Name at least 5 lab abnormalities seen in DIC.
What is thrombocytopenia, prolonged aPTT and PT, elevated INR, hypofibrinogenemia, and elevated D-dimer levels?
This is the treatment for hypofibrinogenemia and DIC. It is usually thawed at 1-4 degrees C to prepare.
What is cryoprecipitate?
Describe the smear finding (1) and what condition is it associated with(1) ?

What is Auer Rods and AML ?
Patient comes to your office complaining of headache, cough, hoarseness, and facial flushing. Imaging shows the following. Name the phenomenon going on?

What is SVC syndrome?
A low dose CT scan should be performed for lung cancer screen for these individuals_______________________
Adults aged 50 to 80 years who have a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
Patient was newly diagnosed with ITP. When the platelets are below ___________ you treat with steroids.
What is 30,000?
Patient presents with dyspnea, fever, hypotension. CXR shows bilateral lung opacities. 6 hours ago he received a blood transfusion. What phenomenon is going on?
What is Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)?
A 50-year-old man presents to his PCP for an annual visit. He has no complaints. His PMH includes hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and rheumatoid arthritis. He goes for routine blood tests today, which reveals marked pancytopenia. A peripheral blood smear is done showing the following:
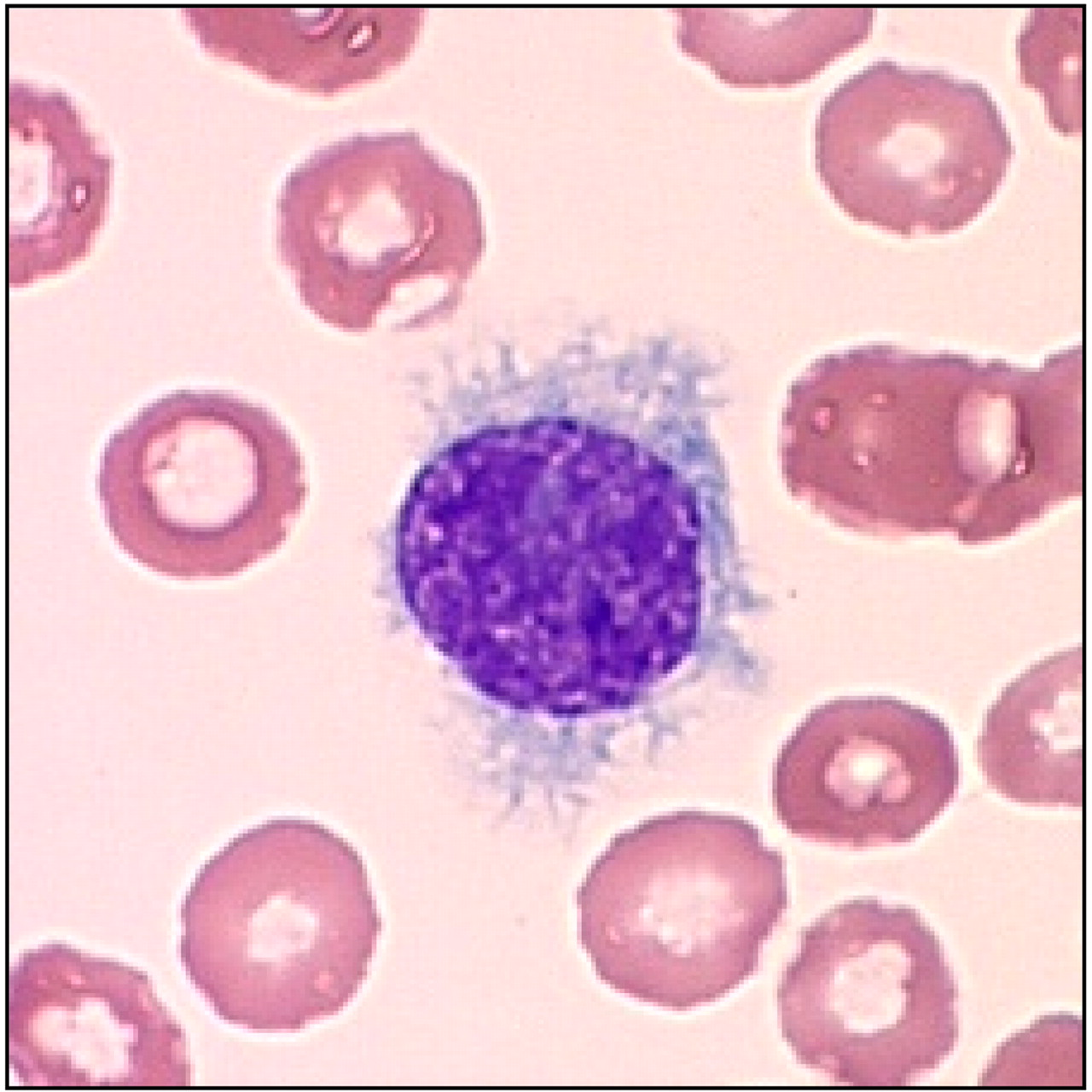
This smear finding is consistent with which condition?
What is hairy cell leukemia?
Patient has lung malignancy with known mets to the brain. He is now presenting with severe headache, nausea, vomiting, new onset lower extremity weakness and decrease in consciousness . CT imaging is as follows. What is phenomenon is going on and what is the initial treatment?

