Initial imaging modality in a patient diagnosed with multiple myeloma, used as screening for lytic lesions
(Name 1/3)
1. Skeletal Survey (plain bone X-rays) [NOT a BONE SCAN] **
Skeletal surveys are used to assess for lytic lesions in multiple myeloma. Bone scans, which detect increased osteoblast activity in most bone metastases, may not detect the more purely lytic lesions
2. PetCT
3. Whole Body MRI (used in select patients with negative skeletal survey but positive/suspicious bone symptoms)
32F with sickle cell disease presents with fever and shortness of breath on exertion. Her hemoglobin is 4.2 and reticulocyte % is 0.2%. Diagnosis?
Aplastic Anemia
Most commonly associated with parvovirus in patients with sickle cell. Treatment of patients with prolonged viremia due to Parvo is IVIG
3 Most Common Causes of Anemia in Adults
1. Iron Deficiency
2. EPO Deficiency (Inflammatory/Kidney)
3. Blood Loss
What percentage of blasts is required in the bone marrow or peripheral smear for a diagnosis of acute leukemia?
20% or higher
What diagnosis is associated with this bone marrow specimen?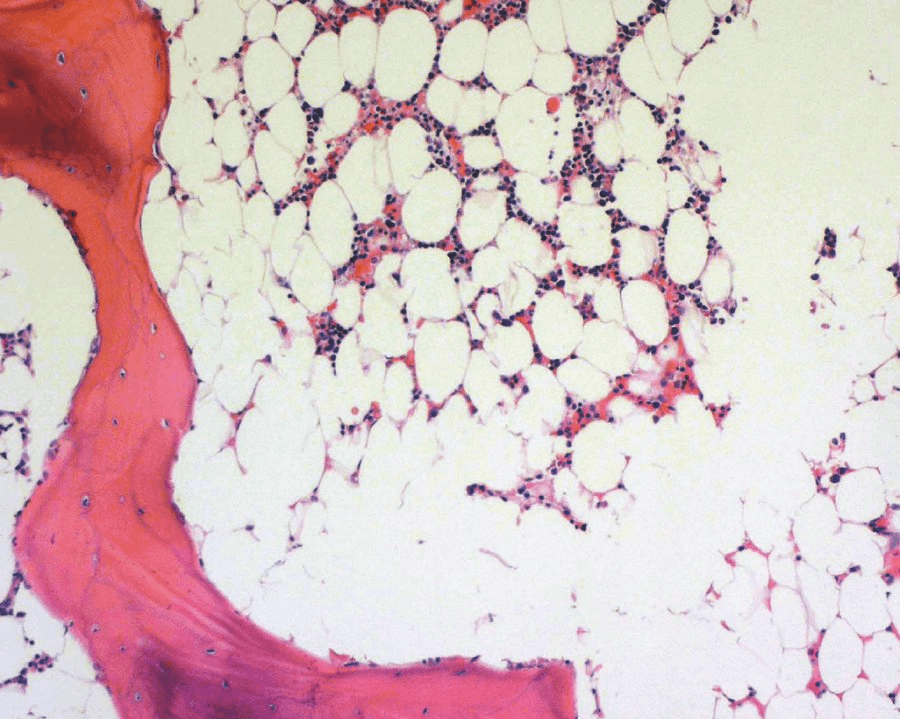
(The biopsy specimen shows profound hypocellularity. Fat and marrow stroma are the major components present, and there is no evidence of malignant cells or fibrosis. This is consistent with a diagnosis of aplastic anemia. Aplastic anemia is characterized by diminished or absent hematopoietic precursors in the bone marrow)
Name the medication used in patients requiring treatment for Multiple Myeloma that has shown to improve survival.
Bonus: Name the 2 complications patients on this medication should be monitored for
Zoledronic Acid
Bisphosphonates do not reduce the rate of progression in patients with Smoldering Myeloma or myeloma not requiring treatment and should not be used.
