity of his symptoms, the urgent care provider started him on empiric penicillin VK. Today, he presents with continued symptoms, but now has a diffuse rash. What is the appropriate treatment?
Discontinue PCN
Supportive care with ibuprofen, tylenol, close follow up and encourage PO fluids.
What should you counsel this patient on to prevent a well known complication of this dx?
No contact sports!
Due to risk of splenic rupture 2/2 hepatosplenomegaly in mono
A 62 year old male presents to your primary care office with complaints of left sided facial swelling associated with pain and fever x 2 days. He has recently started taking benadryl nightly to sleep. On exam you appreciate the the following: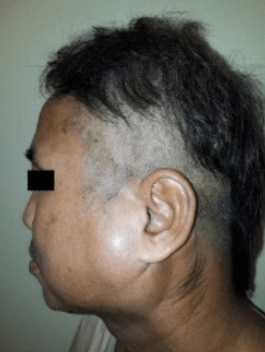
What is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute parotitis
Tx?
Antibiotics
Sour lozenges
massage duct
10-14 days
+/- ENT referral
This is the most common form of thyroid cancer
What is papillary thyroid cancer?
A 26 year old male presents to the ED with unilateral erythematous eye lids, pain with EOMs in the affected eye, decreased visual acuity. He notes that over the past 2 weeks he has had nasal discharge, dental pain, and headache. Physical exam reveals proptosis, erythema of the upper and lower lids and orbital area of the affected eye. Visual acuity is 20/20 in the non affected eye and 20/60 in the affected eye. What is the most appropriate first intervention?
CT head/orbit, Urgent ophthalmology referral
What are the most common pathogens involved? Staphylococcus aureus, and streptococci species, including Strep pneumonia, Strep anginosus, and Strep pyogenes
Tx?
Ceftriaxone IV and Vancomycin (if trauma associated)
A 12-year-old girl comes to your office with a 2-day history of right ear pain. She has been taking swimming lessons over the past two weeks. Past medical history is unremarkable. She has no allergies and she is taking acetaminophen for pain relief. The patient experiences pain with the examination and you note edema of the external auditory canal. The tympanic membrane appears normal. This is the most likely diagnosis.
What is otitis externa?
All of the following are risk factors for what common issue?
<10 years
Between 45-65 years
More frequent in winter months
Increased incidence with ASA, warfarin, plavix, xarelto
Cocaine use
Trauma /picking
What is epistaxis?
Most common location of epistaxis?
Anterior nose bleed
Location? Kiesselbach's plexus
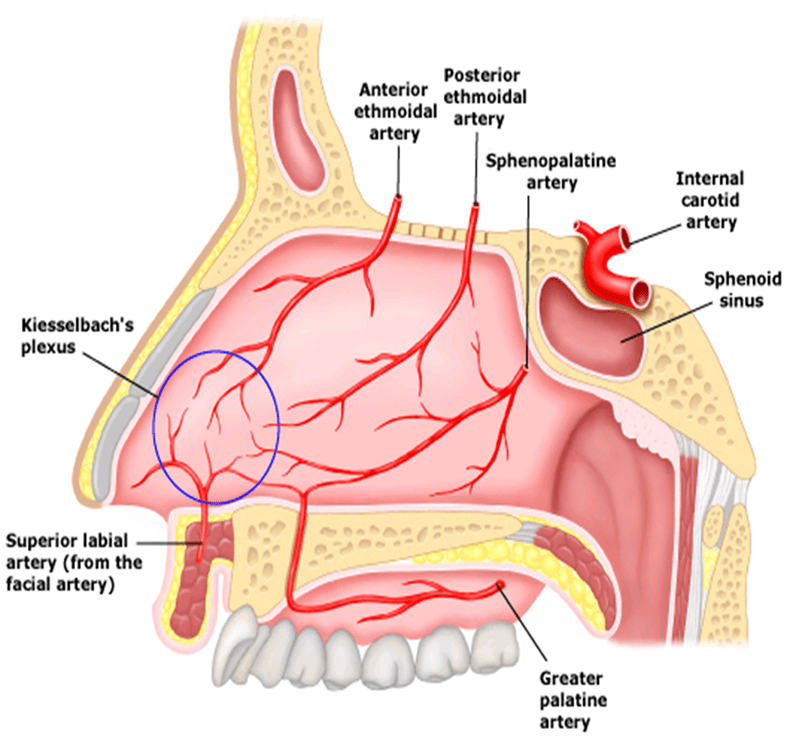
What is the most common vessel involved in a posterior nose bleed?
