What is a normal cardiac output?
5-6 L/min
What is the equation for cardiac output?
CO = SV x HR
SV = Stroke Volume
HR = Heart Rate
Your patient's arterial line only has a good arterial waveform when you hyperextend the patient's wrist.
At rest (without hyperextending the wrist), the cardiac index is 1.3. Do you trust this value?
No
What does it mean when a cardiac output is low?
Your heart does not pump enough blood to supply your organs and tissues with adequate oxygen
Your patient is in Afib. Would a FloTrac benefit them and why?
While it would not give the most accurate information, it may be valuable in monitoring trends.
Which of the following is an abnormal hemodynamic value?
CO: 5.6
CI: 4.7
SVV: 8
Preload: 4
CO: 5.6 (5-6 L/min)
CI: 4.7 (2.5-4 L/min/m2)
SVV: 8 (10-13%)
Preload: 4 (2-6mmHg)
What does cardiac output mean?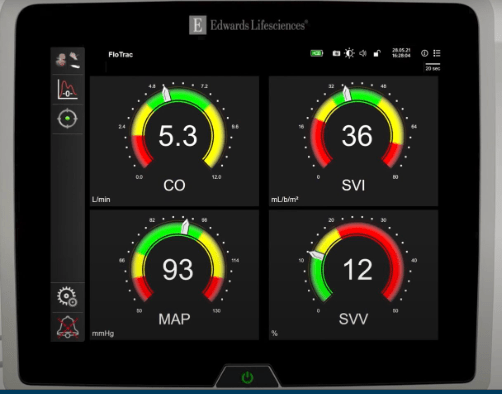
CO = The amount of blood the heart pumps in one minute
What patients would benefit from FloTrac monitoring?
Name two things that contribute to increased oxygen demand.
• Nursing assessments and interventions
• Shivering
• Seizures
• Hyperthermia
• Visitors
What is the difference between CO vs. CI?
CO: Cardiac Output
CI: Cardiac Output adjusted for BSA
Where do these two cords plug into?
Red- art line cable that connects to the monitor
Green- cable that connects to FloTrac
The provider asks for the patient's CO and an interpretation of the value. What do you tell the provider?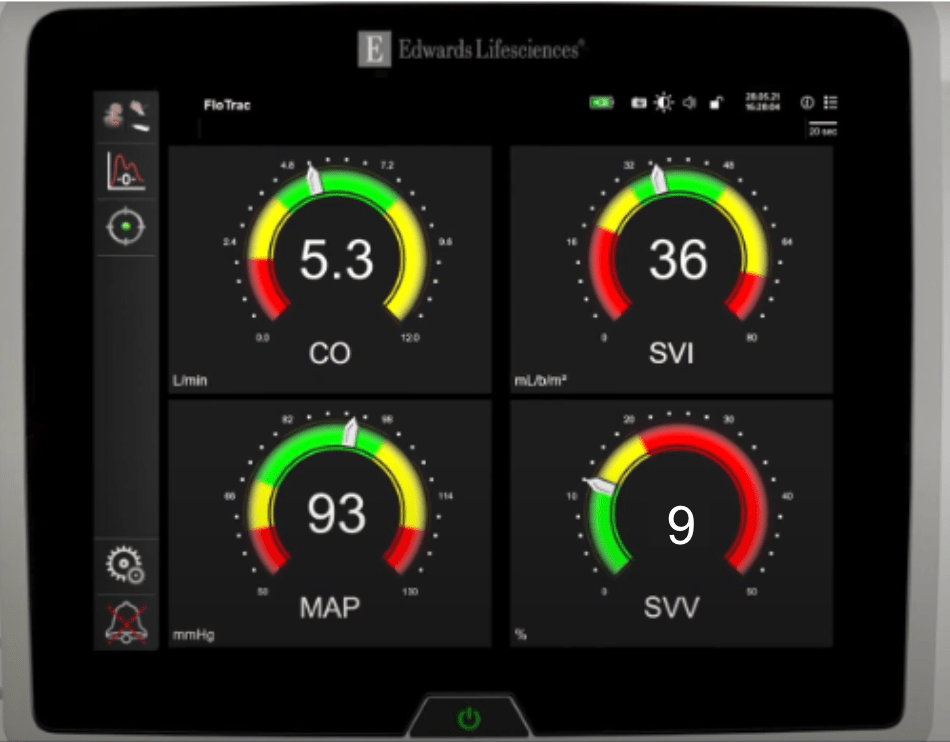
CO: 5.3
Interpretation: WNL. The patient's hemodynamics are stable and do not require intervention.