Osteonecrosis of the jaw/Hypocalcemia
Indications for exchange transfusions as treatment in patients with sickle cell disease:
acute stroke, ACS, fat embolism
indicated for prophylaxis only in patients with history of ischemic stroke
What factors are included in 4 factor prothrombin concentrate?
(Bonus: what syndrome is the use of PCC contraindicated?)
PCC contains factors II, VII, IX, and X
Primary use is life threatening warfarin toxicity
PCCs contain residual heparin and are contraindicated in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia.
Name the syndrome that presents with hyperkalemia, hyperuricemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia and DIC; AND Identify the type of leukemia most likely to present with this syndrome
Tumor lysis Syndrome
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
What is the most likely diagnosis in a patient with a platelet count of 70k that presents with this smear?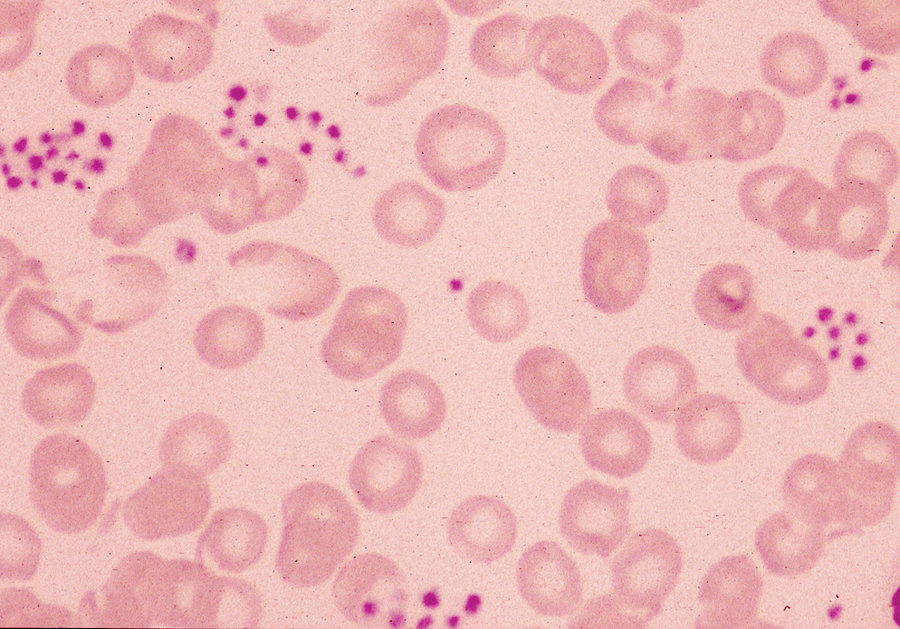
Pseudothrombocytopenia
Pseudothrombocytopenia is an artifact in which platelets agglutinate and the clumped platelets are not recognized by automated blood counters. On average peripheral smears have approx 7 platelets per hPF
This dyscrasia is characterized by an M protein level less than 3 g/dL, clonal plasma cells comprising less than 10% of the bone marrow cellularity, and the absence of related signs and symptoms of end-organ damage.
Bonus: This disorder can be classified into 3 types, name 2 of the 3
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
Non-IgM, IgM, Light Chain
Non-IgM progresses to MM at a rate of 1%/yr, IgM can progress to WM at a rate of 1.5%/yr, and Light Chain can progress to other PCDs at a rate of 0.3%/yr
Use of anticoagulation as treatment of HIT without thrombosis should be continued for how long after diagnosis?
2-3mo
With Thrombosis - 3-6mo
In patients with Hereditary Hemochromatosis, how often are ferritin levels monitored?
(Bonus: goal for the levels at which ferritin should be maintained; low-high)
every 3 months
Ferritin should be maintained between 50-100
Treatment for elevated ferritin is phlebotomy - maintenance phlebotomy for stable patients includes removing approx 2-6U/yr
What form of leukemia requires CNS prophylaxis?