Sphenopalatine artery
A 3 year old girl presents to the ED with low grade temp and mild respiratory distress. On exam you note stridor and a barking cough. You order a plain film which is + for steeple sign and confirms your suspected diagnosis. What is the most likely pathogen involved?
Parainfluenza virus
Croup
A 50-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of dry eyes and dry mouth. She reports feeling like there is "sand" in her eyes and has difficulty swallowing dry foods. On further questioning, she also mentions joint pain in her hands and fatigue. Physical examination reveals dry mucous membranes and bilateral parotid gland enlargement. Blood tests show positive anti-Ro (SSA) and anti-La (SSB) antibodies. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is Sjogren's syndrome
Identify each of the following non-painful cystic lesions: 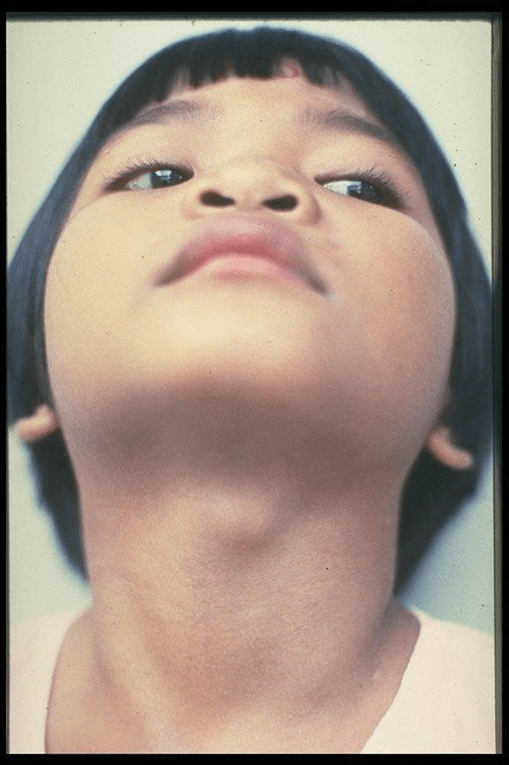
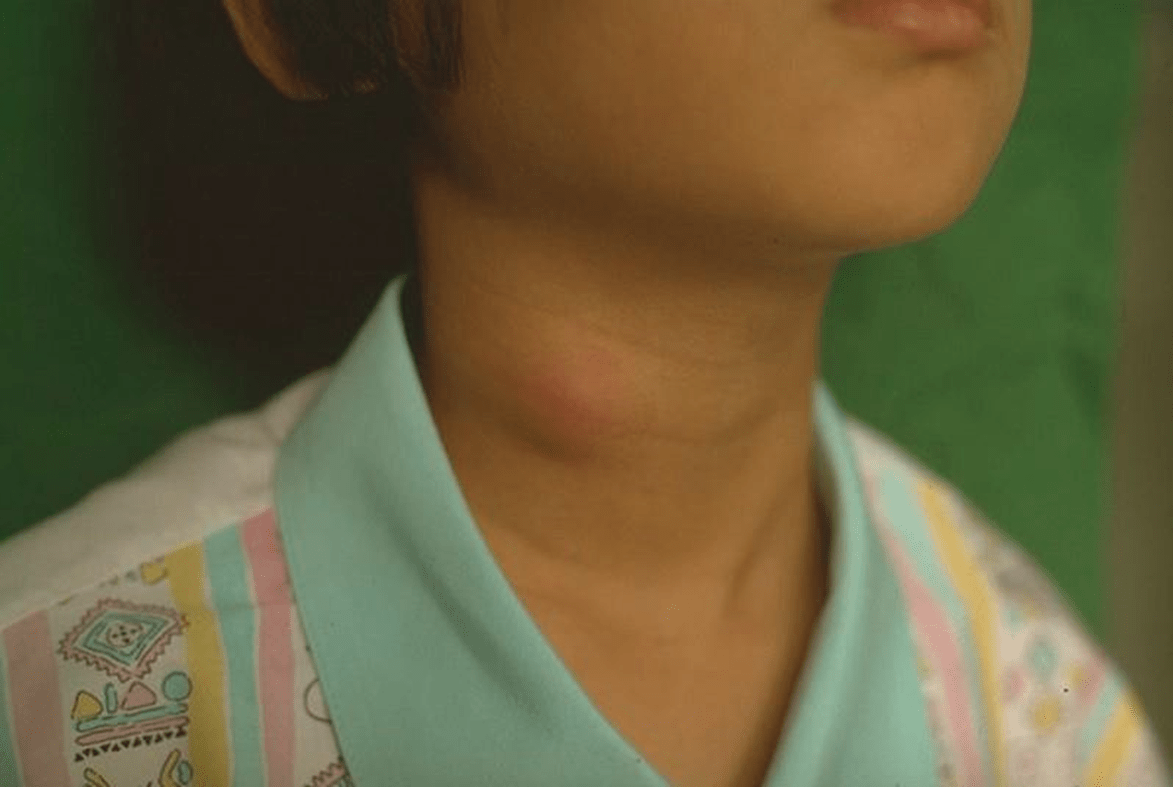
Thyroglossal duct cyst - midline
Branchial cleft cyst - lateral to either side of the trachea
Name the physical exam findings associated with the image below, and the condition. 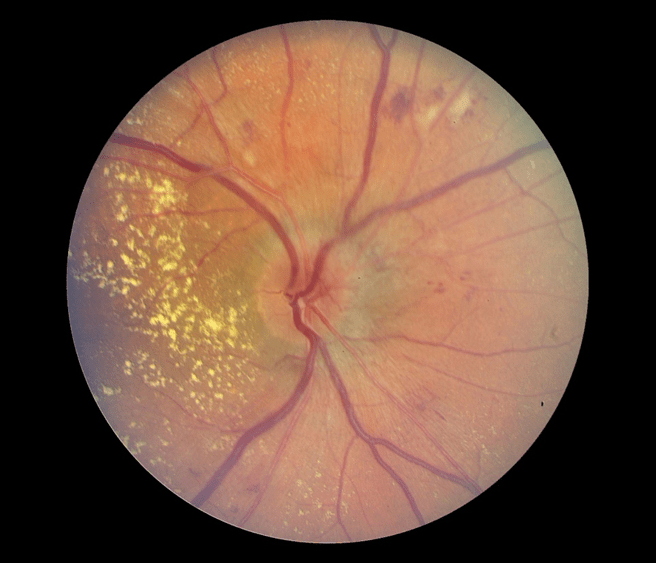
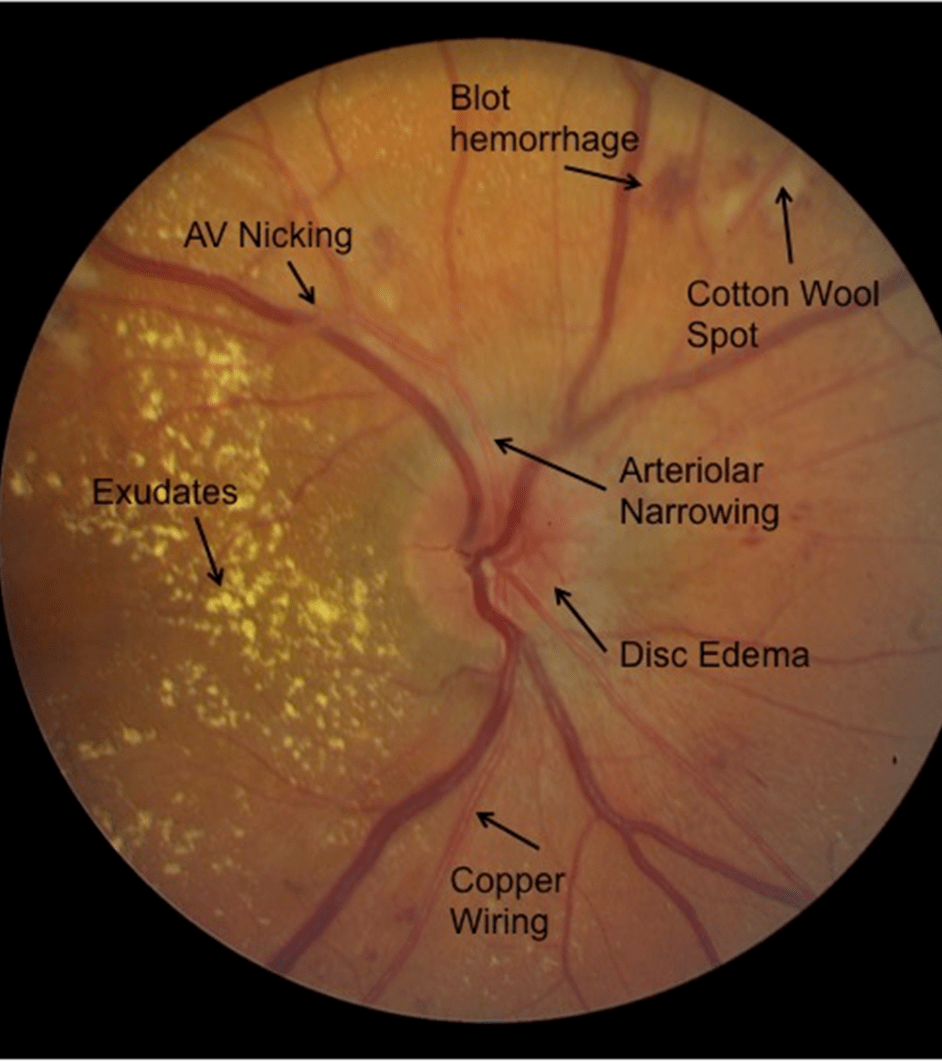