What is increased intracranial pressure from cerebral edema. What is dexamethasone?
For females with hormone receptor positive breast cancer, these are the two classes of antiestrogen adjuvant therapy__________
What is selective estrogen receptor module ( Tamoxifen ) and what is aromatase inhibitor( letrozole, anastrozole, and exemestane).
Diagnosis of HIT requires a screening test (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for platelet factor 4 antibodies) followed by a confirmatory test which is called ___________.
What is serotonin release Assay or heparin induced platelet aggregation assay?
A ferritin Level above this level rules out iron deficiency anemia even in the setting of inflammation.
What is ferritin > 100 ?
A 12-year-old boy presents to the ED for jaundice. He is recovering from a recent upper respiratory infection. He is noted to have splenomegaly and to be mildly jaundiced. Right upper quadrant ultrasound shows gallstones present. Suspicious for a familial hemolytic disorder, the physician orders an osmotic fragility test, which comes back as abnormal.

Name the condition that is being described?
What is hereditary Spherocytosis?
Name at least 4 lab abnormalities seen in Tumor Lysis Syndrome.
What is hyperuricemia, hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, and hypocalcemia, elevated creatinine?
This is a lymphoma associated with H pylori
What is MALT?
Name at least 3 inherited hypercoaguble disorders.
What is antithrombin III, Protein C/S deficiency, prothrombin mutation, Factor V leiden ?
23-year-old woman has β-thalassemia major for which she has received approximately 15 transfusions since childhood; She becomes symptomatic when the hemoglobin level is less than 7 g/dL (70 g/L). Hepatosplenomegaly is present.
Labs show: Hgb: 7.9; Ferritin : 3228; Iron: 212; Transferrin : 56%
What is the most appropriate treatment?
What is iron chelation therapy (deferoxamine ,deferasirox , deferiprone)?
Phlebotomy is the wrong answer as she is transfusion dependent to prevent symptoms of anemia.
A 70 yo M with PMH of HTN and HLD sees his PCP for his annual exam. He has no complaints, and his physical exam is normal. Labs showing WBC count is 30,000/μL with 90% lymphocytes. Peripheral blood smear shows the following:
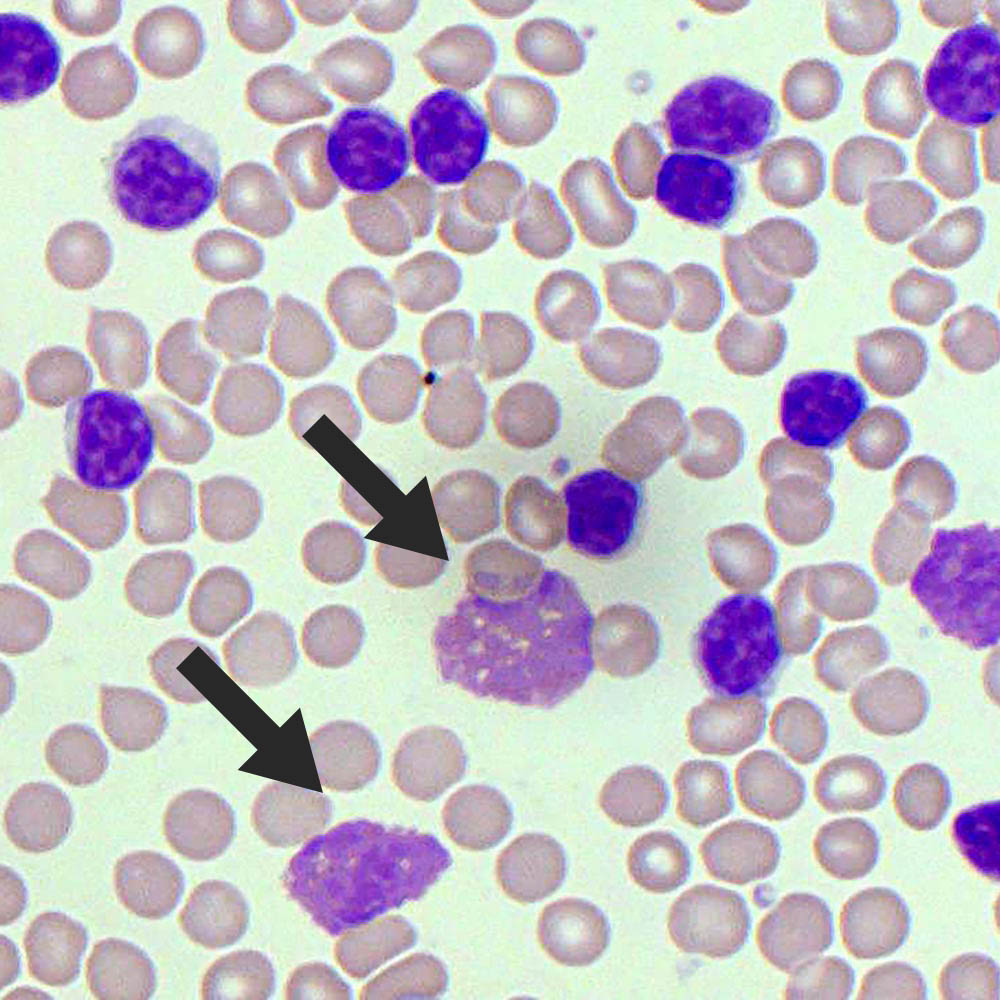