Your cardiac output is 2.6. Is this high or low? What are two interventions that could improve this value?
Low.
Fluids, pressors
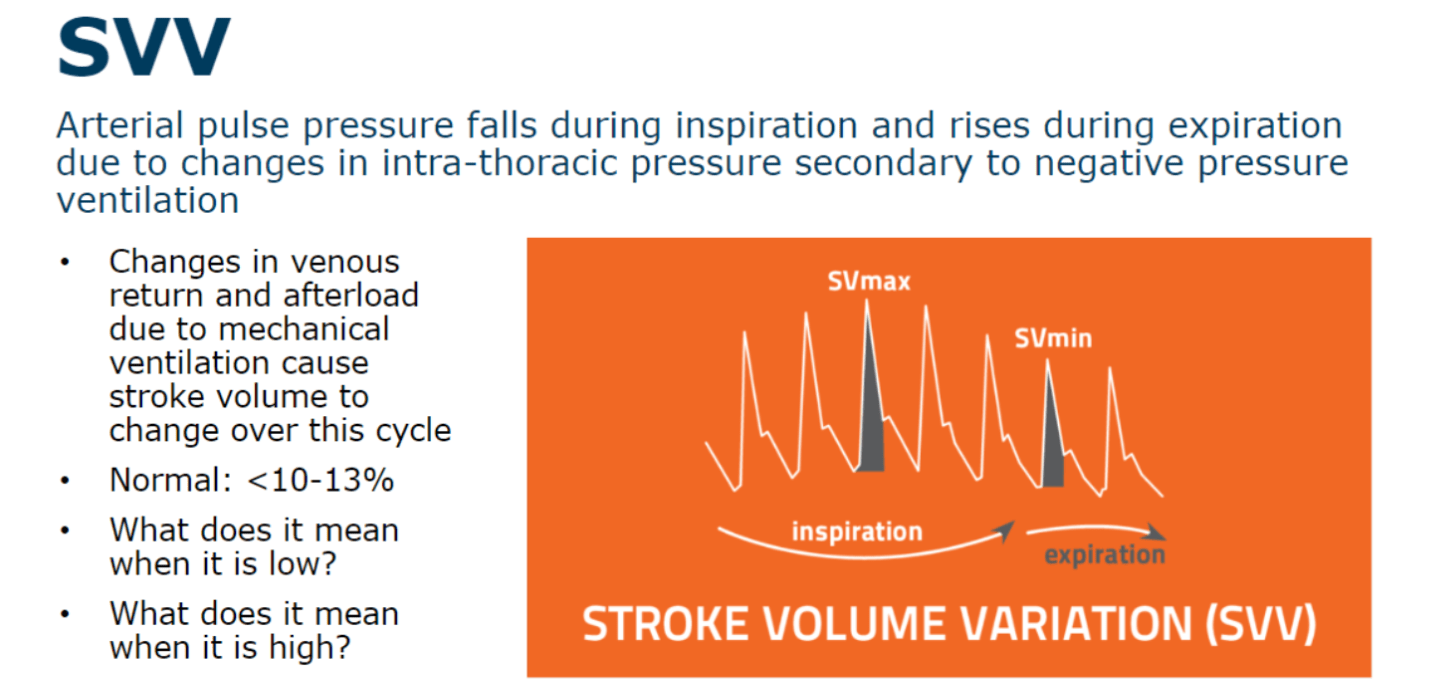
What is the meaning of SVV and what is a normal SVV value?
SVV: Stroke Volume Variation
-Indication of fluid responsiveness
Normal: <10-13%
Your patient is in septic shock and has already gotten 3L 0.9 NS. You have the following information:
Cardiac Output (CO): 3.1
HR: 122
BP: 82/41 (52)
Preload: 10 mmHg
What would be your recommendation?
Begin vasopressors.