What is hypertensive retinopathy?
Chronic otitis media can result in this complication which erodes bone. Otoscopic examination reveals tympanic membrane perforation which exudes keratin debris ("wax over the attic")
What is cholesteatoma?
Bacterial rhinosinusitis is commonly caused by these pathogens. Name at least two.
What is
1. Moraxella catarrhalis
2. H. influenzae
3. S pneumoniae
4. S auerus
5. streptococci
Examination of a 14-year old female patient shows elevated temp of 102 degrees, pain with swallowing and opening her mouth, and cervical lymph node enlargement. An image from her exam is shown below.
This is the most likely diagnosis. 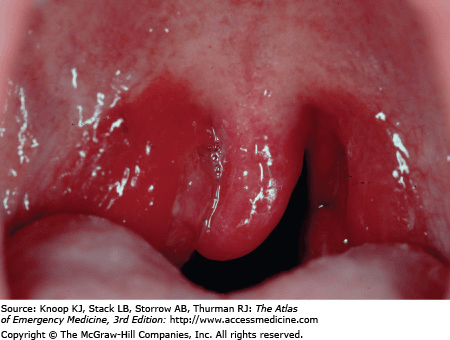
What is Peritonsillar Abscess (PTA)
The total number of teeth there are in the primary dentition.
And the total number of permanent teeth. 
What is 20, and 32
These symptoms are likely describing a patient with this condition.
- Localized headache: Commonly on one side of the head, often near the temples.
- Scalp tenderness: Pain when touching the scalp.
- Jaw claudication: Pain in the jaw with chewing.
- Systemic symptoms: Such as fatigue and malaise.
- History of polymyalgia rheumatica: a condition characterized by muscle pain and stiffness.
What is Giant Cell Arteritis
Tx: steroids
Dx: Biopsy
Sudden, painless loss of vision, pale retinal swelling, and an afferent pupillary defect (pupil dilates with light) are classic signs of this condition.
What is CRAO (central retinal artery occlusion)?
What is the first step in treatment if the patient presents to your primary care office?
immediately refer the patient to an emergency department or ophthalmologist for urgent evaluation and treatment. Time is critical because the prognosis for vision recovery is highly dependent on the rapid restoration of blood flow to the retina
This treatment improves the odds of recovery from sudden sensorineural hearing loss, which requires prompt evaluation and treatment.
Oral corticosteroids
What are nasal polyps
Nasal polyps, Asthma, Aspirin sensitivity
A 4-year-old boy without vaccinations presents with a sore throat. Mom has also noted that the patient's voice sounds muffled. On physical examination, the patient is ill-appearing, sitting forward with some drooling. This exam maneuver should be avoided to prevent an acute airway.
What is examining the posterior oropharynx which might elicit a gag or cough.