What condition is being described?
What is CLL?
Patient presenting with confusion, lethargy, nausea, vomiting and diffuse bone pain. On exam, mucous membranes are dry.
Results of laboratory studies show an albumin level of 3.8 g/dL (38 g/L), calcium level of 17 mg/dL (3.7 mmol/L), and creatinine level of 2.5 mg/dL (221 µmol/L).
Name 2 treatments you would give immediately.
What is Isotonic saline and calcitonin?
In addition to induction chemotherapy, this additional therapy is needed in patients with ALL
What is CNS prophylaxis ( intrathecal chemo)?
A 42yo F with no PMH evaluated in the ED for 2-day history of headache, fevers, confusion, easy bruising.
Labs showing the Following:
Haptoglobin: Undetectable
Hemoglobin: 8.2 g/dL ; Leukocyte count: 10,200/μL
Platelet count: 8000/μL ; Creatinine : 1.5 mg/dL
The following treatment should be considered______


What is plasma Exchange?
A 30-year-old woman receives 6 units of PRBCs following an episode of trauma with bleeding. Three weeks later she develops a fever, maculopapular skin rash that becomes desquamative, diarrhea, and icterus. Laboratory studies show pancytopenia.
what phenomenon is going on?
What is Transfusion-associated graft versus host disease?
A 56-year-old man presents with headache, fatigue, pallor, and abdominal pain. The patient reports memory loss and upon further questioning, reveals that he works at a battery recycling plant. He is noted to have a foot drop in both lower extremities Peripheral smear is shown as follows:

What finding is shown in the smear and what condition is is associated with:
What is basophilic stippling? What is Lead Poisoning?
A 63-yo M presents with fever, increasing fatigue, and actively bleeding gums. Physical exam reveals several oral mucosal petechiae.
CBC: Low platelets and hemoglobin
PT/PTT/D-Dimer : elevated
Fibrinogen: low
Peripheral Smear: >30% blasts and schistocytes
He is diagnosed with DIC and give FFP
Further workup reveals that he has translocation 15;17
What is his diagnosis and what treatment should be given as soon as possible?
What is acute promyelocytic leukemia ? What is ATRA?
All drugs in this class of molecular targeted therapy including such drugs as imatinib and sorafenib can prolong the QT interval and periodic EKG monitoring recommended.
What is tyrosine kinase inhibitors?