(Bonus: Name the medication used, or the way it is given, or how many doses patients receive)
ALL
Methotrexate/LP/4 doses (one every other cycle)
Name the inclusion body seen AND the disease it is diagnostic of: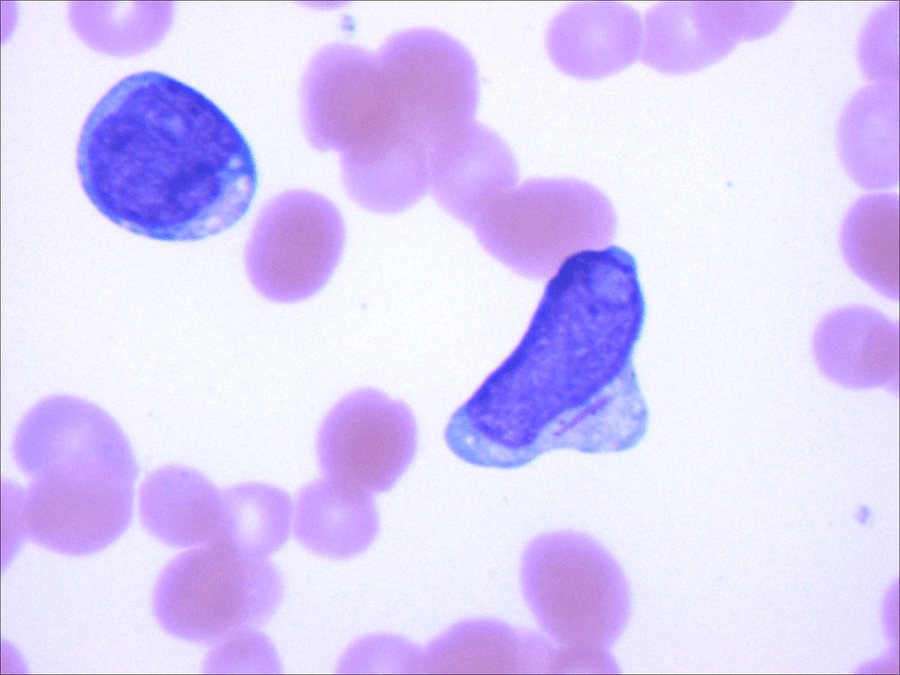
Auer Rod
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Auer rods represent linear collections of granules and are virtually diagnostic of acute myeloid leukemia.
Hereditary Spherocytosis is an autosomal dominant disorder associated with mutations of multiple proteins known as scaffolding proteins that causes an adverse effect in the cytoskeleton of red blood cells. Name 2 of these proteins (there are 5 total)
α spectrin, β spectrin, ankyrin, band 3, and protein 4.2 have been described in patients with HS.
Typically do not present until adulthood and asymptomatic until after an infection leading to acute bone marrow suppression. In addition to anemia, symptomatic patients typically present with splenomegaly or, more rarely, splenic infarction or rupture, and calcium bilirubinate (pigmented) gallstones are common.
Diagnosed via osmotic fragility test or flow cytometry
Patients should receive supplementation with folate
2 Primary Indications for hydroxyurea in patients with SCD
(Bonus: What patients is it contraindicated in? 2 classes)
>2 VOC events/yr &/or history of ACS
Pregnancy and CKD
Fever with in 4 hours of a transfusion associated with chills/rigors
Febrile Non hemolytic Transfusion Reaction
Febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reaction (FNHTR) is common, occurring in about 1% of transfusionepisodes, and is mediated by proinflammatory cytokines elaborated by donor leukocytes during storage. Rule out infection with cultures and symptomatic treatment with anti-pyretics.
Myeloproliferative disorder that carries the worst prognosis, has a characteristic marrow fibrosis, extra medullary hematopoiesis and biopsy is associated with a Dry Tap
(Bonus: 50% of these patients are associated with what genetic mutation?)