Dx?
Epiglottitis
Plain film finding?
Thumbprint sign
This medium best supports the survival of an avulsed tooth.
What is Replant/natural tissue
Replant > Hanks > Milk > Saliva > Saline > water
A bacterial infection of the submandibular space that begins in the floor of the mouth and spreads rapidly. It is most often secondary to a dental infection.
What is Ludwig's Angina
Which of the following are vision threatening causes of red eye?
Acute angle closure glaucoma
Chalazion
Conjunctivitis
Corneal abrasion
Corneal infection
Herpes keratitis
Hordeolum
Orbital cellulitis
Orbital injuries
Subconjunctival hemorrhage
Traumatic hyphema
Acute angle closure glaucoma
corneal infection
herpes keratitis
orbital cellulitis
orbital injury
traumatic hyphema
Jim is a 68 year old man who presents with a painful left sided ear rash x 1 day (shown below). He does not complain of any other symptoms.
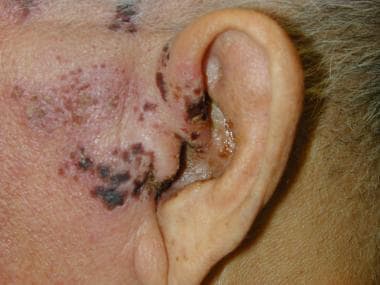
Jane is a 68 year old woman who presents with a similar rash x two days associated with vertigo and left sided facial paralysis.
Name the most likely diagnosis for each patient?
What is:
-Zoster oticus affecting Jim.
-Ramsay Hunt syndrome affecting Jane.
Ramsay Hunt typically affects the facial nerve. L facial paralysis = CN VII affected, vertigo = CN VIII affected.
A 45-year-old woman with a history of chronic sinusitis presents with a 3-day history of worsening headache, fever, and left eye swelling. She reports new-onset double vision and pain around her left eye. On exam, she has left eye proptosis, chemosis, periorbital edema, and restricted eye movements. Additionally, there is decreased sensation over the left forehead and cheek, with reduced corneal reflex. Her right eye now shows mild proptosis and conjunctival injection. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis
What are some complications?
Meningitis
Sepsis
Seizure
Intracranial abscess
AMS
-----------------
A 45-year-old woman with a history of chronic sinusitis presents with a 3-day history of worsening headache, fever, and left eye swelling. On exam, she has proptosis, chemosis, periorbital edema, restricted eye movements. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Orbital Cellulitis or CST are appropriate differential diagnoses for the patient above.
 This disease is caused by Corynebacterium and is fatal in up to 10% of those it affects. It is now very rarely seen in the United States secondary to high vaccination rates.
This disease is caused by Corynebacterium and is fatal in up to 10% of those it affects. It is now very rarely seen in the United States secondary to high vaccination rates.
What is Diphtheria?
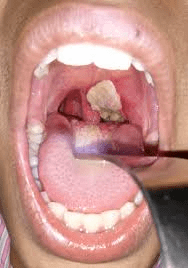
A 66 year old male with PMHx of tobacco use presents with a white patch on his oral mucosa at the gumline that has been present for over a month and is not resolving. On exam you see: 
What is the patient at risk for?
Malignancy development
A 23 year-old female presents with gradual onset dizziness x 48 hours. She describes a constant sensation of the room spinning around her, and she also has uncontrollable nausea and vomiting. She denies hearing loss, tinnitus or ear aches. Five days ago she started to have symptoms of rhinorrhea, sore throat, and a nonproductive cough. This is the likely cause of her symptoms.
What is Vestibular neuritis?
Labyrinthitis = severe vertigo lasting days to weeks +tinnitus +hearing loss. (If post-viral setting and hearing affected, then labyrinthitis).
Menieres = SNHL, vertigo, tinnitus/aural fullness which is EPISODIC with progressive hearing loss.
A 16 year old male presents with blunt force trauma to the left orbit.
Name the physical exam finding shown, most likely diagnosis, and precautions pre and post-operatively.
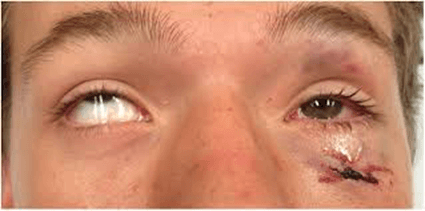
What are:
Extraocular muscle entrapment
Orbital blowout fracture
No straw sucking, coughing, blowing nose
A 45-year-old woman complains of sudden onset hearing loss in her left ear, accompanied by tinnitus and a sensation of fullness for the past 2 days. She denies vertigo or ear pain. Physical examination reveals a Weber test that lateralizes to the right ear and a Rinne test that is positive (air conduction > bone conduction) bilaterally. Otoscopic examination shows no abnormalities, and the tympanic membranes are intact. What type of hearing loss is described?
What is L sensorineural hearing loss
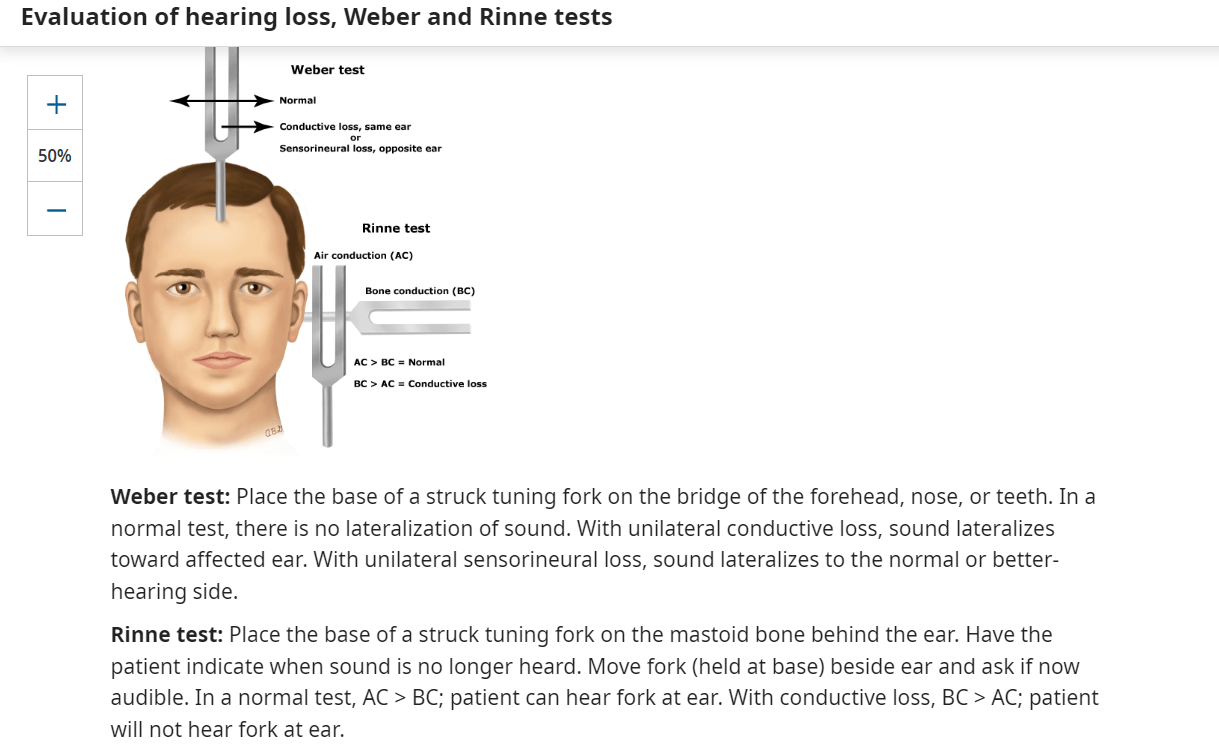
Know causes of sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
This tumor results from osteomyelitis of the frontal bone associated with frontal sinusitis.
What is Potts Puffy Tumor
A 44 year old female presents to your ED with complaints of neck and tongue swelling. On exam, she has a temperature of 102 F, sublingal, tongue and neck swelling, drooling and signs that she is struggling to breathe. You are concerned about this most likely diagnosis?
What is ludwig's angina?
What is the most important initial step in management?
- protect the airway/intubate
Risk factors for developing caries in childhood include?
What are dental caries in caretakers (vertical), and siblings (horizontal).
What can you do as a primary care PA to reduce caries in your patient population?
- Fluoride varnish