Primary Myelofibrosis
JAK2
This specific cell type shown below is associated with an acquired form of anemia. Name at least 2 medications or Vitamins/minerals (or 1 of each) that can lead to this finding: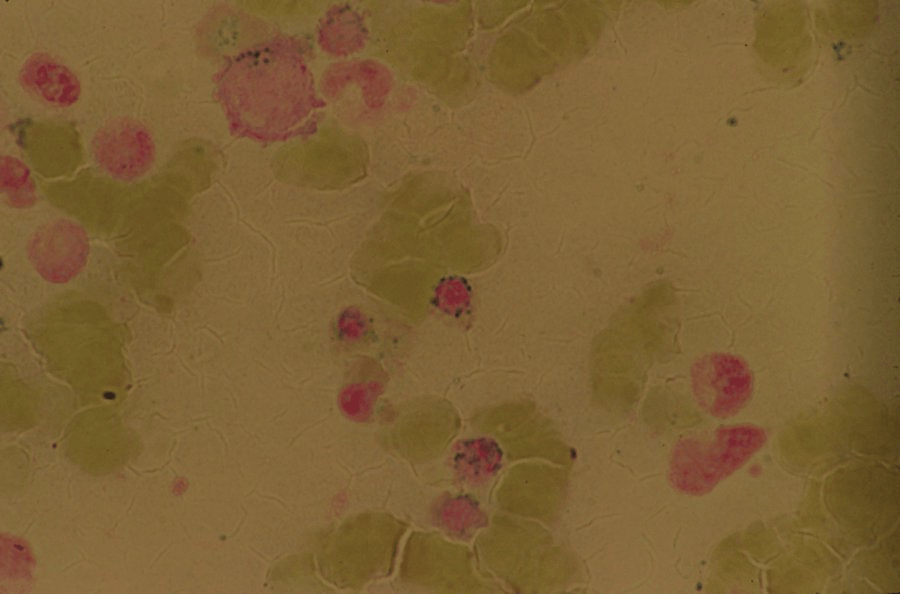
Sideroblastic Anemia/Ringed Sideroblasts are associated with Copper deficiency, lead toxicity, Vitamin B6 deficiency, Isoniazid, Linezolid, Chloramphenicol, and alcohol
Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia is an indolent B cell lymphoma that presents with classic b symptoms and occasionally hyper viscosity syndrome. 20% of patients with this disorder develop significant peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy. What protein is associated with the development of neuropathy in these patients?
Bonus: What is the primary cause for the development of hyper viscosity in these patients?
Circulating IgM increases serum viscosity when at an increased concentration and if not treated leads to hyperviscosity syndrome.
Hyperviscosity is one of the few emergent hematologic conditions and requires emergent plasmapheresis
5 major indications to initiate an extensive workup in a patient with thrombophilia. Name 3/5
1. Thrombosis/es at unusual sites
2. Recurrent idiopathic thrombosis
3. Unprovoked thrombosis in patient with platelet count < 45k
4. Family hx in 1 or more 1st degree relatives of clotting disorder
5. Warfarin Induced Skin Necrosis
Including HIV and Hepatitis C, blood products are screened for approx 9 infectious diseases. Name 3 (other than HIV/HepC)
- Donated whole blood and platelets are screened for hepatitis B and C viruses, HIV, human T-cell lymphotropic virus I/II, and West Nile virus; undergo serologic testing for syphilis; and, in select regions of the country, are tested for antibodies to Trypanosoma cruzi, Babesia, and most recently, Zika virus.
What is the specific medical terminology for a physical exam finding of blood blisters in the mouth that is associated with ITP and indicates an emergent need for treatment and hospitalization?
Wet Purpura
- usually not seen until platelet count drops below 10k and much more likely to be associated with an acute drug induced ITP or vaccine/illness induced ITP
Most patients with ITP do not require hospitalization and can be managed outpatient - this finding is one major exception to that rule
What is the most likely cause of the erythrocyte inclusion body seen in the smear below?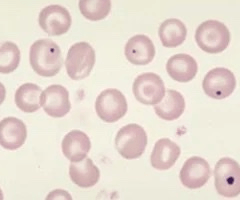
Asplenia
Howell-Jolly bodies (the most reliable sign of splenic hypofunction). Howell-Jolly bodies are dense, blue, spherical cellular inclusions that represent a small nuclear remnant and are normally removed by the spleen.